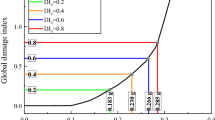
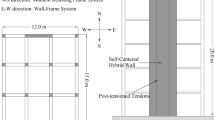
Abstract
Performance indicators such as energy, stiffness and displacement are the key parameters to evaluate the damage degree of structures or members subjected to earthquake. Establishing accurate and effective damage models based on these parameters is very necessary for performance-based seismic design. The current damage models have some deficiencies in dynamic mechanism, threshold range, accuracy and applicability. According to the mechanism of energy dissipation, it is assumed that the damage of structures and members is closely related to the difference between the ideal elastic–plastic deformation energy and the actual elastic–plastic deformation energy. This differential ratio can be used to represent the damage degree and damage evolution. Based on this, the damage model based on differential ratio of elastic plastic dissipated energy is proposed, and the specific calculation methods under monotonic static load, quasi-static load and dynamic load are given, respectively. Further, the damage index ranges corresponding to different damage grades are determined, and the application ranges and characteristics of different damage models are compared. The applicability and accuracy of damage model based on differential ratio of elastic plastic dissipated energy in members and structures subjected to different load are verified by damage assessment of the shear wall (static load), one 6-story RC frame structure (static load, seismic load) and one 12-story RC frame structure (shaking table test). The analysis results proved the damage model proposed in this paper has the advantages of clear mechanism, strict threshold, widely application range and can characterize the dynamic evolution of damage.

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
ATC-58 (2009) Guidelines for seismic performance assessment of buildings. Applied Technology Council, Washington
Akiyama H (1985) Earthquake resistant limit state design for buildings. University of Tokyo Press, 1985
ASCE, SEI 41–13 (2014) Seismic rehabilitation of existing buildings. ASCE, Reston
Bertero RD, Bertero VV (2002) Performance-based seismic engineering: the need for a reliable conceptual comprehensive approach. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 31(3):627–652. https://doi.org/10.1002/eqe.146
Casotto C, Silva V, Crowley H (2015) Seismic fragility of Italian RC precast industrial structures. Eng Struct 94:122–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2015.02.034
Decanini LD, Mollaioli F (2001) An energy-based methodology for the assessment of seismic demand. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 21:113–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0267-7261(00)00102-0
Dolce M, Goretti A (2015) Building damage assessment after the 2009 Abruzzi earthquake. Bull Earthq Eng 13:2241–2264
Dipasquale E, Ju JW, Askar A (1999) Relation between global damage indexes and local stiffness degradation. J Struc Eng-ASCE 116(5):1440–1456. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1990)116:5(1440)14
Erberik A (2008) Fragility-based assessment of typical mid-rise and low-rise RC buildings in Turkey. Eng Struct 30(5):1360–1374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2007.07.016
FEMA 356 (2000) Prestandard and commentary for the seismic rehabilitation of buildings. Federal Emergency Management Agency, Washington
Fajfar P, Vidic T (1994) Consistent inelastic design spectra hysteretic and input energy. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 23(5):523–537. https://doi.org/10.1002/eqe.4290230505
Ghobarah A, Abou-Elfath H, Biddah A (1999) Response based damage assessment of structures. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 28(1):79–104
GB50011-2010 (2010) National Standard of the People’s Republic of China, Code for seismic design of building. China Architecture and Building Press, Beijing
Gosain NK, Brown RH, Jirsa JO (1997) Shear requirements for load reversals on RC members. J Struc Eng 103(7):1461–1476
Housner GW (1959) Behavior of structures during earthquake. Eng Mec-ASCE 85(4):109–129
He HX, Cong ML, Lv YW (2013) Earthquake damage assessment for RC structures based on fuzzy sets. Math Probl Eng (22). Article ID 254865. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/254865
Huang W, Qian J, Zhou Z (2016) Seismic damage assessment of steel reinforced concrete members by a modified Park-Ang model. J Asian Archit Build Eng 15:605–611. https://doi.org/10.3130/jaabe.15.605
Hancilar U, Cakti E, Erdik M, Franco G, Deodatis G (2014) Earthquake vulnerability of school buildings: probabilistic structural fragility analyses. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 67:169–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2014.09.005
Hindi RA, Sexsmith RG (2001) A proposed damage model for RC bridge columns under cyclic loading. Earthq Spectra 17(2):261–290. https://doi.org/10.1193/1.1586175
Ibarra LF, Medina RA, Krawinkler H (2005) Hysteretic models that incorporate strength and stiffness deterioration. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 34(12):1489–1511. https://doi.org/10.1002/eqe.495
Jiang HJ, Fu B, Lu XL, Chen LZ (2015) Seismic damage assessment of RC members by a modified Park & Ang model. Adv Struct Eng 18:353–364. https://doi.org/10.1260/1369-4332.18.3.353
Kaplan O, Guney Y, Topcu A, Ozcelikors Y (2018) A rapid seismic safety assessment method for mid-rise reinforced concrete buildings. Bull Earthq Eng 16(2):889–915. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-017-0229-0
Khampanit A, Leelataviwat A, Kochanin J, Warnitchai P (2014) Energy-based seismic strengthening design of non-ductile reinforced concrete frames using buckling-restrained braces. Eng Struct 81:110–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2014.09.033
Krätzig WB, Meyer IF, Meskouris K (1989) Damage evolution in reinforced concrete members under cyclic loading. In: Proceedings of 5th international conference on structural safety and reliability, San Francisco
Krawinkler H, Zohrei M (1983) Cumulative damage in steel structures subjected to earthquake ground motion. Comput Struc 16(14):531–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-7949(83)90193-1
Kunnath SK, Chai YH (2004) Cumulative damage-based inelastic cyclic demand spectrum. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 33(3):499–520. https://doi.org/10.1002/eqe.363
Krajcinovic D, Lemaitre J (1987) Continuum damage mechanics theory and applications. Springer Verilag, New York
Lagomarsino S, Cattari S, Ottonelli D, Giovinazzi S (2019) Earthquake damage assessment of masonry churches: proposal for rapid and detailed forms and derivation of empirical vulnerability curves. Bull Earthq Eng 17(6):3327–3364
Lu XZ, Xie LL, Guan H (2015) A shear wall element for nonlinear seismic analysis of super-tall buildings using OpenSees. Finite Elem Anal Des 98(1):14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.finel.2015.01.006
Lu X L, Li P Z, Chen Y Q (2004) Complete data of the shaking table test of a concrete frame model with 12 levels. Shanghai: Tongji University, pp 2–5. http://risedr.tongji.edu.cn/
Mihai MA (2013) A theoretical review of the damage indices used to model the dynamic nonlinear behavior of reinforced concrete structures. Bull Polytech Inst Iasi 63(2):109–119
Mahboubi S, Shiravand MR (2019) Proposed input energy-based damage index for RC bridge piers. J Bridge Eng 24(1):04018103. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0001326
Park Y, Ang AHS (1985) Mechanistic seismic damage model for reinforced concrete. J Struc Eng-ASCE 111(4):722–739. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)07339445(1985)111:4(722)
Rossetto T, Elnashai A (2003) Derivation of vulnerability functions for European-type RC structures based on observational data. Eng Struct 25:1241–1263. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0296(03)00060-9
Shahnazaryan D, O’Reilly GJ (2015) Integrating expected loss and collapse risk in performance-based seismic design of structures. Bull Earthq Eng 19(2):987–1025
Su JS, Dhakal RP, Wang JJ (2017) Fiber-based damage analysis of reinforced concrete bridge piers. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 96:13–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2017.01.029
Ye L, Otani S (1999) Maximum seismic displacement of inelastic systems based on energy concept. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 28(6):1483–1499. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)10969845(199912)28:12%3c1483::AID-EQE877%3e3.0.CO;2-0
Zameeruddin M, Sangle KK (2016) Review on recent developments in the performance-based seismic design of reinforced concrete structures. Structures 6:119–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2016.03.001
Funding
This work is partially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China under Grant Nos. 2017YFC1500604 and 2017YFC1500603 and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 51878017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, H., Cheng, S. & Chen, Y. Earthquake damage assessment model based on differential ratio of elastic–plastic dissipated energy. Bull Earthquake Eng 20, 2719–2749 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-022-01341-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-022-01341-y