Summary
The influence of insulin on the intestinal absorption of glucose, water, sodium and potassium was investigated in man using a triple lumen tube technique. After an absorption period of 60 min 1 g of tolbutamide was injected in order to stimulate endogenous insulin secretion. Alternatively 20 units of regular insulin were applied intravenously. Thereafter absorption was studied over 4 periods of 15 min duration.
Results:
-
1.
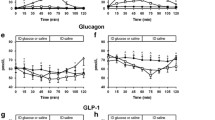
In healthy subjects the absorption of glucose water, sodium and potassium was decreased after the injection of tolbutamide as well as after the injection of insulin.
-
2.
The decrease in absorption was also demonstrable when the insulin induced reduction of blood sugar levels was abolished by intravenous glucose infusion.
-
3.
In insulin dependent diabetics there was no decrease in absorption after injection of tolbutamide. This was due to the unability to secrete insulin. On the other hand a decrease in absorption occurred if insulin was applied in insulin dependent diabetics.
These results demonstrate that the absorption of glucose, water, sodium and potassium from the human intestine is reduced by insulin.
Zusammenfassung
Der Einfluß von Insulin auf die Resorption von Glucose, Wasser, Natrium und Kalium wurde mittels der segmentalen Dünndarmperfusion mit einer dreilumigen Sonde untersucht. Nach Messung der Resorption über zwei 30 min-Perioden wurden den Probanden 1,0 g Tolbutamid (Rastinon®) bzw. 20 IE Insulin (Actrapid®) intravenös injiziert und danach die Resorption über vier 15 min-Perioden bestimmt.
Ergebnisse
-
1.
Stoffwechselgesunde zeigten sowohl nach Injektion von Tolbutamid und dadurch induzierter Erhöhung des Seruminsulinspiegels als auch nach Insulininjektion eine signifikante Minderung der Resorption.
-
2.
Diese Resorptionsminderung war auch nachweisbar, wenn Glucose zur Verhinderung des Blutzuckerabfalls unmittelbar nach der Insulininjektion infundiert wurde.
-
3.
Insulinbedürftige Diabetiker lassen nach der Injektion von Tolbutamid — offenbar infolge fehlender Insulinsekretion — keine Resorptionsänderungen erkennen, zeigen aber eine Transportminderung nach Insulininjektion.
Diese Befunde belegen, daß die Glucose-, Wasser-, Natrium- und Kaliumresorption im menschlichen Dünndarm durch Insulin reduziert wird.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Aulsebrook, K. A.: Intestinal transport of glucose and sodium: Changes in alloxan-diabetes and effects of insulin. Experientia (Basel)21, 346–347 (1965)
Beyreiss, K., Müller, F., Strack, E.: Über die Resorption von Monosacchariden. I. Der Einfluß von Insulin auf die Resorption der Galactose. Z. ges. exp. Med.138, 277–288 (1964)
Beyreiss, K., Müller, F., Strack, E.: Über die Resorption von Monosacchariden. III. Der aktive Transport von D(+)-Xylose gegenüber L—(+)-Arabinose. Z. ges. exp. Med.138, 546–560 (1965)
Bloch, R., Menge, H., Lorenz-Meyer, H., Riecken, E. O.: Automatisierte segmentale Dünndarmperfusion. Eine Methode zur Messung der intestinalen Resorption. Klin. Wschr.49, 1218–1222 (1971)
Capps, J. C., Shetlar, M. R., Bradford, R. H.: Hexosamine metabolism. II. Effect of insulin and phlorizin on the absorption and metabolismin vivo, of D-glucosamine and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine in the rat. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)127, 205–212 (1966)
Cooper, H., Levitan, R., Fordtran, J. S., Ingelfinger, F. J.: A method for studying absorption of water and solute from the human small intestine. Gastroenterology50, 1–7 (1966)
Cori, C. F.: The fate of sugar in the animal body: III. The rate of glycogen formation in the liver of normal and insulinized rats during the absorption of glucose, fructose and galactose. J. biol. Chem.70, 577–585 (1926)
Dubois, R. S., Roy, C. C.: Insulin stimulated transport of 3-O-methyl-glucose across the rat jejunum. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.)130, 931–934 (1969)
Flores, P., Schedl, H. P.: Intestinal transport of 3-O-methyl-D-glucose in the normal and alloxan diabetic rat. Amer. J. Physiol.214, 725–729 (1968)
Fromm, D., Field, M., Silen, W.: Effect of insulin on sugar and amino acid transport across isolated small intestine. Amer. J. Physiol.217, 53–57 (1969)
Gottesbüren, H., Schmitt, E., Menge, H., Bloch, R., Lorenz-Meyer, H., Riecken, E. O.: Untersuchungen zum Einfluß des Insulins auf die intestinale Resorption beim Menschen. I. Vergleich der Glucose-, Wasser- und Elektrolytresorption bei Diabetikern und stoffwechselgesunden Probanden. Res. exp. Med.160, 326–330 (1973)
Grimminger, H., Kallee, E.: Die Inselzellhormone: Der Abbau von Insulin. In: E. F. Pfeiffer, Handbuch des Diabetes mellitus, Band I, S. 257–280. München: Lehmanns 1969
Horváth, J., Wix, G.: Hormonal influences on glucose resorption from the intestine. Acta physiol. hung.2, 435–467 (1951)
Lequin, H. C., Steyn-Parvé, E. P.: Some aspects of glucose metabolism in normal and alloxan-diabetic rats. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)58, 439–448 (1962)
Lourau, M.: Mode d'action de l'insuline sur l'absorption intestinale du glucose. C. R. Acad. Sci. (Paris)236, 1376–1378 (1953)
Love, A. H. G., Canavan, D. A.: Effect of insulin on intestinal glucose absorption. Lancet1968 II, 1325–1326
Manome, S. H., Kuriaki, K.: Effect of insulin, phlorizin and some metabolic inhibitors on the glucose absorption from the intestine. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn.130, 187–194 (1961)
Mehnert, H., Förster, H., Haslbeck, G.: Zur Frage der Wirkung von Insulin auf die intestinale Resorption von Glucose und Fructose. Diabetologia3, 23–29 (1967)
Olsen, W. A., Rosenberg, J. H.: Intestinal transport of sugars and amino acids in diabetic rats. J. clin. Invest.49, 96–105 (1970)
Pauls, F., Drury, D. R.: The rate of glucose absorption from the intestine of diabetic rats. Amer. J. Physiol.137, 242–245 (1942)
Soulairac, A.: La regulation neuro-endocrinienne de l'absorption intestinale des glucides. Ann. Endocr. (Paris)8, 377–393 (1947)
Varro, V., Csernay, L.: The effect of intra-arterial insulin and glucagon on the glucose metabolism of the small intestine in the dog. Scand. J. Gastroent.1, 232–237 (1966)
Vinnik, J. E., Kern, F., Sussman, K. E.: The effect of diabetes mellitus and insulin on glucose absorption by the small intestine. J. Lab. clin. Med.66, 131–136 (1965)
Wide, L., Porath, J.: Radioimmuno assay of proteins with the use of sephadexcoupled antibodies. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)130, 257–260 (1966)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit Unterstützung durch die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gottesbüren, H., Schmitt, E., Menge, H. et al. Untersuchungen zum Einfluß des Insulins auf die intestinale Resorption beim Menschen. Res. Exp. Med. 161, 262–271 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01851450
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01851450