Summary
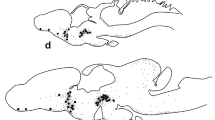
Dopaminergic and peptidergic nerve fibers were simultaneously demonstrated with a double-labeling technique at the ultrastructural level. The first antibody, raised against tyrosine hydroxylase, was applied during the preembedding phase and visualized with the peroxidase method. The second antibody, raised against one of the peptides met-enkephalin, somatostatin or gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), was applied to the ultrathin sections and visualized with gold-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG. The fibers of both categories were present in the zona externa of the median eminence, frequently contacting the basal lamina of the portal vessels. In addition, topographical relationships between different types of nerve fibers were observed in the perivascular areas, although there were no morphological signs of synaptic specializations. Using serial sections, it could be established that one GnRH-fiber contacted both a dopaminergic fiber and a fiber immunoreactive for met-enkephalin. The observations support earlier physiological data concerning the regulation of the hypothalamo-hypophyseal axis, with special emphasis on the release of neurohormones in the median eminence of the newt.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajika K (1979) Simultaneous localization of LHRH and catecholamines in rat hypothalamus. J Anat 128:331–347
Aldes LD, Boone TB (1984) A combined flat-embedding, HRP histochemical method for correlative light and electron microscopic study of single neurons. J Neurosci Res 11:27–34
Arluison M, Dietl M, Thibault J (1984) Ultrastructural morphology of dopaminergic nerve terminals and synapses in the striatum of the rat using tyrosine hydroxylase immunocytochemistry: a topographical study. Brain Res Bull 13:269–295
Ball JN (1981) Hypothalamic control of the pars distalis of fishes, amphibians and reptiles. Gen Comp Endocrinol 44:135–170
Calas A (1985) Morphological correlates of chemically specified neuronal interactions in the hypothalamo-hypophyseal area. Neurochem Int 7:927–940
Chetverukhin VK, Belenky MA, Polenov AL (1986) The hypothalamo-hypophysial system of the frogRana temporaria. Ultrastructure of the median eminence in the adult frog, with reference to the distribution of serotoninergic terminals. Cell Tissue Res 243:649–654
Corio M, Doerr-Schott J (1988) The monoaminergic system in the diencephalon of the tadpole,Triturus alpestris (Mert). A histofluorescence study. J Hirnforsch 29:377–384
Decavel C, Dubourg P, Leon-Henri B, Geffard M, Calas A (1989) Simultaneous immunogold labeling of GABAergic terminals and vasopressin-containing neurons in the rat paraventricular nucleus. Cell Tissue Res 255:77–80
Doerr-Schott J, Follénius E (1970) Identification et localisation des fibres aminergiques dans l'eminence mediane de la grenouille verte (Rana esculenta L.) par autoradiographie au microscope électronique. Z Zellforsch 111:427–436
Doerr-Schott J, Follénius E (1972) Innervation adrenergique de l'hypophyse deTriturus alpestris C R Acad Sci III 274:2712–2714
Doerr-Schott J, Clauss RO, Dubois MP (1978) Localisation immunohistochimique au microscope électronique d'une hormone GnRH dans l'éminence mediane deXenopus laevis Daud. C R Acad Sci III 286:477–479
Doerr-Schott J, Dubois MP, Lichte C (1981) Immunohistochemical localization of substances reactive to antisera against α andβ endorphin and met-enkephalin in the brain ofRana temporaria. Cell Tissue Res 217:79–82
Dubois MP (1975) Immunoreactive somatostatin is present in discrete cells of the endocrine pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:1340–1343
Dubois MP, Barry J (1974) Repartition comparée de trois neurofacteurs hypothalamiques: LHRH, SRIF et neurophysine dans l'hypothalamus et l'éminence médiane: étude en immunofluorescence. Ann Endocrinol (Paris) 35:663–664
Fasolo A, Franzoni MF, Mazzi V (1973) The neurohypophysis of the crested newt. III Fine structure of the median eminence. Z Zellforsch 141:203–221
Foord SM, Peters JR, Dieguez C, Scanlon MF, Hall R (1983) Dopamine receptors on rat anterior pituitary cells in culture: functional correlation with the inhibition of TSH and PRL secretion. Endocrinology 112:1567–1577
Franzoni MF, Thibault J, Fasolo A, Martinoli MG, Scaranari F, Calas A (1986) The organization of TH-immunopositive neurons in the brain of the crested newt,Triturus cristatus carnifex. J Comp Neurol 251:121–134
Franzoni MF, Martinoli MG, Thibault J (1987) Tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive neurons in the hypothalamus of the crested newt. An electron microscopic study. Basic Appl Histochem 31:63–72
Fuxe K, Agnati LF, Calza L, Andersson K, Giardino L, Benfenati F, Camurri M, Goldstein M (1984) Quantitative chemical neuroanatomy gives new insights into the catecholamine regulation of the peptidergic neurons projecting to the median eminence. In: Usdin E, Carlsson A, Dahlstrom A, Engel J (eds) Catecholamines: neuropharmacology and central nervous system. Liss, New York, pp 441–449
Hall TR, Chadwick A (1983) Effects of synthetic mammalian thyrotrophin releasing hormone, somatostatin and dopamine on the secretion of prolactin and growth hormone from amphibian and reptilian pituitary glands incubated in vitro. J Endocrinol 102:175–180
Jacobowitz DM (1988) Multifactorial control of pituitary hormone secretion: the “wheels” of the brain. Synapse 2:186–192
Kordon C, Enjalbert A, Herg M, Joseph-Bravo PI, Rotsztejn W, Ruberg M (1980) Role of neurotransmitters in the control of adenohypophyseal secretion. In: Morgane PJ, Panksepp J (eds) Handbook of the hypothalamus, Vol 2. Dekker, New York Basel, pp 253–306
Liposits ZS, Phelix C, Paull WK (1987a) Synaptic interaction of serotonergic axons and corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) synthesizing neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of the rat. Histochemistry 86:541–549
Liposits ZS, Paull WR, Wu P, Jackson IMD, Lechan RM (1987b) Hypophysiotrophic thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) synthesizing neurons. Ultrastructure, adrenergic innervation and putative transmitter action. Histochemistry 88:1–10
Nakai Y, Shinkawa Y (1971) Electron microscopic autoradiography of the localization of serotonin in the frog median eminence. Z Zellforsch 119:326–333
Nakai Y, Shioda S, Ochiai H, Kudo J, Hoshimoto A (1983) Ultrastructural relationship between monoamine- and TRH-containing axons in the rat median eminence as revealed by combined autoradiography and immunocytochemistry in the same tissue section. Cell Tissue Res 230:1–14
Nakai Y, Shioda S, Ochiai H, Kozasa K (1986) Catecholaminepeptide interactions in the hypothalamus. In: Ganten D, Pfaff D (eds) Current topics in neuroendocrinology, Vol 7: Morphology of hypothalamus and its connections. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 135–160
Negro-Vilar A (1982) The median eminence as a model to study presynaptic regulation of neural peptide release. Peptides 3:305–310
Ochiai H, Iwai C, Nakai Y (1988) Ultrastructural demonstration of the catecholaminergic innervation of vasopressin neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the rat by double-labeling immunocytochemistry. Neurosci Lett 85:14–18
Oksche A, Zimmermann P, Oehmke H-J (1972) Morphometric studies of the tubero-eminential systems controlling reproductive functions. In: Knigge KM, Scott DE, Weindl A (eds) Brain-endocrine interaction. Median eminence: structure and function. Karger, Basel, pp 142–153
Omeljaniuk RJ, Peter RE (1989) In vitro binding characteristics of [3H]Spiperone to the pituitary of the goldfish (Carrassius auratus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 74:57–67
Rostene WH, Drouva SV, Pollard H, Sokoloff P, Patton E, Kordon C (1982) Further evidence for the existence of opiate binding sites on neurosecretory LHRH mediobasal hypothalamic terminals. Eur J Pharmacol 80:139–141
Scharrer E (1965) The final common path in neuroendocrine integration. Arch Anat Microsc Morphol Exp 54:359–370
Tapia FJ, Varndell IM, Probert L, De Mey J, Polak JM (1983) Double immunogold staining method for the simultaneous ultrastructural localization of regulatory peptides. J Histochem Cytochem 31:977–981
Thibault J, Vidal D, Gros F (1981) In vivo translation of mRNA from rat pheochromocytoma tumors, characterization of tyrosine hydroxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 99:960–968
Van den Pol AN (1985a) Silver-intensified gold and peroxidase as dual ultrastructural immunolabels for pre- and postsynaptic neurotransmitters. Science 228:332–335
Van den Pol AN (1985b) Dual ultrastructural localization of two neurotransmitter-related antigens: colloidal gold-labeled neurophysin-immunoreactive supraoptic neurons receive peroxidase-labeled glutamate decarboxylase- or gold-labeled GABA-immunoreactive synapses. J Neurosci 11:2940–2954
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corio, M., Thibault, J. & Peute, J. Topographical relationships between catecholamine-and neuropeptide-containing fibers in the median eminence of the newt,Triturus alpestris . Cell Tissue Res. 259, 561–566 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01740784
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01740784