Summary
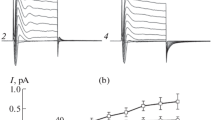
Exposure of the mucosal side of toad(Bufo bufo) urinary bladder and frog(Rana ridibunda) skin to the polyene ionophore nystatin, resulted in stable preparations in which the apical resistance was negligible compared to the basolateral resistance. The preparations support passive K currents in both directions and an amiloride-insensitive Na current in the apicalserosal direction which is blocked by ouabain. The nystatintreated toad bladder was used to study the electrical properties of the basolateral membrane by means of current-voltage curves recorded transepithelially. The K current showed strong rectification at cellular potentials negative with respect to the interstitial space. The ouabain-sensitive current increased with membrane voltage at negative voltages but saturated above+20 mV.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chapman, J.B., Johnson, E.A. 1978. The reversal potential of an electrogenic sodium pump. A method for determining the free energy of ATP breakdown?J. Gen. Physiol. 72:403–408
Chase, H.S., Al-Awqati, Q. 1981. Regulation of the sodium permeability of the luminal border of toad bladder by intra-cellular sodium and calcium. Role of sodium-calcium exchange in the basolateral membrane.J. Gen. Physiol. 77:693–712
Davis, C.W., Finn, A.L. 1982. Sodium transport inhibition by amiloride reduces baso-lateral membrane potassium conductance in tight epithelia.Science 216:525–527
Eaton, D.C., Frace, A.M., Silverthorn, S.U. 1982. Active and passive Na+ fluxes across the basolateral membrane of rabbit urinary bladder.J. Membrane Biol. 67:219–229
Erecin'ska, M., Wilson, D.F. 1982. Regulation of cellular energy metabolism(Topical Review).J. Membrane Biol. 70:1–14
Fromter, E., Gebler, B. 1977. Electrical properties of amphibian urinary bladder epithelia. III. The cell membrane resistances and the effect of amiloride.Pflugers Arch. 371:99–108
Gebhardt., U., Lindemann, B. 1974. Speed of voltage threshold shift after step change of Na o and Ca o at the outer surface of frog skin.Pflugers Arch. 347:9–18
Glynn, I.M., Karlish, S.J.D. 1975. The sodium pump.Annu. Rev. Physiol. 37:13–55
Goldman, D.E. 1943. Potential, impedance and rectification in membranes.J. Gen. Physiol. 27:30–60
Helman, S.I., Fisher, R.S. 1977. Microelectrode studies of the active transport pathway of frog skin.J. Gen. Physiol. 69:571–604
Karlish, S.J.D., Lieb, W.R., Stien, W.D. 1982. Combined effects of ATP and phosphate on rubidium exchange mediated by Na−K-ATPase reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles.J. Physiol. (London) 328:333–350
Kedem, O., Caplan, S.R. 1965. Degree of coupling and its relation to efficiency of energy conversion.Trans. Faraday Soc. 61:1897–1911
Koefoed-Johnson, V., Ussing, H.H. 1958. The nature of the frog skin potential.Acta Physiol. Scand. 42:298–308
Lewis, S.A., Eaton, D.C., Clausen, C., Diamond, J.M. 1977. Nystatin as a probe for investigating the electrical properties of a tight epithelium.J. Gen. Physiol. 70:427–440
Lewis, S.A., Wills, N.K. 1982. Electrical properties of the rabbit urinary bladder assessed using gramicidin D.J. Membrane Biol. 67:45–53
Lichtenstein, N.S., Leaf, A. 1965. Effect of amphotericin B. on the permeability of the toad bladder.J. Clin. Invest. 44:1328–1342
Macknight, A.D.C., DiBona, D.R., Leaf, A. 1980. Sodium transport across toad urinary bladder: A model tight epithelium.Physiol. Rev. 60:615–617
Marmor, M.F. 1971. The independence of electrogenic sodium transport and membrane potential in a molluscan neurone.J. Physiol. (London) 218:599–608
Meer, R., van der, Akerboom, T.P.M., Groen, A.K., Tager, J.M. 1978. Relationship between oxygen uptake of perfused rat-liver cells and the cytosolic phosphorylation state calculated from indicator metabolites and a redetermined equilibrium constant.Eur. J. Biochem. 84:421–428
Nagel, W. 1979. Inhibition of potassium conductance by barium in frog skin epithelium.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 552:346–357
Nielsen, R. 1977. Effect of the polyene antibiotic filipin on the permeability of inward- and outward-facing membrane of the isolated frog skin.Acta Physiol. Scand. 99:399–411
Nielsen, R. 1979. Coupled transepithelial sodium and potassium transport across isolated frog skin: Effect of ouabain, amiloride and the polyene antibiotic filipin.J. Membrane Biol. 51:161–184
Palmer, L.G., Edelman, I.S., Lindemann, B. 1980. Current-voltage analysis of apical sodium transport in toad urinary bladder: Effects of inhibitors of transport and metabolism.J. Membrane Biol. 57:59–71
Russell, J.M., Eaton, D.C., Brodwick, M.S. 1977. Effects of nystatin on membrane conductance and internal ion activitics inAplysia neurons.J. Membrane Biol. 37:137–156
Schultz, S.G. 1981. Homocellular regulatory mechanism in sodium-transporting epithelia: Avoidance of extinction by “flush-through.”Am. J. Physiol. 241:F579-F590
Sharp, G.W.G., Coggins, C.H., Lichtenstein, N.S., Leaf, A. 1966. Evidence for a mucosal effect of aldosterone on sodium transport in the toad bladder.J. Clin. Invest. 45:1640–1647
Von Hedenstrom, M., Joffer, M. 1979. The effect of nystatin on active transport inRhodotorula glutinis (gracilis) is restricted to the plasma membrane.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 555:169–174
Warncke, J., Slayman, C.L. 1980. Metabolic modulation of stoichiometry in a proton pump.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 591:224–233
Williamson, J.R., Steinman, R., Coll, K., Rich, T.L. 1981. Energetics of citrulline synthesis by rat liver mitochondria.J. Biol. Chem. 256:7287–7297
Wills, N.K. 1981. Antibiotics as tools for studying the electrical properties of tight epithelia.Fed. Proc. 40:2202–2205
Wills, N.K., Eaton, D.C., Lewis, S.A., Ifshin, M.S. 1979. Current voltage relationship of the basolateral membrane of a tight epithelium.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 555:519–523
Zeiske, W., Van Driessche, W. 1979. Saturable K+ pathway across the outer border of frog skin (Rana temporaria): Kinetics and inhibition by Cs+ and other cations.J. Membrane Biol. 47:77–96
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garty, H. Current-voltage relations of the basolateral membrane in tight amphibian epithelia: Use of nystatin to depolarize the apical membrane. J. Membrain Biol. 77, 213–222 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870570
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870570