Summary
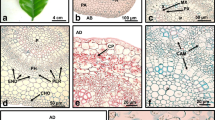
Embryoids which developed from callus obtained from leaves ofMedicago sativa L. (alfalfa) were studied with the light and scanning electron microscopes; embryoids are not common in leguminous plants. Sections showed that in organised callus embryoids apparently originated from groups of embryonic cells, whereas in friable callus, and in the epidermis of cotyledons, hypocotyls and roots of callus-derived plantlets, they often originated from single cells. Many early stages of embryogenesis (1, 2, 3- and 4-celled stages) were observed, particularly in epidermal sites. Stages in somatic embryogenesis, though variable, resembled those described for the normal zygotic embryos of alfalfa. A suspensor-like structure was sometimes present in the embryoids. Numbers of cotyledons, up to six, were observed. The SEM provided confirmation of the many stages of development and the very large number of embryoids present, as well as evidence of the range of form resulting from differential growth of regions of the embryos.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Backs-Hüsemann, D., Reinert, J., 1970: Embryobildung durch isolierte Einzelzellen aus Gewebekulturen vonDaucus carota. Protoplasma70, 49–60.
Broertjes, C., 1972: Use in plant breeding of acute, chronic or fractionated doses of X-rays or fast neutrons as illustrated with leaves ofSaintpaulia. Agric. Res. Repts. 776, Centre for Agricultural Publishing and Documentation, Wageningen.
Cooper, D. C., 1935: Macrosporogenesis and embryology ofMedicago. J. Agric. Res.51, 471–477.
Danilina, A. N., 1972: Morphogenesis in tissue cultures ofDaucus carota. Phytomorphology22, 160–164.
Dodds, J. H., Reynolds, T. L., 1980: A scanning electron microscope study of pollen embryogenesis inHyoscyamus niger. Z. Pflanzenphysiol.97, 271–276.
Fridriksson, S., Bolton, J. L., 1963: Development of the embryo ofMedicago sativa L. after normal fertilization and after pollination by other species ofMedicago. Can. J. Bot.42, 23–33.
Haccius, B., Lakshmanan, K. K., 1969: Adventiv-Embryonen — Embryoide — Adventiv — Knospen. Ein Beitrag zur Klärung der Begriffe. Österr. bot. Z.116, 145–158.
Halperin, W., Jensen, W. A., 1967: Ultrastructural changes during growth and embryogenesis in carrot cell cultures. J. Ultrastruct. Res.18, 428–443.
Haydu, Z., Vasil, I. K., 1981: Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from leaf tissues and anthers ofPennisetum purpureum Schum. Theor. appl. Genet.59, 269–273.
Hu, C. Y., Ochs, J. D., Mancini, F. M., 1978: Further observations onIlex embryoid production. Z. Pflanzenphysiol.89, 41–49.
—,Sussex, I. M., 1971:In vitro development of embryoids on cotyledons ofIlex aquifolium. Phytomorphology21, 103–107.
Johnson, L. B., Stuteville, D. L., Higgins, R. K., Skinner, D. Z., 1981: Regeneration of alfalfa plants from protoplasts of selected Regen S clones. Plant Sci. Lett.20, 297–304.
Kao, K. N., Michayluk, M. R., 1980: Plant regeneration from mesophyll protoplasts of alfalfa. Z. Pflanzenphysiol.96, 135–141.
Konar, R. N., Nataraja, K., 1965: Experimental studies inRanunculus sceleratus L. Development of embryos from the stem epidermis. Phytomorphology15, 132–137.
— —, 1969: Morphogenesis of isolated floral buds ofRanunculus sceleratus L.in vitro. Acta Bot. Neerl.18, 680–699.
—,Oberoi, Y. P., 1965:In vitro development of embryoids on the cotyledons ofBiota orientalis. Phytomorphology15, 137–140.
—,Thomas, E., Street, H. E., 1972a: The diversity of morphogenesis in suspension cultures ofAtropa belladonna L. Ann. Bot.36, 249–258.
— — —, 1972b: Origin and structure of embryoids arising from epidermal cells of the stem ofRanunculus sceleratus L. J. Cell Sci.11, 77–93.
Lu, C., Vasil, I. K., 1981: Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from leaf tissues ofPanicum maximum Jacq. Theor. appl. Genet.59, 275–280.
Martin, J. N., 1914: Comparative morphology of someLeguminosae. Bot. Gaz.58, 154–167.
McWilliam, A. A., Smith, S. M., Street, H. E., 1974: The origin and development of embryoids in suspension cultures of carrot (Daucus carota). Ann. Bot.38, 243–250.
Ozias-Akins, P., Vasil, I. K., 1982: Plant regeneration from cultured immature embryos and inflorescences ofTriticum aestivum L. (wheat): evidence for somatic embryogenesis. Protoplasma110, 95–105.
Phillips, G. C., Collins, G. B., 1980: Somatic embryogenesis from cell suspension cultures of red clover. Crop. Sci.20, 323–326.
Raghavan, V., 1976: Experimental Embryogenesis in Vascular Plants. London-New York: Academic Press.
Rao, P. S., Narayanaswami, S., 1972: Morphogenetic investigations in callus cultures ofTylophora indica. Physiol. Plant.27, 271–276.
Reinert, H. J., 1958: Untersuchungen über die Morphogenese an Gewebekulturen. Ber. dtsch. bot. Ges.71 (15).
—, 1959: Über die Kontrolle der Morphogenese und die Induktion von Adventivembryonen an Gewebekulturen aus Karotten. Planta53, 318–333.
—,Bajaj, Y. P. S., Zbell, B., 1977: Aspects of organization-organogenesis, embryogenesis, cytodifferentiation. In: Plant Tissue and Cell Culture (Street, H. E., ed.), pp. 389–427. Oxford-London: Blackwell Scientific Publications.
Santos, A. V. dos, Outka, D. E., Cocking, E. C., Davey, M. R., 1980: Organogenesis and somatic embryogenesis in tissues derived from leaf protoplasts and leaf expiants ofMedicago sativa. Z. Pflanzenphysiol.99, 261–270.
Sass, J. E., 1966: Botanical microtechnique. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State College Press.
Saunders, J. W., Bingham, E. T., 1972: Production of alfalfa plants from callus tissue. Crop. Sci.12, 804–808.
Sharman, B. C., 1943: Tannic acid and iron alum with safranin and orange G in studies of the shoot apex. Stain Technol.18, 105–111.
Sondahl, M. R., Salisbury, J. L., Sharp, W. R., 1979: SEM characterization of embryogenie tissue and globular embryos during high frequency somatic embryogenesis in coffee callus cells. Z. Pflanzenphysiol.94, 185–188.
Thomas, E., Hoffmann, F., Potrykus, I., Wenzel, G., 1976: Protoplast regeneration and stem embryogenesis of haploid androgenetic rape. Molec. gen. Genet.145, 245–247.
Thomas, E., Konar, R. N., Street, H. E., 1972: The fine structure of the embryogenic callus ofRanunculus sceleratus L. J. Cell Sci.11, 95–109.
Uchimiya, H., Murashige, T., 1974: Evaluation of parameters in the isolation of viable protoplasts from cultured tobacco cells. Plant. Physiol.54, 936–944.
Vasil, V., Vasil, I. K., 1982: Characterization of an embryogenie cell suspension culture derived from cultured inflorescences ofPennisetum americanum (pearl millet,Gramineae). Amer. J. Bot.69, 1441–1449.
Weatherhead, M. A., Grout, B. W. W., 1979: A scanning electron microscope study of embryoid development in the anthers ofNicotiana tabacum L. Ann. Bot.44, 631–632.
Wetherell, D. F., 1978:In vitro embryoid formation in cells derived from somatic plant tissues. In: Propagation of higher plants through tissue culture: A bridge between research and application. U.S.A. Dept. of Energy. 102–124.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
On leave from Divisão de Botanica, CEPEC/CEPLAC, C.P. 7, 45600 Itabuna, BA, Brasil.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santos, A.V.P.d., Cutter, E.G. & Davey, M.R. Origin and development of somatic embryos inMedicago sativa L. (alfalfa). Protoplasma 117, 107–115 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01288349
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01288349