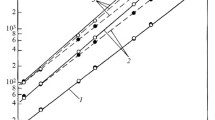
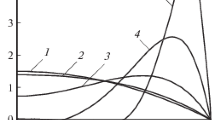
Abstract
The heat transfer and fluid flow are determined for fully developed laminar flow in a vertical channel. The effects of natural and forced convection and thermal radiation are included in the analysis. The spectral variation of the radiation properties are included through the use of the total band absorptance. The analysis is general and specific numerical results have been obtained for the 15 micron band of carbon dioxide. A simplified approach for large path is also presented which is in excellent agreement with the more exact results.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a, b :
-
exponential kernel approximation (0.9, 1.8, respectively)
- c p :
-
specific heat at constant pressure
- e ω :
-
black body spectral emissivity
- f 2 :
-
pressure broadening parameter
- g :
-
acceleration of gravity
- K T :
-
thermal conductivity
- k ω :
-
spectral absorption coefficient
- L :
-
channel spacing
- p :
-
static fluid pressure
- q R :
-
radiant heat flux
- q1, total:
-
total wall heat flux = (q1, conduction) with rad. present +q1, radiation
- Ra :
-
Rayleigh =βgL 3 τ/να
- T :
-
fluid temperature
- u :
-
axial velocity
- \(\bar u\) :
-
non-dimensional velocity
- \(\underset{\raise0.3em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle-}$}}{u} \) :
-
optical depth =C 20 ρ LY
- x :
-
axial coordinate
- y :
-
transverse coordinate
- Y :
-
non-dimensional transverse coordinate
- α :
-
thermal diffusivity
- β :
-
thermal coefficient of volume expansivity
- γ :
-
\( - \left( {\frac{1}{{\rho 0}}\frac{{\partial p}}{{\partial x}} + g} \right)\frac{{L^3 }}{{v\alpha }}\)
- μ :
-
direction cosine
- ν :
-
kinematic viscosity
- ρ :
-
mass density
- τ :
-
=L(dT 1/dx)
- φ :
-
=(T 1−T)/τγ
- 0:
-
evaluated at origin
- 1:
-
evaluated at wall
- ωc :
-
evaluated at band center
- m :
-
mean value
References
Gebhart, B., Heat Transfer, McGraw-Hill Publ. Co., N. Y., 1971.
Martinelli, R. C. andL. M. K. Boelter, University of California, Publication in Eng.5 (1942) 23.
Ostrach, S., NACA Tech. Note 3141 (1954).
Ostrach, S., Grenzschichtforschung (Ed. H. Görtler) Springer, 1958.
Hallman, T. M., ASME Transactions78 (1965) 1831.
Morton, B. R., J. Fluid Mechanics8 (1960) 227.
Greif, R., I. S. Habib andJ. C. Lin, J. Fluid Mechanics46 (1971) 513.
Bratis, J. C. andJ. L. Novotny, Int. J. of Heat and Mass Transfer17 (1974) 23–36.
Cess, R. D., P. Mighdoll andS. N. Tiwari, Int. J. of Heat and Mass Transfer10 (1967) 1521.
Wilson, K. H. andR. Greif, J. of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer8 (1968) 1061.
Sparrow, E. M. andR. D. Cess, Radiation Heat Transfer, Brooks/Cole Publ. Co., Belmont, Calif., 1966.
Viskanta, R., Advances in Heat Transfer, Irvine, T. F., Jr., and Hartnett, J. P., eds., Vol. III, Academic Press, N. Y., 1966, 175.
Greif, R. andI. S. Habib, J. of Heat Transfer91 (1969) 282.
Tien, C. L. andJ. E. Lowder, Int. J. of Heat and Mass Transter9 (1966) 698.
Edwards, D. K. andW. A. Menard, Appl. Optics3 (1964) 621.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Donovan, T.E., Greif, R. Laminar convection with an absorbing and emitting gas. Appl. Sci. Res. 31, 110–122 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01795830
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01795830