Abstract
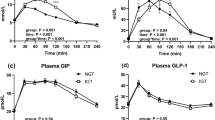
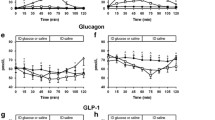
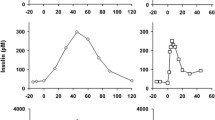
There is a well documented increase in the incidence of abnormal glucose tolerance in patients with Turner syndrome. To elucidate the pathophysiology of this phenomenon, we studied the serum concentrations of gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) — as probably the most important hormonal factor of the entero-insular axis — in relation to impaired glucose tolerance in this syndrome. Oral glucose tolerance tests were performed in 12 Turner patients with simultaneous determination of plasma glucose, insulin and GIP. An impaired glucose tolerance (iGT) was found in four patients with a chronological age between 12.3 and 14.9 years. These patients were compared with found Turner patients of similar age and weight and a normal glucose tolerance (nGT). The highest insulin level occurred 90 min after stimulation in the patients with iGT compared to 30 min in the nGT group. Interestingly, the total areas under the insulin curves were not different. Stimulated plasma GIP concentrations and the areas under the GIP curves wer significantly lower in iGT compared to nGT patients. A disturbed entero-insular axis might contribute to the delayed — rather than diminished — release of insulin in patients with Turner syndrome and impaired glucose tolerance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GIP:
-
gastric inhibitory peptide
- iGT:
-
impaired glucose tolerance
- nGT:
-
normal glucose tolerance
- OGTT:
-
oral glucose tolerance test
References
Beck B (1989) Gastric inhibitory polypeptide: a gut hormone with anabolic functions. J Mol Endocrinol 2:169–174
Bright GM, Blizzard RM, Kaiser DL, Clarke WL (1982) Organ-specific autoantibodies in children with common endocrine diseases. J Pediatr 100:8–14
Cassidy SB, Niblack GD, Lorber CA, Mann JM, Engel E (1978) HLA frequencies, diabetes mellitus and autoimmunity in Turner's patients and their relatives. Ann Genet 21:204–208
Cicognani A, Mazzanti L, Taasinari D, Pellacani A, Forabosco A, Landi L, Pifferi C, Cacciari E (1988) Differences in carbohydrate tolerance in Turner syndrome depending on age and karyotype. Eur J Pediatr 148:64–68
Costin G, Kogut MD (1985) Carbohydrate intolerance in gonadal dysgenesis. Evidence for insulin resistence and hypeglycagonemia. Horm Res 22:260–269
Creutzfeldt W, Ebert R (1985) New developments in the incretin concept. Diabetologia 28:565–573
Creutzfeldt W, Ebert R, Willms B, Frerichs H, Brown JC (1978) Gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) and insulin in obesity: increased response to stimulation and defective feedback control of serum levels. Diabetologia 14:15–24
Forbes AP, Engel E (1963) The high incidence of diabetes mellitus in 41 patients with gonadal dysgenesis and their close relatives. Metabolism 12:428–439
Greulich WW, Pyle SI (1959) Radiographic atlas of skeletal development of the hand and wrist, 2nd edn. University Press, Standford
Kreymann B, Williams G, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR (1987) Glucagon-like peptide 1 (7–36): a physiological incretin in man. Lancet II:1900–1904
Marner B, Bille G, Christy M, Damsgaard EM, Garne S, Heinze E, Larsen S, Lenmark Å, Mandrup-Poulsen T, Nerup J, Schroll M (1990) Disease-specificity of islet cytoplasmic antibodies (ICA): Type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes compared to other disorders associated with glucose intolerance. Diabetologia (in press)
Polychronakos C, Letarte J, Collu R, Ducharme JR (1980) Carbohydrate intolerance in children and adolescents with Turner syndrome. J Pediatr 96:1009–1014
Rasio E, Antaki A, Van Campenhout J (1976) Diabetes mellitus in gonadal dysgenesis: Studies of insulin and growth hormone secretion. Eur J Clin Invest 6:59–66
Seltzer HJ, Smith WL (1959) Plasma insulin activity after glucose. An index of insulingogenic reserve in normal and diabetic man. Diabetes 8:417–419
Smith CP, Williams AJK, Thomas JM, Archibald HR, Algar VD, Botazzo GF, Gale EAM, Savage MO (1988) The pattern of basal and stimulated insulin responses to intravenous glucose in first degree relatives of Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic children and unrelated adults aged 5 to 50 years. Diabetologia 31:430–434
Van Campenhout J, Rasio EL (1979) Carbohydrate tolerance in gonadal dysgenesis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 135:863–875
World Health Organization (1980) Second report of the expert committee on diabetes. WHO Tech Rep Ser:646
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Deceased February 21, 1987
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heinze, E., Schlickenrieder, J., Holl, R.W. et al. Reduced secretion of gastric inhibitory polypeptide in turner patients with impaired glucose tolerance. Eur J Pediatr 150, 339–342 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01955936
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01955936