Abstract
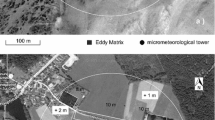
A pilot study to measure methane flux using eddy correlation sensors was conducted in a peatland ecosystem in north central Minnesota. A prototype tunable diode laser spectrometer system was employed to measure the fluctuations in methane concentration.
The logarithmic cospectrum of methane concentration and vertical wind velocity fluctuations under moderately unstable conditions had a peak nearf = 0.10 (wheref is the nondimensional frequency) and was quite similar to the cospectra of water vapor and sensible heat. Daytime methane flux during the first two weeks of August ranged from 120 to 270 mg m-2 day-1. The temporal variation in methane fluxes was consistent with changes in peat temperature and water table elevation. Our results compared well with the range of values obtained in previous studies in Minnesota peatlands.
These field observations demonstrate the utility of the micrometeorological eddy correlation technique for measuring surface fluxes of methane. The current state-of-the-art in tunable diode laser spectroscopy makes this approach practical for use in key ecosystems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, D. E., Verma, S. B., and Rosenberg, N. J.: 1984, ‘Eddy Correlation Measurements of CO2, Latent Heat and Sensible Heat over a Crop Surface’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 29, 263–272.
Anderson, D. E. and Verma, S. B.: 1985, ‘Turbulence Spectra of CO2, Water Vapor, Temperature and Wind Velocity Fluctuations Over a Crop Surface’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 33, 1–14.
Crill, P. M., Bartlett, K. B., Harriss, R. C., Gorham, E., Verry, E. S., Sebacher, D. I., Madzar, L., and Sanner, W.: 1988, ‘Methane Flux from Minnesota Peatlands’,Global Biogeochem. Cycles 2, 371–384.
Dise, N. B.: 1991, ‘Methane Emission from Peatlands in Northern Minnesota’, Ph.D. Dissertation. University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN. 138pp.
Harriss, R. C., Gorham, E., Sebacher, D. I., Bartlett, K. B., and Flebbe, P. A.: 1985, ‘Methane Flux from Northern Peatlands’,Nature 315, 652–654.
Hartman, R. K. and Gay, L. W.: 1981,Improvements in the Design and the Calibration of Temperature Measurement Systems, Proceedings of the 15th Conference on Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 210 pp.
Hastie, D. R., Mackay, G. I., Iguchi, T., Ridley, B. A., and Schiff, H. I.: 1983, ‘Tunable Diode Laser Systems for Measuring Trace Gases in Tropospheric Air’,Environ. Sci. and Tech. 17, 352A-364A.
Hicks, B. B. and McMillen, R. T.: 1988, ‘On the Measurement of Dry Deposition Using Imperfect Sensors and in Non-ideal Terrain’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 42, 79–94.
Ingram, H. A. P.: 1983, ‘Hydrology’, in A. J. P. Gore (ed.),Mires. Swamp, Bog, Fen, and Moor. A. General Studies, Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, Chap 3, pp. 67–158.
Kimball, B. A., Jackson, R. D., Nakayama, F. S., Idso, S. B., and Reginato, R. J.: 1976, ‘Soil-heat Flux Determination: Temperature Gradient Method with Computed Thermal Conductivities’,Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. J. 40, 25–28.
Leclerc, M. Y. and Thurtell, G. W.: 1990, ‘Footprint Prediction of Scalar Fluxes Using a Markovian Analysis’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 52, 247–258.
Legg, B. J., Long, I. F., and Zemrock, P. J.: 1981, ‘Aerodynamic Properties of Field Bean and Potato Crops’,Agric. Meteorol. 23, 21–43.
Lenschow, D. H. and Hicks, B. B. (eds.): 1989,Global Tropospheric Chemistry: Chemical Fluxes in the Global Atmosphere, Report of the Workshop on Measurements of Surface Exchange and Flux Divergence of Chemical Species in the Global Atmosphere, October 1987. Prepared by the National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO, for the National Science Foundation, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, 107 pp.
Leuning, R. and Moncrieff, J.: 1990, ‘Eddy-covariance CO2 Flux Measurements Using Open- and Closed-path CO2 Analyzers: Corrections for Analyzer Water Vapor Sensitivity and Damping of Fluctuations in Air Sampling Tubes’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 53, 63–76.
Matthews, E. and Fung, I.: 1987, ‘Methane Emission from Natural Wetlands: Global Distribution, Area, and Environmental Characteristics of Sources’,Global Biogeochem. Cycles 1, 61–86.
National Research Council: 1984,Global Tropospheric Chemistry: A Plan for Action, National Academy Press, Washington, DC, 194 pp.
Ohtaki, E.: 1984, ‘Application of an Infrared Carbon Dioxide and Humidity Instrument to Studies of Turbulent Transfer’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 29, 85–107.
Parhami, B.: 1971, ‘Spectral Analysis by Fast Fourier Transform’, Contributed computer program and write-up to the Computation Center, Department of Meteorology, The Pennsylvania State University. 24 pp.
Philip, J. R.: 1961, ‘The Theory of Heat Flux Meters’,J. Geophys. Res. 66, 571–579.
Schuepp, P. H., Leclerc, M. Y., MacPherson, J. I., and Desjardins, R. L.: 1990, ‘Footprint Prediction of Scalar Fluxes from Analytical Solutions of the Diffusion Equation’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 50, 355–373.
University Corporation for Atmospheric Research: 1986,Global Tropospheric Chemistry/Plans for the U.S. Research Effort, OIES Report 3, University Corporation for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO, 110 pp.
Verma, S. B., Baldocchi, D. D., Anderson, D. E., Matt, D. R., and Clement, R. J.: 1986, ‘Eddy Fluxes of CO2, Water Vapor, and Sensible Heat Over a Deciduous Forest’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 36, 71–91.
Verma, S. B., Kim, J., and Clement, R. J.: 1989, ‘Carbon Dioxide, Water Vapor and Sensible Heat Exchanges of a Tallgrass Prairie’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 46, 53–67.
Verma, S. B.: 1990, ‘Micrometeorological Methods for Measuring Surface Fluxes of Mass and Energy’,Remote Sens. Rev. 5(1), 99–115.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Published as Paper No. 9556, Journal Series, Nebraska Agricultural Research Division.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, S.B., Ullman, F.G., Billesbach, D. et al. Eddy correlation measurements of methane flux in a northern peatland ecosystem. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 58, 289–304 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02033829
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02033829