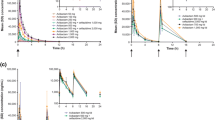
Summary
A 200 mg oral dose of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin or ofloxacin was administered to six healthy male volunteers in a three way cross-over study in order to examine the kinetics in humans in relation to the bactericidal activity in serum and urine. Serum concentrations for ciprofloxacin were similar to norfloxacin and lower than ofloxacin. Despite this fact, ciprofloxacin showed the highest serum bactericidal titers compared to norfloxacin and ofloxacin when serum-resistantEscherichia coli C14 was used as a test organism. These results correlate with observations from timekill curve studies in human whole blood, where ciprofloxacin showed superior bactericidal activity compared to norfloxacin or ofloxacin. The amounts of unchanged drug excreted in urine (48 h period) were found to be 35%, 24% and 77% for ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin respectively, indicating different excretion kinetics. The volumes of urine excreted in the different collection periods were comparable for the three drugs tested. Mean urine concentrations for ciprofloxacin were higher during the 0 to 4 h collection periods, whereas ofloxacin was excreted into the urine over a longer time period. Measurements of urine bactericidal activity showed that ciprofloxacin hat the highest titers during the early collection periods, whereas the prolonged excretion of ofloxacin did not result in higher urine bactericidal titers, compared to ciprofloxacin.
Zusammenfassung
In einer dreifachen Cross-over-Studie wurden Ciprofloxacin, Norfloxacin und Ofloxacin oral in einer Dosis von 200 mg an sechs Probanden verabreicht, um die Kinetik dieser Präparate in Relation zur bakteriziden Wirkung in Serum und Urin zu untersuchen. Die Serumkonzentrationen für Ciprofloxacin waren ähnlich denen von Norfloxacin und niedriger als mit Ofloxacin. Trotzdem zeigte Ciprofloxacin die höchsten bakteriziden Titer im Serum — als Testorganismus wurdeEscherichia coli C14 verwendet — im Vergleich zu Norfloxacin oder Ofloxacin, die etwa gleich wirksam waren. Diese Ergebnisse zeigen eine gute Korrelation mit Beobachtungen bei Abtötungskurven in menschlichem Vollblut, wobei Ciprofloxacin eine überlegene bakterizide Wirkung zeigte im Vergleich zu Norfloxacin oder Ofloxacin. Die im Urin innerhalb 48 Stunden ausgeschiedenen Mengen an unveränderter Substanz betrugen 35%, 24% und 77% entsprechend für Ciprofloxacin, Norfloxacin und Ofloxacin, was auf ein unterschiedliches Ausscheidungsverhalten von Ofloxacin hinweist. Die Urinmengen in den einzelnen Sammelperioden lagen für alle drei Präparate in vergleichbaren Größenordnungen. Die mittleren Urinkonzentrationen waren für Ciprofloxacin in der 0–4-Stunden-Sammelperiode höher als für Norfloxacin oder Ofloxacin, während Ofloxacin über einen längeren Zeitraum im Urin ausgeschieden wurde. Die Messungen der bakteriziden Wirkung im Urin zeigen, daß Ciprofloxacin in den frühen Sammelperioden die höchsten Titer aufweist, während die längere Ausscheidung von Ofloxacin nicht zu höheren bakteriziden Titern führte im Vergleich zu Ciprofloxacin.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Bauernfeind, A., Petermüller, C. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and nalidixic acid. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2 (1983) 111–115.
Wise, R., Andrews, J. M., Edwards, L. J. In vitro activity of Bay 0 9867, a new quinolone derivative, compared with those of other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 23 (1983) 559–564.
Fass, R. J. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin (Bay 0 9867). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 24 (1983) 568–574.
Reeves, D. S., Bywater, M. J., Holt, H. A., White, L. O. In vitro studies with ciprofloxacin, a new 4-quinolone compound. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 13 (1984) 333–346.
Zeiler, H.-J., Grohe, K. Thein vitro andin vivo activity of ciprofloxacin. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 3 (1984) 339–343.
Felmingham, D., O'Hare, M. D., Robbins, M. J., Wall, R. A., Williams, A. H., Cremer, A. W., Ridgeway, G. L., Grüneberg, R. N. Comparativein vitro studies with 4-quinolone antimicrobials. Drugs Exptl. Clin. Res. XI (1985) 317–329.
Van Caekenberghe, D. L., Pattyn, S. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin compared with those of other new fluorinated piperazinyl-substituted quinolone derivatives. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 25 (1984) 518–521.
Wingender, W., Graefe, K. H., Gau, W., Förster, D., Beermann, D., Schacht, P. Pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin after oral and intravenous administration in healthy volunteers. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 3 (1984) 355–359.
Crump, B., Wise, R., Dent, J. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 24 (1983) 784–786.
Dalhoff, A., Eickenberg, H.-U. Tissue distribution of ciprofloxacin following oral and intravenous administration. Infection 13 (1985) 78–81.
Beermann, D., Wingender, W., Zeiler, H.-J., Förster, D., Graefe, K.-H., Schacht, P. Comparative pharmacokinetics of three new quinolone carboxylic acid antibiotics after oral administration in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 24 (1984) 403.
Klastersky, J. The bactericidal activity in serum and its prognostic clinical value. Infection 11 (1983) Suppl. 2, 93–96.
Klastersky, J., Zinner, S. H. Synergistic combinations of antibiotics in gram-negative bacillary infections. Rev. Infect. Dis. 3 (1980) 74–83.
Klastersky, J., Daneau, D., Swings, G., Weerts, D. Antibacterial activity in serum and urine as a therapeutic guide in bacterial infections. J. Infect. Diseases 129 (1974) 187–193.
Brittain, D. C., Scully, B. E., McElrath, M. J., Steinman, R., Labthavikul, P., Neu, H. C. The pharmacokinetics and serum and urine bactericidal activity of ciprofloxacin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 25 (1985) 82–88.
Flepp, M., Joos, B., Hugentobler, H., Ledergerber, B., Bettex, J.-D., Lüthy, R.: Bactericidal activity (BA) of ciprofloxacin in serum (S) and urine (U): Correlation of BA with ciprofloxacin-concentrations (CC) and minimal bactericidal concentrations (MBC). 24th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, Washington, October 1984, Abstract No. 763.
Lagast, H., Husson, M., Klastersky, J. Bactericidal activity in serum and urine againstEscherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus andStreptococcus faecalis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 16 (1985) 341–347.
Zeiler, H.-J., Metzger, K. G., Schacht, P., Grohe, K. Assessment of thein vitro andin vivo activity of ciprofloxacin measured against current standards of therapy. Drugs Exptl. Clin. Res. XI (1985) 343–350.
Wise, R. Norfloxacin — a review of pharmacology and tissue penetration. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 13 Suppl. B (1984) 59–64.
Lockley, M. R., Wise, R., Dent, J. The pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of ofloxacin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 14 (1984) 647–652.
Naber, K., Bartosik-Wich, B. Serum- und Urinkonzentrationen von Norfloxacin, Ciprofloxacin und Ofloxacin bei älteren urologischen Patienten. Fortschr. Antimikr. Antineoplast. Chemother. 3–5 (1984) 701–709.
Ratcliffe, N. T., Smith, J. T.: Ciprofloxacin's bactericidal and inhibitory actions in urine. 4th Mediterranean Congress of Chemotherapy, Rhodes, October 1984, Abstract no. 608.
Ratcliffe, N. T., Smith, J. T. The mechanism of reduced activity of 4-quinolone agents in urine. Fortschr. Antimikr. Antineoplast. Chemother. 3–5 (1984) 563–569.
Reller, L. B., Stratton, C. W. Serum dilution test for bactericidal activity. II. Standardization and correlation with antimicrobial assays and susceptibility tests. J. Infect. Dis. 136 (1977) 196–204.
Zeiler, H.-J. Influence of pH and human urine on the antibacterial activity of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin. Drugs Exptl. Clin. Res. 11 (1985) 335–338.
Shah, P. M., Ottrad, M., Stille, W. In vitro activity of norfloxacin in urine compared to that of cinnoxacin, nalidixic acid and pipemidic acid. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2 (1983) 272–274.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeiler, H.J., Förster, D., Beermann, D. et al. Bactericidal activity of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin in serum and urine after oral administration to healthy volunteers. Infection 16 (Suppl 1), S19–S23 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01650502
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01650502