Summary
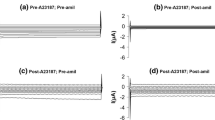
Ca2+-activated K+ channels were studied in cultured medullary thick ascending limb (MTAL) cells using the patch-clamp technique in the inside-out configuration. The Ca2+ activation site was modified using N-bromoacetamide (NBA). 1mm NBA in the bath solution, at 2.5 μm Ca2+ reduces the open probability,P o , of the channel to <0.01, without an effect on single-channel conductance. NBA-modified channels are still Ca2+-sensitive, requiring 25mm Ca2+ to raiseP o to 0.2. Both before and after NBA modification channel openings display at least two distributions, indicative of more than one open state. High Ca2+ (1mm) protects the channels from modification. Also presented is a second class of Ca2+-activated K+ channels which are normally present in MTAL cells which open infrequently at 10 μm Ca2+ (P o =0.01) but have aP o of 0.08 at 1mm Ca2+. We can conclude (i) that NBA modifies the channel by shifting Ca2+-sensitivity to very high Ca2+, (ii) that NBA acts on a site involved in Ca2+ gating, and (iii) that a low affinity channel is present in the apical cell membrane with characteristics similar to those of normal channels modified with NBA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barett, J.N., Magleby, K.L., Pallotta, B.S. 1982. Properties of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle.J. Physiol. (London) 331:211–230
Berman, M., Shahn, E., Weiss, M.F. 1962. The routine fitting of kinetic data to models: A mathematical formalism for digital computers.Biophys. J. 2:275–287
Berman, M., Weiss, M.F. 1978. SAAM Manual. U.S. DHEW Publication No. (NIH) 78-180
Blair, L.A.C., Dionne, V.E. 1985. Developmental acquisition of Ca2+ sensitivity by K+ channels in spinal neurons.Nature (London) 315:329–331
Green, N., Algren, A., Hoyer, J., Triche, T., Burg, M. 1985. Differentiated lines of cells from rabbit renal medullary thick ascending limbs grown on amnion.Am. J. Physiol. 249:C97-C104
Guggino, S.E., Guggino, W.B., Green, N., Sacktor, B. 1987a. Ca2+-activated K+ channels in cultured medullary thick ascending limb cells.Am. J. Physiol. 252:C121-C127
Guggino, S.E., Guggino, W.B., Green, N., Sacktor, B. 1987b. Blocking agents of Ca2+-activated K+ channels in cultured medullary thick ascending limb cells.Am. J. Physiol. 252:C128-C137
Guggino, S.E., Suarez-Isla, B.A., Guggino, W.B., Sacktor, B.. 1985. Forskolin and ADH stimulate a Ca2+-activated K+ channel in cultured kidney cells.Am. J. Physiol. 249:F448-F455
Hamill, O.P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B., Sigworth, F.J. 1981. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches.Pfleugers Arch. 391:85–100
Hunter, M., Lopes, A.G., Boulpaep, E.L., Giebisch, G.H. 1984. Single channel recordings of calcium-activated potassium channels in the apical membrane of rabbit cortical collecting tubules.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:4237–4239
Kawa, K. 1987. Transient outward currents and changes of their gating properties after cell activation in thrombocytes of the newt.J. Physiol. (London) 385:189–205
Kawahara, K., Hunter, M., Giebisch, G. 1987. Intracellular Na+ blocks outward current through calcium-activated potassium channels in the luminal membrane ofAmphiuma diluting segment.Am. J. Physiol. (in press)
Magleby, K.L., Pallotta, B.S. 1983. Calcium dependence of open and shut interval distributions from calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle.J. Physiol. (London) 344:585–604
Moczydlowski, E., Latorre, R. 1983. Gating kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rat muscle incorporated into planar lipid bilayers: Evidence for two voltage dependent Ca2+-binding sites.J. Gen. Physiol. 82:511–542
Pallotta, B.S. 1985. N-bromoacetamide removed a calcium-dependent component of channel opening from calcium-activated potassium channels in rat skeletal muscle.J. Gen. Physiol. 86:601–611
Patlak, J., Horn, J. 1982. Effect of N-bromoacetamide on single sodium channel currents in excised membrane patches.J. Gen. Physiol. 79:333–351
Vergara, C., Latorre, R. 1983. Kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rabbit muscle incorporated into planar bilayers.J. Gen. Physiol. 82:543–568
Vergara, C., Moczydlowski, E., Latorre, R. 1984. Conduction, blockade, and gating in a Ca2+-activated K+ channel incorporated into planar lipid bilayers.Biophys. J. 45:73–76
Yellen, G. 1984. Ionic permeation and blockade of Ca2+-activated K+ channels of bovine chromaffin cells.J. Gen. Physiol. 84:157–186
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cornejo, M., Guggino, S.E. & Guggino, W.B. Modification of Ca2+-activated K+ channels in cultured medullary thick ascending limb cells by N-bromoacetamide. J. Membrain Biol. 99, 147–155 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871234
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871234