Summary
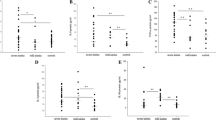
We carried out a study of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) proteins in 180 patients with sciatica caused by lumbar disc herniation to elucidate further the degree and mechanisms of protein elevations. The 63 controls were patients with tension headache or migraine without aura. The CSF/serum albumin ratios were higher in the patients (mean 8.84, SD 5.16) than in the controls (mean 5.60, SD 2.33). Similar differences were found for the CSF/serum IgG ratios and the CSF-total proteins. The CSF/serum albumin ratios, CSF/serum IgG ratios and the CSF-total protein concentrations were higher in men than in women among the patients. We suggest that the significant difference in ratio parameters between patients and controls indicates a leak of plasma albumin, most likely IgG, into the CSF in patients with sciatica. The leak was more pronounced in men. Also in the control group the CSF/serum albumin and CSF/serum IgG ratios were higher in men.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahonen A, Myllyla VV, Hokkanen E (1978) Measurement of reference values for certain proteins in cerebrospinal fluid. Acta Neurol Scand 57:358–365
Ahonen A, Myllyla VV, Hokkanen E (1979) Cerebrospinal fluid protein findings in various lower back pain syndromes. Acta Neurol Scand 60:93–99
Altman DG (1991) Practical statistics for medical research. Chapman and Hall, London
Arnold F (1966) Liquor-Untersuchungen an Gesunden und Multiple Sclerose-Kranken. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 96: 1098–1103
Atack JR (1988) Cerebrospinal fluid cholinesterases in aging and in dementia of the Alzheimer type. Ann Neurol 23:161–167
Conrad A, Schurmann J, Kreutz FH, Sieber A (1978) Ausarbeitung einer Methode zur quantitativen Proteinbestimmung mit Hilfe eines Laser-Nephelometers im Routinelabor. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 16:299–305
Darn PT, Huszka E] (1982) Der Eiweissgehalt des Liquors bei Patienten mit lumbalen Diskushernien. Neurochirurgia 25:132–134
Dencker SJ (1963) Studies on variation of CSF total proteins and cells with sex and age. Kungl Fysiogr SOlskapet I, Lund Forhandlingar 33/1
Dixon WJ, Brown MB, Engelman L, Jennrich RI (1990) BMDP statistical software manual. University of California Press, Berkeley
Felgenhauer S, Schliep G, Rapic N (1976) Evaluation of the blood-CSF barrier by protein gradients and the humoral immune response within the central nervous system. J Neurol Sci 30:113–128
Henry RJ, Carmon DC, Winkleman JW (1970) Clinical chemistry — principle and technics. Harper and Row, NY, pp 423–427
Jensen K (1978) Cerebrospinal fluid proteins in neurological diseases. Acta Neurol Scand 58:220–228
Jung PR, Rieder HP, Jeltsch C (1973) Normalwerte des total Proteins im Lumbal-Liquor; Alters-, Geschlechts- und Umweltabhängigkeit. Klin Wochenschr 51:810–816
Kawai T (1973) Clinical aspects of plasma proteins. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Kostulas VK, Link H, Lefvert AK (1987) Oligoclonal IgG bands in cerebrospinal fluid. Principles for demonstration and interpretation based on findings in 1114 neurological patients. Arch Neurol 44:1041–1044
Lefvert AK, Link H (1985) IgG production within the central nervous system: a critical review of proposed formulae. Ann Neurol 17:13–20
Link H, Kostulas V (1983) Utility of isoelectric focusing of cerebrospinal fluid and serum on agarose evaluated for neurological patients. Clin Chem 29:810–815
Link H, Tibbling G (1977) Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. II. Relation of the concentration of the proteins in serum and cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 37:391–396
May C, Kaye JA, Atack JR, Schapiro MB, Friedland RP, Rapport SI (1990) Cerebrospinal fluid production is reduced in healthy aging. Neurology 40:500–503
Mertin E, Wisser H, Doerr P (1971) Untersuchung über den Normalbereich des Gesamt-Eiweisses und der Eiweissfraktionen des Liquor cerebrospinalis nach elektrophoretischer Trennung auf Celluloseacetatfolie. Z Klin Chem 9:337–340
Olsson T, Kostulas V, Link H (1984) Improved detection of oligoclonal IgG in cerebrospinal fluid by isoelectric focusing in agarose, double-antibody peroxidase labeling, and avidin-biotin amplification. Clin Chem 30:1246–1249
Rieder HP, Wuthrich R (1962) Die Cu-folin-Methode zur Bestimmung des Gesamteiweiss-Gehaltes im Liquor. Klin Wochenschr 40:1070–1075
Roström B, Link H (1981) Oligoclonal immunoglobulins in cerebrospinal fluid in acute cerebrovascular disease. Neuroloy 31:590–596
Tibbling G, Link H, Ohman S (1977) Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. I. Establishment of reference values. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 37:385–390
Tourtellotte W (1959) Study of lipids in cerebrospinal fluid. Minneapolis, Neurol 9
Tourtellotte WW, Staugaitis SM, Walsh MJ, Shapshak P, Baumhefner RW, Portvin AR, Syndulko K (1985) The basis of intra-blood-brain barrier IgG synthesis. Ann Neurol 17:21–27
Tunevall TG (1984) Cerebrospinal fluid protein — an aid in the diagnosis of herniated discs. Acta Chir Scand 520:85–86
Wilkinson L (1990) SYGRAPH. The system for graphics. SYSTAT, Evanston, Ill.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skouen, J.S., Larsen, J.L., Vollset, E. et al. Elevated cerebrospinal fluid proteins in sciatica caused by disc herniation. Eur Spine J 3, 107–111 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02221449
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02221449