Abstract
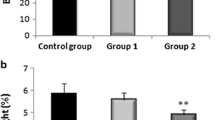
The toxic effects of bis (tributyltin) oxide (TBTO) on the rat liver were studied with an electron microscope and the accumulation sites of tin were determined with an X-ray microanalyzer. The activities of serum enzymes and the concentration of serum bilirubin were also analyzed. Male Wistar rats received an intramuscular injection of 0.5 ml/kg of TBTO. Marked swelling of the mitochondria appeared in the hepatocytes 4 h after injection of TBTO. Cytoplasmic vacuoles, which contained degenerated mitochondria, gradually increased in number in these hepatocytes. This in turn may have caused a decrease in the volume of hepatic cell cords and an enlargement of sinusoids in the entire hepatic lobule. However, fine structures of intrahepatic bile ducts were not altered. By X-ray microanalysis, tin peaks were preferentially obtained from swollen mitochondria of the hepatocytes. By polarographic analysis of the respiratory responses of mitochondria, it was demonstrated that rates of state 4 respiration and respiratory control ratio were significantly disturbed in TBTO-treated rats in comparison with those of controls. The activities of AST (aspartate aminotransferase) and ALT (alanine aminotransferase) were significantly increased after TBTO treatment, but those of ALP (alkaline phosphatase), LAP (leucine aminopeptidase) and total bilirubin were not changed. These results indicated that parenterally administered TBTO accumulated in the liver cell mitochondria and disturbed oxidative phosphorylation. Mitochondrial dysfunction might induce severe damage of the hepatocytes. Four days after injection of TBTO, hepatic structures and chemical indices were almost restored by the regeneration of hepatocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldridge WN (1958) The biochemistry of organotin compounds. Trialkyltins and oxidative phosphorylation. Biochem J 69: 367–379
Aldridge WN, Street BW, Skilleter DN (1977) Oxidative phosphorylation. Halide-dependent and halide-independent effects of triorganotin and triorganolead compounds on mitochondrial functions. Biochem J 168: 353–364
Cain K, Hyams RL, Griffiths DE (1977) Studies on energy-linked reactions: Inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation and energy-linked reactions by dibutyltin chloride. FEBS Lett 82: 23–28
Davis A, Barale R, Brun G, Forster R, Günther T, Hautefeuille H, van der Heijden CA, Knaap AGAC, Krowke R, Kuroki T, Loprieno N, Malaveille C, Merker HJ, Monaco M, Mosesso P, Neubert D, Norppa H, Sorsa M, Vogel E, Voogd CE, Umeda M, Bartsch H (1987) Evaluation of the genetic and embryotoxic effects of bis(tri-n-butyltin)oxide (TBTO), a broad-spectrum pesticide, in multiple in vivo and in vitro short-term tests. Mutat Res 188: 65–95
Estabrook RW (1967) Mitochondrial respiratory control and polarographic measurement of ADP: O ratio. Methods Enzymol 10: 41–47
Henschler D (1991) Tri-n-butyltin compounds. In: Henschler D (ed) Occupational toxicants: critical data evaluation for MAK values and classification of carcinogens. Vol. 1, VCH Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Weinheim, pp 315–333
Krajnc I, Webster PW, Loeber JG, van Leeuwen FXR, Vos JG, Vaessen HAMG, van der Heijden CA (1984) Toxicity of bis(tri-n-butyltin)oxide in the rat. 1. Short-term effects on general parameters and on the endocrine and lymphoid systems. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 75: 363–386
Ogura R, Sayanagi H, Noda K, Hara H, Shimada T, Murakami M (1978) Biochemical and morphological changes in isolated rat liver mitochondria exposed to ultraviolet light. Kurume Med J 25: 65–75
Stockdale M, Dawson AP, Selwyn MJ (1970) Effects of trialkyltin and triphenyltin compounds on mitochondrial respiration. Eur J Biochem 15: 342–351
Wakashin K (1975) Experimental studies on the toxicity of organic tin compounds — morphology of the butyl-tin intoxication. Tokyo Ikadaigaku Zasshi 33: 573–596 (in Japanese)
WHO (1990) Tributyltin compounds. Environmental Health Criteria Vol. 116, World Health Organization, Geneva
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshizuka, M., Hara, K., Haramaki, N. et al. Studies on the hepatotoxicity induced by bis (tributyltin) oxide. Arch Toxicol 66, 182–187 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01974012
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01974012