Abstract
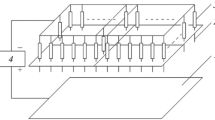
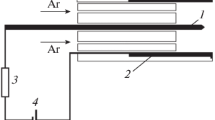
The aim of this paper is to present a new way to produce a high flow of hydrogen radical, at low temperatures. Thirst, an atmospheric pressure plasma of an argon-hydrogen mixture generates a high flow of hydrogen radical at temperatures up to 5 000 K. The applications of these radicals, in such conditions, are limited by thermal aspects which are obviously different from classical reactions of hydropyrolysis or other treatment processings of organic molecules. Our approach is to quench the plasma by a fluidized bed reactor which transport properties are compatible with plasma phase. From this point of view, the plasma/fluidized bed system is qualified in terms of its thermodynamic and hydrodynamical properties and its quenching velocity. The atomic hydrogen flow generated within such conditions is calculated and then experimentally measured.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Nikravech and J.Amouroux, “Hydrocracking process of heavy hydrocarbons and cracking installation for its use”.European Patent n o 88401215-4(1988).
T.G. Beuthe, J.S. Chang, 10thInt.Symp.on Plasma Chemistry, Bochum, Germany, vol. 1, 1.1–29, (1991).
G.L. Matheson, W.A. Herbst “Characteristics of fluid-solid system”,Ind. Eng. Chem.,41, 1099 (1949).
K. Doichev, G. Boichev,Powder Technology, 25,pp85–90, (1980)
P. Fauchais, E. Bourdin, J.F. Coudert, C. Gorse,Actualité Chimique, 10, 15–36 (1981).
B. Pateyron, M.F.Elchinger, G.Deluc, P.Fauchais, Bilan ARCCNRS-PIRSEM, Réacteurs Plasmas en phase hétérogène, (nov. 1991).
D. Geldart, Powder Technology, no7, pp.285–292 (1973)
W.M. Goldberger, J.H. Oxley,A.I.Ch.E. Journal, 9, 6, 778–782 (1963).
J. Amouroux,Thesis of Univerité P. et M. Curie, Paris (1971).
R.W Mac Cormack,AIAA paper, no85-00032 (1985).
J.F. Pernin, C. Motallebi, J.L. Leuenberger, S. Cavvadias and J. Amouroux. “Study of heat and mass transfer in a plasma spouted bed reactor. Application to hydrocarbon hydropyrolysis”J. High Temp. Chem. Proc., 1, 3, 87–93 (1992).
J.F. Pernin, C. Motallebi and al, “Kinetic simulation of the quenching of radicals and of their role on a model hydrocarbon hydrocracking in a plasma spouted-bed reactor”11 th International Symposium on Plasma Chemistry, Loughborough, UK, 22–27th August, Proceeding, 1, 17–22 (1993 b).
J.L. Leuenberger, S. Al Ayoubi, M.N. Mohammedi, E. Francke, J. Amouroux “Application of plasma spouted-bed reactor to hydrocracking of heavy hydrocarbons”,Proceeding of European Conference on Thermal Plasma Processes 3, 19–21 Sept. 1994, Aachen, Verein Deutscher Ingenieure (VDI), Feb. 1995.
J.L. Leuenberger, M.N. Mohammedi, S. Al Ayoubi, E. Francke and J.Amouroux “Hydrocracking of heavy hydrocarbons in a plasma spouted bed reactor”International Symposium of the Engineering Foundation, Fluidization VIII, Tours, France, May 1995.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammedi, M.N., Cavvadias, S., Leuenberger, J.L. et al. CO-processing conception of a quenching plasma reactor associated to a fluidized bed designed to hydrogen radical production at low temperatures. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 16 (Suppl 1), S191–S210 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01512635
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01512635