Summary
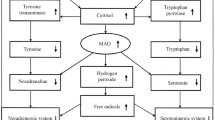
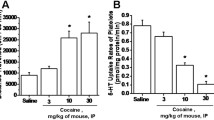
Platelet MAO activity was measured in 79 Parkinson patients (56 males and 23 females) before and during L-deprenyl therapy. Baseline platelet MAO activity was higher in females than in males with no age dependent differences. During chronic L-deprenyl therapy, MAO activity was inhibited greater than 98%. Four hours after the oral administration of the first 5 mg dose of L-deprenyl, platelet MAO activity was inhibited by 86%. By 24 hours, greater than 98%, inhibition was achieved and this degree of inhibition was maintained during continuous L-deprenyl administration. Following oral administration of 10 mg L-deprenyl once a day versus 5 mg L-deprenyl twice a day, the time course of platelet MAO inhibition was similar. Five days after the termination of chronic L-deprenyl therapy, platelet MAO activity was still inhibited by 96%. MAO activity returned to normal by 2 weeks after stopping L-deprenyl. Platelet MAO activity is a useful method of monitoring bioavailability, compliance, dose-response relationship and optimal dosage schedules for L-deprenyl in Parkinson patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnett CD, Fowler JS, MacGregor RR, Wschlyer DJ, Wolf AP, Langstrom B, Hallin C (1987) Turnover of brain monoamine oxidase measured in vivo by positron emission tomography using L-(11 C)-deprenyl. J Neurochem 49: 522–527
Birkmayer W, Riederer P, Ambrozi L, Youdim MBH (1977) Implications of combined treatment with “Madopar” and L-deprenil in Parkinson's disease. Lancet i: 439–443
Fowler CJ, Tipton KF, MacKay AVP, Youdim MBH (1980 a) Human platelet monoamine oxidase—a useful enzyme in the study of psychiatric disorders? Neuroscience 7: 1577–1594
Fowler CJ, Wiberg Å, Oreland L, Marcusson J, Winblad B (1980 b) The effect of age on the activity and molecular properties of human brain monoamine oxidase. J Neural Transm 49: 1–20
Glover V, Sandler M, Owen F, Riley GJ (1977) Dopamine is a monoamine oxidase B substrate in man. Nature 265: 80–81
Johnson JP (1968) Some observation upon a new inhibitor of monoamine oxidase in brain tissue. Biochem Pharmacol 17: 1285–1297
Krajl M (1965) A rapid microfluorometric determination of monoamine oxidase. Biochem Pharmacol 14: 1683–1685
Lowry OH, Roseburg NJ, Farr AL, Radnall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–275
Oreland L, Johansson F, Ekstedt J (1983) Dose regimen of deprenyl (Selegiline) and platelet MAO activities. Acta Neurol Scand [Suppl] 95: 87–89
Penington DG (1981) Formation of platelets. In: Gordon JL (ed) Platelet in biology and pathology, vol 2. North-Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, pp 63–76 [Dingle JT (ed) Research monographs in cell and tissue physiology, vol 5]
Reynold GP, Elsworth JD, Blau K, Sandler M, Lees AJ, Stern GM (1978) Deprenyl is metabolized to metamphetamine and amphetamine in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol 6: 542–544
Reynold GP, Riederer P, Sandler M, Jellinger K, Seeman D (1978) Amphetamine and 2-phenylethylamine in post-mortem parkinsonian brain after (-)deprenyl administration. J Neural Transm 43: 271–277
Riederer P, Youdim MBH (1986) Monoamine oxidase activity and monoamine metabolism in brains of parkinsonian patients treated with L-deprenyl. J Neurochem 46: 1359–1365
Riederer P, Youdim MBH, Rausch WD, Birkmayer W, Jellinger K, Seeman D (1978) On the mode of action of L-deprenyl in the human central nervous system. J Neural Transm 43: 217–226
Riederer P, Reynold GP, Youdim MBH (1981) Selectivity of MAO inhibitors in human brain and their clinical consequences. In: Youdim MBH (ed) Monoamine oxidase inhibition—the state of the arts. John Wiley, Chichester, pp 63–76
William CH (1984) Selective inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A and B. Biochem Pharmacol 33: 334–337
Yahr MD (1978) Overview of present day treatment of Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm 43: 227–238
Youdim MBH (1976) Preparation of human platelet. In: Wolstenholme GEW, Knight J (eds) Monoamine oxidase and its inhibition. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 405–406
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D.H., Mendoza, M., Dvorozniak, M.T. et al. Platelet monoamine oxidase in Parkinson patients: effect of L-deprenyl therapy. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 1, 189–194 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02248668
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02248668