Abstract
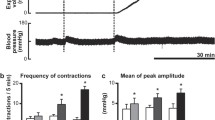
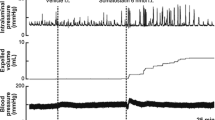
The influence of intermittent colorectal distension (CRD) on proximal colonic motility and abdominal pain perception was investigated in awake rats equipped with intraparietal electrodes on the cecum, proximal colon, and abdomen, before and three days after rectocolitis induction by trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNB)/ethanol. The normal myoelectrical activities of cecum and proximal colon [5.2±0.5 and 9.7±0.7 long spike bursts (LSB) per 5 min, respectively] were significantly (P<0.05) and gradually decreased by control CRD, at diameters above 9 mm. At the maximum CRD diameter (13.7 mm), 1.6±0.6 cecal and 3.9±0.8 colonic spike bursts occurred per 5 min (respectively, 69 and 60% decreases). This upstream inhibition was accompanied by a significant (P<0.05) and gradual increase in abdominal contractions (0.4±0.4 per 5 min in control vs 23.4±1.9 in response to 13.7 mm in diameter). Three days after TNB/ethanol, visceromotor and abdominal responses were significantly (P<0.05) enhanced at the least CRD diameter of 9 mm (cecum: 3.1±0.4 after TNB vs 5.0±0.7 in control; proximal colon: 5.1±0.9 vs 9.3±2.2; abdomen: 7.7±1.5 vs 0.5±0.4). We conclude that in awake rats, CRD evokes both abdominal contractions in response to pain and inhibition of cecal and proximal colonic motility, which thresholds are both lowered by TNB-induced rectocolitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roth LA: Ulcerative colitis.In Gastroenterology, Vol. II. HL Bockus (ed). New York, WB Saunders, 1976, pp 645–749
Donaldson RM Jr: Crohn's disease.In Gastrointestinal Disease, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Management. MH Sleizenger, JS Fordtran (eds). New York, WB Saunders, 1989, p 1435
Kern FJ, Almy TP, Abbot FK, Bogdonoff MD: The motility of the distal colon in nonspecific ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 19:492–503, 1951
Spriggs EA, Code CF, Bargen JA, Curtiss RK, Hightower NC Jr: Motility of the pelvic colon and rectum of normal persons and patients with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 19:480–491, 1951
Snape WJ, Matarazzo SA, Cohen S: Abnormal gastrocolonic response in patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut 21:392–396, 1980
Morris GP, Beck PL, Herridge MS, Depew WT, Szewczuk MR, Wallace JL: Hapten-induced model of chronic inflammation and ulceration in the rat colon. Gastroenterology 96:795–803, 1989
Pons L, Droy-Lefaix MT, Buéno L: Participation of leukotriene D4 in the early colonic transit disturbances induced by intracolonic administration of trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid in rats. Gastroenterology 102:149–156, 1991
Morteau O, Moré J, Pons L, Buéno L: Platelet-activating factor and interleukin-1 are involved in colonic dismotility of experimental colitis in rats. Gastroenterology 104:47–56, 1993
Peh KH, Wan BYC, Parke DV: Determination of glutathione content and myeloperoxidase activity in rat models of induced rectocolonic inflammation. Br J Pharmacol 97:548P, 1989
Allgayer H, Deschriyer K, Stenson WF: Treatment with 16,16′-dimethyl PGE2 before and after induction of colitis with trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid in rats decreases inflammation. Gastroenterology 96:1290–1300, 1989
Rachmilewitz R, Simon PL, Schwartz LW, Griswold DE, Fondacaro JD, Wasserman MA: Inflammatory mediators of experimental colitis in rats. Gastroenterology 97:326–337, 1989
Vilaseca J, Salas A, Guarner F, Rodriguez R, Malagelada JR: Participation of thromboxane and other eicosanoid synthesis in the course of experimental inflammatory colitis. Gastroenterology 98:269–277, 1990
Wallace JL, Keenan CM: Leukotriene B4 potentiates colonic ulceration in the rat. Dig Dis Sci 35(5):622–629, 1990
Wallace JL, Keenan CM: An orally active inhibitor of leukotriene synthesis accelerates healing in a rat model of colitis. Am J Physiol 258:G527-G534, 1990
Wallace JL: Release of platelet-activating factor (PAF) and accelerated healing induced by a PAF antagonist in an animal model of chronic colitis. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 6(4):422–425, 1988
Rachmilewitz D, Simon PL, Sjogren R, Fondacaro JD, Wasserman MA, Boedecker E. Interleukin-1: A sensitive marker of colonic inflammation. Gastroenterology 94:A263, 1988
Nosaka S, Murase S, Murata K: Arterial baroreflex inhibition by gastric distension in rats: mediation by splanchnic afferents. Am J Physiol 260:R985-R994, 1991
Moss HE, Sanger GJ: The effects of granisetron, ICS 205-903 and ondansetron on the visceral pain reflex induced by duodenal distension. Br J Pharmacol 100:497–501, 1990
Colburn RW, Coombs DW, Degnan CC, Rogers LL: Mechanical visceral pain model: Chronic intermittent intestinal distension in the rat. Physiol Behav 45:191–197, 1989
Lembeck F, Skofitsch G: Visceral pain reflex after pretreatment with capsaicin and morphine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 321:116–122, 1982
Clarck SJ, Smith TW: Opiate-induced inhibition of the visceral distension reflex by peripheral and central mechanisms. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 330:179–183, 1985
Maggi CA, Manzini S, Meli A: Contribution of neurogenic and myogenic factors in the response of rat proximal colon to distension. Am J Physiol 252:G447-G457, 1987
Sawyer DC, Rech RH, Durham RA, Adams T, Richter MA, Striler EL: Dose response to butorphanol administered subcutaneously to increase visceral nociceptive threshold in dogs. Am J Vet Res 52(11):1826–1830, 1991
Ness TJ, Gebhart GF. Colorectal distension as a noxious visceral stimulus: Physiologic characterization of pseudaffective reflexes in the rat. Brain Res 450:153–169, 1988
Danzebrink RM, Gebhart GF: Antinociceptive effects of intrathecal adrenoceptor agonists in a rat model of visceral nociception. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 253(2):698–705, 1990
Ness TJ, Randich A, Gebhart GF: Further behavioral evidence that colorectal distension is a “noxious” visceral stimulus in rats. Neurosci Let 131:113–116, 1991
Ruckebusch Y, Fioramonti J: Electrical spiking activity and propulsion in small intestine in fed and fasted rats. Gastroenterology 69:1045–1047, 1975
Sun WM, Read NW, Prior A, Daly JA, Cheak SK, Grundy D: Sensory motor responses to rectal distension vary according to rate and pattern of balloon inflation. Gastroenterology 99:1008–1015, 1990
Hermann H, Morin G: Mise en évidence d'un réflexe inhibiteur intestino-intestinal. CR Soc Biol Paris 115:529–531, 1934
Frantzides CT, Sarna KS, Matsumoto T, Lang IM, Condon RE: An intrinsic neural pathway for long intestino-intestinal inhibitory reflexes. Gastroenterology 92:594–603, 1987
Szurszewski JH: Physiology of mammalian prevertebral ganglia. Annu Rev Physiol 43:53–68, 1981
Youmans WB: Innervation of the gastrointestinal tract.In Handbook of Physiology, Alimentary Canal, Vol. IV: Motility. CF Code (ed). Washington, DC, Waverly Press, 1968, pp 1655–1663
Rouillon JM, Azpiroz F, Malagelada JR: Reflex changes in intestinal tone: Relationship to perception. Am J Physiol 261:G280-G286, 1991
Koster R, Anderson M, De Beer EJ: Acetic acid for analgesic screening. Fed Proc 18:412–413, 1959
Gebhart GF, Ness TJ: Central mechanisms of visceral pain. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 69:627–634, 1990
Garrison DW, Chandler MJ, Foreman RD: Viscerosomatic convergence onto feline spinal neurons from esophagus, heart and somatic fields: Effects of inflammation. Pain 49:373–382, 1992
Kubota Y, Petras RE, Ottaway CA, Tubbs RR, Farmer RG, Fiocchi C: Colonic vasoactive peptide nerves in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 102:1242–1251, 1992
Rao SC, Read NW, Davison PA, Bannister JJ, Holdsworth CD: Anorectal sensitivity and responses to rectal distension in patients with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 93:1270–1275, 1987
Jalan KN, Walker RJ, Prescott RJ, Butterworth STG, Smith AN, Sircus W: Faecal stasis and diverticular disease in ulcerative colitis. Gut 11:688–696, 1970
Lennard-Jones JE, Langman MJS, Avery Jones F: Faecal stasis in proctocolitis. Gut 3:301–306, 1962
Cowan GO, Das KM, Eastwood MA: Further studies of sulphasalazine metabolism in the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Br Med J 2:1055–1057, 1977
Allison MC, Vallance R: Prevalence of proximal faecal stasis in active colitis. Gut 32:179–182, 1991
Rao SSC, Holdsworth CD, Read NW: Symptoms and stool patterns in patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut 29:342–345, 1988
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors thank INRA for its financial support.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morteau, O., Hachet, T., Caussette, M. et al. Experimental colitis alters visceromotor response to colorectal distension in awake rats. Digest Dis Sci 39, 1239–1248 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02093789
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02093789