Abstract
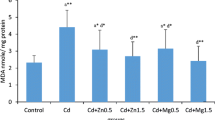
Administration ofN-benzyl-N-lactyl dithiocarbamate (BLDTC) to mice after chronic cadmium (Cd) administration evoked a prompt, dose-dependent reduction of the whole body burden; 75% of the retained Cd was mobilized and excreted after 20 i.p. injections of BLDTC at 1.0 mmol/kg/injection. This same dose regimen produced 71% and 98% reductions of the renal and hepatic Cd concentrations, respectively. There was no reduction by BLDTC of the endogenous level of any of seven other metals measured: iron, magnesium, selenium, copper, calcium, zinc, and manganese. Renal proximal tubular damage in mice which received Cd followed by BLDTC was much less than that observed in kidneys from mice which received Cd alone. Chronic Cd administration led to substantial epithelial vacuolar damage to renal distal tubules, and this process was not apparently reversed or antagonized by BLDTC treatment to the extent observed in proximal tubules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friberg L (1956) Edathamil calcium-disodium in cadmium poisoning. AMA Arch Indust Health 13: 18–23
Gale GR, Atkins LM, Walker EM Jr, Smith AB (1983) Comparative effects of diethyldithiocarbamate, dimercaptosuccinate, and diethylenetriaminepentaacetate on organ distribution and excretion of cadmium. Ann Clin Lab Sci 13: 33–44
Gale GR, Atkins LM, Smith AB, Jones SG, Basinger MA, Jones MM (1988a) N-Alkyl-N-dithiocarboxy-D-glucamine analogs as cadmium antagonists: synthesis and evaluation of then-propyl,n-butyl, andn-amyl derivatives. Arch Toxicol 62: 428–434
Gale GR, Atkins LM, Smith AB, Jones SG, Jones MM (1988b) Dithiocarbamate treatment of chronic cadmium intoxication in mice. Toxicol Lett 44: 77–84
Gale GR, Walker EM Jr, Smith AB, Jones MM, Stone A, Basinger M (1991) Treatment of chronic cadmium intoxication in mice withN-benzyl-N-lactyl dithiocarbamate (Abst). Ann Clin Lab Sci 21: 367
Gilman A, Philips FS, Allen RP, Koelle ES (1946) The treatment of acute cadmium intoxication in rabbits with 2,3-dimercaptopropanol (BAL) and other mercaptans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 87: 85–101
Jones MM, Cherian MG (1990) The search for chelate antagonists for chronic cadmium intoxication. Toxicology 62: 1–25
Jones MM, Singh PK, Jones SG (1990) Optimization of chelating agent structure for the mobilization of aged renal and hepatic cadmium deposits: sodiumN-benzyl-4-0-(β-d-galactopyranosyl)-d-glucamine-N-carbodithioate. Chem Res Toxicol 3: 248–253
Jones MM, Singh PK, Jones SG, Mukundan CR, Banton JA, Gale GR, Atkins LM, Smith AB (1991a) Chirality, charge, and chain branching effects on dithiocarbamate-induced mobilization of cadmium from intracellular deposits in mice. Chem Res Toxicol 4: 27–34
Jones MM, Singh PK, Gale GR, Atkins LM, Smith AB (1991b) Structure-activity relationships for intracellular cadmium mobilization byN-alkyl-4-0-(β-d-galactopyranosyl)-d-glucamine-N-carbodithioates. Chem Res Toxicol 4: 496–502
Jones SG, Mitchell WM, Jones MM (1986) Effects of the mobilization of aged tissue cadmium by chelating agents. J Toxicol Environ Health 19: 267–278
Jones SG, Singh PK, Jones MM (1988) Use of the Topliss scheme for the design of more effective chelating agents for cadmium decorporation. Chem Res Toxicol 1: 234–237
Kojima S, Ono H, Kiyozumi M, Honda T, Takadate A (1989) Effects ofN-benzyl-d-glucamine dithiocarbamate on the renal toxicity produced by subacute exposure to cadmium in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 98: 39–48
Kojima S, Kawagoe M, Kiyozumi M, Shimada H (1990) Effects of three dithiocarbamates on tissue distribution and excretion of cadmium in mice. Chem Pharm Bull 38: 3136–3139
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gale, G.R., Walker, E.M., Smith, A.B. et al. N-benzyl-N-lactyl dithiocarbamate treatment of mice after chronic cadmium administration. Arch Toxicol 66, 713–718 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01972622
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01972622