Abstract
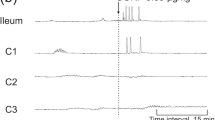
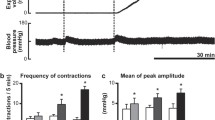
Rectal distension (RD) is known to induce intestinal dysmotility. Few studies were performed to compare effects of RD, colon distension (CD) and duodenal distension (DD) on small bowel motility. This study aimed to investigate effects and underlying mechanisms of distensions in these regions on intestinal motility and slow waves. Eight dogs chronically implanted with a duodenal fistula, a proximal colon fistula, and intestinal serosal electrodes were studied in six sessions: control, RD, CD, DD, RD + guanethidine, and CD + guanethidine. Postprandial intestinal contractions and slow waves were recorded for the assessment of intestinal motility. The electrocardiogram was recorded for the assessment of autonomic functions. (1) Isobaric RD and CD suppressed intestinal contractions (contractile index: 6.0 ± 0.4 with RD vs. 9.9 ± 0.9 at baseline, P = 0.001, 5.3 ± 0.2 with CD vs. 7.7 ± 0.8 at baseline, P = 0.008). Guanethidine at 3 mg/kg iv was able to partially block the effects. (2) RD and CD reduced the percentage of normal intestinal slow waves from 92.1 ± 2.8 to 64.2 ± 3.4 % (P < 0.001) and from 90 ± 2.7 to 69.2 ± 3.7 % (P = 0.01), respectively. Guanethidine could eliminate these inhibitory effects. (3) DD did not induce any changes in small intestinal contractions and slow waves (P > 0.05). (4) The spectral analysis of the heart rate variability showed that both RD and CD increased sympathetic activity (LF) and reduced vagal activity (HF) (P < 0.05). Isobaric RD and CD could inhibit postprandial intestinal motility and impair intestinal slow waves, which were mediated via the sympathetic pathway. However, DD at a site proximal to the measurement site did not seem to impair small intestinal contractions or slow waves.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mollen, R. M., Hopman, W. P., Kuijpers, H. H., & Jansen, J. B. (1999). Abnormalities of upper gut motility in patients with slow-transit constipation. European Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 11, 701–708.
Boccia, G., Buonavolonta, R., Coccorullo, P., Manguso, F., Fuiano, L., & Staiano, A. (2008). Dyspeptic symptoms in children: the result of a constipation-induced cologastric brake? Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 6, 556–560.
Bassotti, G., Stanghellini, V., Chiarioni, G., et al. (1996). Upper gastrointestinal motor activity in patients with slow-transit constipation. Further evidence for an enteric neuropathy. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 41, 1999–2005.
Abo, M., Kono, T., Wang, Z., & Chen, J. D. (2000). Impairment of gastric and jejunal myoelectrical activity during rectal distension in dogs. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 45, 1731–1736.
Reynolds, J. C., Ouyang, A., Lee, C. A., Baker, L., Sunshine, A. G., & Cohen, S. (1987). Chronic severe constipation. Prospective motility studies in 25 consecutive patients. Gastroenterology, 92, 414–420.
van der Sijp, J. R., Kamm, M. A., Nightingale, J. M., et al. (1993). Disturbed gastric and small bowel transit in severe idiopathic constipation. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 38, 837–844.
Yin, J., & Chen, J. D. (2011). Electroacupuncture improves rectal distension-induced delay in solid gastric emptying in dogs. American Journal of Physiology: Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 301, R465–R472.
Seidl, H., Gundling, F., Pehl, C., Pfeiffer, A., Schepp, W., & Schmidt, T. (2009). Small bowel motility in functional chronic constipation. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 21, 1278–e1122.
Shafik, A. (1998). Effect of duodenal distension on the pyloric sphincter and antrum and the gastric corpus: Duodenopyloric reflex. World Journal of Surgery, 22, 1061–1064.
Coremans, G., Geypens, B., Vos, R., et al. (2004). Influence of continuous isobaric rectal distension on gastric emptying and small bowel transit in young healthy women. Neurogastroenterology and Motility, 16, 107–111.
Kellow, J. E., Gill, R. C., & Wingate, D. L. (1987). Modulation of human upper gastrointestinal motility by rectal distension. Gut, 28, 864–868.
Bojo, L., & Cassuto, J. (1992). Gastric reflex relaxation by colonic distension. Journal of the Autonomic Nervous System, 38, 57–64.
Iwa, M., Strickland, C., Nakade, Y., Pappas, T. N., & Takahashi, T. (2005). Electroacupuncture reduces rectal distension-induced blood pressure changes in conscious dogs. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 50, 1264–1270.
Luo, Z. H., Chen, J. H., & Tao, Z. Z. (2009). Hyoid suspension treatment of obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi, 44, 877–880.
Li, F., Chen, J. H., Ma, S., Zhang, L., & Xiao, Y. H. (2009). Fang M [Antibacterial effects of a dental adhesive incorporating a quaternary ammonium monomer against Streptococcus mutans]. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi, 44, 621–625.
Chen, J., Xing, J., & Chen, J. D. (2009). Effects of muscarinic receptor stimulation and nitric oxide synthase inhibition on gastric tone and gastric myoelectrical activity in canines. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 24, 1130–1135.
Oliveira, H. M., Sallam, H. S., Espana-Tenorio, J., et al. (2009). Gastric and small bowel ileus after severe burn in rats: The effect of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Burns, 35, 1180–1184.
Song, J., Yin, J., Chen, J. D. (2013). Acute and chronic effects of desvenlafaxine on gastrointestinal transit and motility in dogs. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 25, 824–e637.
Chen, J. H., Lin, L., & Chen, J. D. Z. (2009). Colorectal and rectocolic reflexes in canines: involvement of tone, compliance and anal sphincter relaxation. Neurogastroenterology and Motility, 21, 20.
Chen, J., Stewart, W. R., & McCallum, R. W. (1993). Adaptive spectral analysis of episodic rhythmic variations in gastric myoelectric potentials. IEEE Transactions on BioMedical Engineering, 40, 128–135.
Lin, X., Peters, L. J., Hayes, J., & Chen, J. D. (2000). Entrainment of segmental small intestinal slow waves with electrical stimulation in dogs. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 45, 652–656.
Lin, X., Hayes, J., Peters, L. J., & Chen, J. D. (2000). Entrainment of intestinal slow waves with electrical stimulation using intraluminal electrodes. Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 28, 582–587.
Ouyang, H., Yin, J., Wang, Z., Pasricha, P. J., & Chen, J. D. (2002). Electroacupuncture accelerates gastric emptying in association with changes in vagal activity. American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 282, G390–G396.
Wang, Z. S., & Chen, J. D. Z. (2000). Robust ECG R-R wave detection using evolutionary-programming-based inference system (EPFIS) and its application to assessing brain-gut interaction. IEEE Proceedings-Science, Measurement and Technology, 147, 351–356.
Glia, A., & Lindberg, G. (1998). Antroduodenal manometry findings in patients with slow-transit constipation. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 33, 55–62.
Preston, D. M., & Lennard-Jones, J. E. (1986). Severe chronic constipation of young women: ‘idiopathic slow transit constipation’. Gut, 27, 41–48.
Zagorodnyuk, V. P., Kyloh, M., Gregory, S. J., et al. (2011). Loss of visceral pain following colorectal distension in an endothelin-3 deficient mouse model of Hirschsprung’s disease. Journal of Physiology, 589, 1691–1706.
Qi, H., & Chen, J. D. (2006). Effects of intestinal electrical stimulation on postprandial small-bowel motility and transit in dogs. American Journal of Surgery, 192, e55–e60.
Xu, X., Pasricha, P. J., Sallam, H. S., Ma, L., & Chen, J. D. (2008). Clinical significance of quantitative assessment of rectoanal inhibitory reflex (RAIR) in patients with constipation. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, 42, 692–698.
Guinet, A., Jousse, M., Damphousse, M., et al. (2011). Modulation of the rectoanal inhibitory reflex (RAIR): Qualitative and quantitative evaluation in multiple sclerosis. International Journal of Colorectal Disease, 26, 507–513.
Bajwa, A., Thiruppathy, K., Trivedi, P., Boulos, P., & Emmanuel, A. (2010). Effect of rectal distension on voluntary external anal sphincter function in healthy subjects. Colorectal Disease, 13, 1173–1179.
Chen, J., Song, G. Q., Yin, J., Koothan, T., & Chen, J. D. (2008). Electroacupuncture improves impaired gastric motility and slow waves induced by rectal distension in dogs. American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 295, G614–G620.
Lei, Y., Zhu, H., Xing, J., & Chen, J. D. (2005). Rectal distension modulates canine gastric tone and accommodation. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 50, 2134–2140.
Rao, S. S., Kuo, B., McCallum, R. W., et al. (2009). Investigation of colonic and whole-gut transit with wireless motility capsule and radiopaque markers in constipation. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 7, 537–544.
Zarate, N., Knowles, C. H., Yazaki, E., Lunnis, P. J., & Scott, S. M. (2009). Clinical presentation and patterns of slow transit constipation do not predict coexistent upper gut dysmotility. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 54, 122–131.
Shafik, A., Shafik, A. A., & Ahmed, I. (2003). Effect of colonic distention on ileal motor activity with evidence of coloileal reflex. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery, 7, 701–705.
Shafik, A., Shafik, A. A., El, S. O., & Shafik, I. A. (2007). Study of the effect of ileal distension on the motor activity of the jejunum, and of jejunal distension on the motor activity of the ileum. Hepato-Gastroenterology, 54, 2007–2010.
Qi, H., Brining, D., & Chen, J. D. (2007). Rectal distension inhibits postprandial small intestinal motor activity partially via the adrenergic pathway in dogs. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 42, 807–813.
Chen, J. H., Sallam, H. S., Lin, L., & Chen, J. D. (2010). Colorectal and rectocolonic reflexes in canines: Involvement of tone, compliance, and anal sphincter relaxation. American Journal of Physiology: Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 299, R953–R959.
Conflicts of interest
No conflicts of interest are declared by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, J., Yin, J. & Chen, J.D.Z. Inhibitory Effects and Sympathetic Mechanisms of Distension in the Distal Organs on Small Bowel Motility and Slow Waves in Canine. Cell Biochem Biophys 73, 665–672 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0679-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0679-4