Abstract
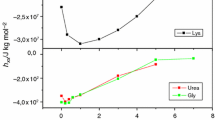
The disulfide reduction kinetics in equine lysozyme (ELZ), which is a Ca2+-binding lysozyme, and human (HLA) and equineα-lactalbumin (ELA) at pH 8.5 and 25°C by excess dithiothreitol were studied, and it was found that in ELZ there is no superreactive disulfide bond, while one of the disulfides is reduced very quickly by the reducing agent in HLA and ELA, as in bovineα-lactalbumin. The local conformation around the surface disulfide in ELZ seems to be more similar to that in hen egg-white lysozyme than inα-lactalbumin. The four disulfides in ELZ were reduced slowly in an apparently single-exponential form, and the bound Ca2+ lowered the reduction rate. The torsion energy on each of the disulfides in threeα-lactalbumin and eight c-type lysozymes whose native conformations have been experimentally or theoretically analyzed was calculated, and it was found that torsion imposed on the surface disulfide between Cys 6 and Cys 120 inα-lactalbumin is a main cause of the superreactivity and all of lysozymes, including the Ca2+-binding ones, have no such strained surface bond.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya, K. R., Stuart, D. I., Walker, N. P. C., Lewis, M., and Phillips, D. C. (1989).J. Mol. Biol. 208, 99–127.
Artymuik, P. J., and Blake, C. C. F. (1981).J. Mol. Biol. 152, 737–762.
Bell, K., McKenzie, H. A., Muller, V., Rogers, C., and Shaw, D. C. (1981).Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 68B, 225–236.
Ewbank, J. J., and Creighton, T. E. (1991).Nature 350, 518–520.
Ewbank, J. J., and Creighton, T. E. (1993).Biochemistry 32, 3677–3693, 3694–3707.
Harata, K., and Muraki, M. (1992).J. Biol. Chem. 267, 1419–1421.
Hayer-Hartl, M. K., Ewbank, J. J., Creighton, T. E., and Hartl, F. U. (1994).EMBO J. 13, 3192–3202.
Ikeguchi, M., Sugai, S., Fujino, M., Sugawara, T., and Kuwajima, K. (1992).Biochemistry 31, 12695–12700.
Imoto, T., Johnson, L. N., North, A. C. T., Phillips, D. C., and Rupley, J. A. (1972). InThe Enymes, 3rd. Ed., Vol. 7 (Boyer, P. D., ed.), Academic Press, New York, pp. 665–854.
Iwamoto, H., Nitta, K., and Sugai, S. (1990).Rep. Prog. Polym. Phys. Jpn. 33, 579–580.
Iyer, K. S., and Klee, W. A. (1973).J. Biol. Chem. 248, 707–710.
Katz, B. A., and Kossiakoff, A. (1986).J. Biol. Chem. 25, 15480–15485.
Kronman, M. J., and Andreotti, R. E. (1964).Biochemistry 3, 1145–1151.
Kuwajima, K. (1989).Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 6, 87–103.
Kuwajima, K., Nitta, K., Yoneyama, M., and Sugai, S. (1976).J. Mol. Biol. 106, 359–373.
Kuwajima, K., Ikeguchi, M., Sugawara, T., Hiraoka, Y., and Sugai, S. (1990).Biochemistry 29, 8240–8249.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970).Nature 227, 680–685.
McKenzie, H. A., and White, F. H., Jr. (1991).Adv. Protein Chem. 41, 173–315.
Nitta, K., Tsuge, H., Shimazaki, K., and Sugai, S. (1988).Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler 369, 671–675.
Nitta, K., and Sugai, S. (1989).Eur. J. Biochem. 182, 111–118.
Nitta, K., Tsuge, H., and Iwamoto, H. (1993).Int. J. Peptide Protein Res. 41, 118–123.
Nozaka, M., Kuwajima, K., Nitta, K., and Sugai, S. (1978).Biochemistry 17, 3753–3758.
Ptitsyn, O. B. (1992). InProtein Folding (Creighton, T. E., ed.), Freeman, New York, pp. 243–300.
Radford, S. E., and Dobson, C. M. (1995).Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 348, 17–25.
Reisfeld, R. A., Lewis, U. J., and Williams, D. E. (1962).Nature 195, 281–283.
Riddles, P. W., Blakeley, R. L., and Zerner, B. (1979).Anal. Biochem. 94, 75–81.
Schecter, Y., Patchornik, A., and Burstein, Y. (1973).Biochemistry 12, 3407–3413.
Segawa, T., Kuwajima, K., and Sugai, S. (1981).Biochim. Biophys. Acta 668, 89–97.
Sugai, S., and Ikeguchi, M. (1994).Adv. Biophys. 30, 37–84.
Tsuge, H., Koseki, K., Miyano, M., Shimazaki, K., Chuuma, T., Matsumoto, T., Noma, M., Nitta, K., and Sugai, S. (1991).Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1078, 77–84.
Tsuge, H., Ago, H., Noma, M., Nitta, K., Sugai, S., and Miyano, M. (1992).J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 111, 141–143.
Van Dael, H., Haezebrouck, P., Morozova, L., Arico-Muendel, C., and Dobson, C. M. (1993).Biochemistry 32, 11886–11894.
Warme, P. K., Momamy, F. A., Rumball, S. V., Turtle, R. W., and Scheraga, H. A. (1974).Biochemistry 13, 768–782.
Yao, M., Tanaka, I., Hikichi, K., and Nitta, K. (1992).J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 111, 1–3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gohda, S., Shimizu, A., Ikeguchi, M. et al. The superreactive disulfide bonds in α-lactalbumin and lysozyme. J Protein Chem 14, 731–737 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01886912
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01886912