Summary
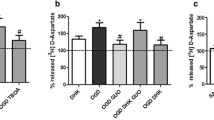
The aim of the present study was to investigate the release of amino-acids in human cerebral cortex during membrane depolarization and simulated ischaemia (energy deprivation). Superfluous tissue from temporal lobe resections for epilepsy was cut into 500 μm thick slices and incubated in vitro. Membrane depolarization with 50 mM K+ caused a release of glutamate, aspartate, GABA and glycine, but not glutamine or leucine. The release of glutamate and GABA was Ca++-dependent. Slices were exposed to simulated ischaemia (energy deprivation; ED) by combined glucose/oxygen deprivation. This caused a Ca++-indepedent release of glutamate, aspartate, GABA, glycine, and taurine which started after 8 min, peaked at the end or shortly after the 27 min period of ED, and returned to control levels within 11 min following termination of ED. Preloaded D-[3H]aspartate was released both during K+-stimulation and ED. Release of D-[3H]aspartate during ED was delayed compared to glutamate supporting an initial phase of synaptic glutamate release. Uptake of L-[3H]glutamate was increased during the period of glutamate release, suggesting passive diffusion across the cell membrane or enhanced transport efficacy in cellular elements with functioning uptake mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aas J, Berg-Johnsen J, Hegstad E, Laake J, Langmoen IA, Ottersen O (1993) Redistribution of glutamate and glutamine in slices of human neocortex exposed to combined hypoxia and glucose deprivation in vitro. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 13: 503–515
Andersen P, Silfvenius H, Sundberg SH, Sveen O, Wigstrøm H (1978) Functional characteristics of unmyelinated fibres in the hippocampal cortex. Brain Res 144: 11–18
Benveniste H, Drejer J, Schousboe A, Diemer N (1984) Elevation of the extracellular concentrations of glutamate and aspartate in rat hippocampus during transient cerebral ischemia monitored by intracerebral microdialysis. J Neurochem 43: 1369–1374
Berg-Johnsen J, Langmoen IA (1987) Isoflurane hypefpolarizes neurones in rat and human cerebral cortex. Acta Physiol Scand 130: 679–685
Berg-Johnsen J, Grøndahl TØ, Langmoen IA, Haugstad TS, Hegstad E (1995) Changes in amino-acid release and membrane potential during cerebral hypoxia and glucose deprivation. Neurol Res 17: 201–208
Bouvier M, Szatkowski M, Amato A, Attwell D (1992) The glial cell glutamate uptake carrier countertransports pH-changing anions. Nature 360: 411–414
Casado M, Bendahan A, Zafra F, Danbolt NC, Aragon C, Gimenez C, Kanner BI (1993) Phosphorylation and modulation of brain glutamate transporters by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 268: 27313–27317
Casado M, Zafra F, Aragon C, Gimenez C (1991) Activation of high-affinity uptake of glutamate by phorbol esters in primary glial cell cultures. J Neurochem 57: 1185–1190
Collingridge GL, Kehl SJ, McLennan H (1983) Excitatory amino-acids in synaptic transmission in the Schaffer collateral-commissural pathway of the rat hippocampus. J Physiol 334: 33–46
Danbolt NC (1994) The high affinity uptake system for excitatory amino-acids in the brain. Progr Neurobiol 44: 377–396
de Belleroche JC, Bradford HF (1972) Metabolism of beds of mammalian cortical synaptosomes: response to depolarizing influences. J Neurochem 19: 585–602
Falconer MA (1979) Anterior temporal lobectomy for epilepsy. In: Symon L (ed) Operative surgery. Fundamental international techniques: neurosurgery. Butterworth, London, pp 315–322
Fonnum F (1984) Glutamate: a neurotransmitter in mammalian brain. J Neurochem 42: 1–11
Fukunaga R, Ninomiya H, Shimohama S, Kimura J, Kameyama M, Taniguchi T (1991) Reassessment of [3H]glutamate binding to human brain membrane preparations. Jpn J Pharmacol 55: 191–196
Gjessing LR, Gjesdahl P, Sjaastad O (1972) The free amino-acids in human cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurochem 19: 1807–1808
Globus MY, Busto R, Dietrich WD, Martinez E, Valdes I, Ginsberg MD (1988) Effect of ischemia on the in vivo release of striatal dopamine, glutamate, and gamma-aminobutyric acid studied by intracerebral microdialysis. J Neurochem 51: 1455–1464
Hablitz JJ, Langmoen IA (1982) Excitation of hippocampal pyramidal cells by glutamate in the guinea-pig and rat. J Physiol 325: 317–331
Hansen AJ (1985) Effect of anoxia on ion distribution in the brain. Physiol Rev 65: 101–148
Hansen AJ, Hounsgaard J, Jahnsen H (1982) Anoxia increases potassium conductance in hippocampal nerve cells. Acta Physiol Scand 115: 301–310
Haugstad TS, Hegstad E, Langmoen IA (1992) Calcium dependent release of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) from human cerebral cortex. Neurosci Lett 141: 61–64
Hegstad E, Haugstad TS, Hauglie-Hanssen E, Langmoen IA (1992) Calcium-dependent release of glutamate from human cerebral cortex. Brain Res 585: 340–342
Hillered L, Persson L, Pontén U, Ungerstedt U (1990) Neurometabolic monitoring of the ischaemic human brain using microdialysis. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 102: 91–97
Haas HL, Schaerer B, Vosmansky M (1979) A simple perfusion chamber for the study of nervous tissue slices in vitro. J Neurosci Meth 1: 323–325
Johnson J (1978) The excitant amino-acids glutamic and aspartic acid as transmitter candidates in the vertebrate central nervous system. Progr Neurobiol 10: 155–202
Katayama Y, Kawamata T, Tamura T, Hovda DA, Becker DP, Tsubokawa T (1991) Calcium dependent release concomitant with massive potassium flux during cerebral ischemia in vivo. Brain Res 558: 136–140
Katz B, Miledi R (1967) The timing of calcium action during neuromuscular transmission. J Physiol 189: 535–544
Langmoen IA, Andersen P (1981) The hippocampal slice in vitro. A description of the technique and some examples of the opportunity it offers. In: Kerkut GA, Wheat HV (eds) Electrophysiology of isolated mammalian CNS preparations. Academic Press, London, pp 51–105
Langmoen I, Hablitz JJ (1981) Reversal potential of glutamate responses in hippocampal pyramidal cells. Neurosci Lett 23: 61–65
Langmoen IA, Berg-Johnsen J (1988) Intracellular recordings from neurones during transient hypoxia. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] 43: 168–171
Lipton P, Wittingham TS (1979) The effect of hypoxia on evoked potentials in the in vitro hippocampus. J Physiol 287: 427–438
Logan WJ, Snyder SH (1971) Unique high affinity uptake systems for glycine, glutamic and aspartic acids in central nervous tissue of the rat. Nature 234: 297–299
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Fair AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–275
Malthe-Sørenssen D, Skrede KK, Fonnum F (1979) Calcium-dependent release of D-[3H]aspartate evoked by selective electrical stimulation of excitatory afferent fibers to hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. Neuroscience 4: 1255–1263
Mayer ML, Westbrook GL (1987) Permeation and block of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor channels by divalent cations in mouse cultured central neurones. J Physiol 394: 501–527
Meldrum BS, Evans MC, Swan JH, Simon RP (1987) Protection against hypoxic/ischaemic brain damage with exitatory amino-acid antagonists. Med Biol 65: 153–157
Murphy SN, Thayer SA, Miller RJ (1987) The effects of excitatory amino-acids on intracellular calcium in single mouse striatal neurons in vitro. J Neurosci 7: 4145–4158
Naito S, Ueda T (1985) Characterization of glutamate uptake into synaptic vesicles. J Neurochem 44: 99–109
Nellgård B, Wieloch T (1992) Postischemic blockade of AMPA but not NMDA receptors mitigates neuronal damage in the rat brain following transient severe cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 12: 2–11
Nicholls D, Attwell D (1990) The release and uptake of excitatory amino-acids. Trends Neurosci 11: 462–468
Olney JW (1969) Brain lesions, obesity, and disturbances in mice treated with monosodium glutamate. Science 164: 719–721
Onodera H, Sato G, Kogure K (1986) Lesions to Schaffer collaterals prevent ischemie death of CA1 pyramidal cells. Neurosci Lett 68: 169–174
Ottersen O, Storm-Mathisen J (1984) Neurons containing or accumulating transmitter amino-acids. Handbook of chemical neuroanatomy: classical transmitters and transmitter receptors in the CNS, Part II. 3: 141–246
Rothman S, Olney J (1987) Excitotoxicity and the NMDA receptor. Trends Neurosci 10: 299–302
Sahai S (1990) Glutamate and the mammalian CNS. Eur Arch Psychiat Clin Neurosci 240: 121–133
Schoepp D, Bockaert J, Sladeczek F (1990) Pharmacological and functional characteristics of metabotrophic excitatory amino-acid receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 11: 508–515
Schwarcz R, Whetsell JWO (1982) Post-mortem high affinity glutamate uptake in human brain. Neuroscience 7: 1771–1778
Silver IA, Erecinska M (1990) Intracellular and extracellular changes of [Ca2+] in hypoxia and ischemia in rat brain in vivo. J Gen Physiol 95: 837–866
Simon RP, Swan JH, Griffiths T, Meldrum BS (1984) Blockade of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors may protect against ischemic damage in the brain. Science 226: 850–852
Szatkowski M, Attwell D (1994) Triggering and execution of neuronal death in brain ischaemia: two phases of glutamate release by different mechanisms. Trends Neurosci 17: 359–365
Wieloch T, Lindvall O, Blomqvist P, Gage H (1985) Evidence for amelioration of ischaemic neuronal damage in the hippocampal formation by lesions of the perforant path. Neurol Res 7: 24–26
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hegstad, E., Berg-Johnsen, J., Haugstad, T.S. et al. Amino-acid release from human cerebral cortex during simulated ischaemia in vitro. Acta neurochir 138, 234–241 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01411367
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01411367