Abstract
Objective
To describe the accuracy and the reproducibility of the thermodilution flow measurements obtained using 3 commercially available cardiac output computers commonly used in intensive care units.
Design
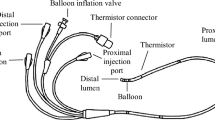
An experimental “in vitro” study. Twelve different values of control flow (Qctr) were measured (Qmsr) using 3 different cardiac output computers (Abbott Critical Care System, Oximetrix 3 SvO2/CO Computer, Baxter Oximeter/Cardiac Output Computer SAT-1TM; American Edwards Laboratories, 9520 A Cardiac Output Computer). Standard equipment and techniques were employed, taking account of the specific weight and heat of warm water relative to blood. In addition, separate sets of measurements were performed in order to investigate the effect on Qmsr of some variables which may influence the “indicator” loss (time for injection, depth of immersion of the catheter, temperature of the injected fluid).
Setting
Our laboratory, inside the intensive care unit.
Measurements and results
The analysis of the linear regression of Qmsr versus Qctr (r values between 0.992 and 0.984; residual standard deviation values comprised between 0.24 and 0.49 l/min; intercepts and slopes not significantly different from identity line), the values of the percentage errors (PE=[Qctr−Qmsr]·100/Qctr; PE mean values 7.9, 5.0 and 13.1), and those of the coefficients of variability (CV=standard deviation mean value, %; CV mean values 5.4, 5.8 and 4.6), show a good level of accuracy and reproducibility of the measurements. Our data confirm previously reported results. Furthermore, the cumulative effect of variables capable of influencing the “indicator” loss, even if corrected according to the “calculation constant” the manufacturers provide, was found to result in statistically significant changes of Qmsr.
Conclusion
The accuracy and reproducibility of the automatic cardiac computers tested is sufficient for practical clinical purpose. It may also depend on the modality of injection of the cooling bolus, which may significantly influence the effective “indicator” losses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fegler G (1954) Measurement of cardiac output in anaesthetized animals by a thermodilution method. Q J Exp Physiol 39:153–164
Ganz W, Donoso R, Marcus SH, Forrester JS, Swan JH (1971) A new technique for measuring cardiac output by thermodilution in man. Am J Cardiol 27:392–396
Weisel RD, Berger RL, Hechtman HB (1975) Measurement of cardiac output by thermodilution. N Engl J Med 292: 682–685
Forrester JS, Ganz W, Diamond G, McHugh T, Chonette DW, Swan JH (1972) Thermodilution cardiac output determination with a single flow-directed catheter. Am Heart J 3:306–311
Powner DJ, Snyder JV (1978) In vitro comparison of six commercially available thermodilution cardiac output systems. Med Instrum 12:122–127
Saadjani A, Quercy JE, Torresani J (1976) Cardiac output measurement by thermodilution (methodological problems). Med Progr Technol 3:161–167
The National Academy of Science, USA (1929) International critical tables of numerical data: physics, chemistry, and technology
Wilson EM, Ranieri AJ, Updike OL, Dammann JF (1972) An evaluation of thermal dilution for obtaining serial measurements of cardiac output. Med Biol Eng 10:179–191
Dizon CT, Gezari WA, Barash PG (1977) Hand held thermodilution cardiac output injector. Crit Care Med 5:210–212
Plachetka JR, Larson DJ, Salomon NW (1981) Comparison of two closed systems for thermodilution cardiac outputs. Crit Care Med 9:487–489
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubini, A., Del Monte, D., Catena, V. et al. Cardiac output measurement by the thermodilution method: An in vitro test of accuracy of three commercially available automatic cardiac output computers. Intensive Care Med 21, 154–158 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01726539
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01726539