Summary
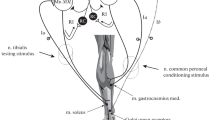
Voluntary muscle movements in mammalian muscles are initiated by short trains of 16 to 60 Hz impulses (Zierler, 1974). Despite this in most neurophysiological and neuropharmacological studies either single stimuli of 0.1 to 2 Hz or 5 to 10 sec 50 to 500 Hz tetani have been employed. Neither of these two types of stimuli are ideal for the testing of the functional integrity of the motor unit. Stimulation with single impulses, at slow rates, does not reveal incipient pathological or drug induced defects. Recovery of neuromuscular (NM) activity after 5 to 10 sec tetanic stimulation is prolonged and after repeated stimulation of this type the preparations decay rapidly. Stimulation with 0.1 sec trains of 50 Hz impulses applied every 10 to 20 sec eliminate the above disadvantages. This type of stimulation represents adequate challenge for revealing more moderate degrees of functional defects of the myoneural apparatus without causing rapid decay of thein vitro orin vivo preparations. In agreement with this the ED50 of NM blocking agents were found to be significantly lower in both thein vitro phrenic nerve-hemidiaphragm preparation and thein vivo sciatic nervetibialis anterior muscle preparation of rats during stimulation with 0.1 sec trains of 50 Hz impulses, than when single stimuli of 0.1 Hz were used. Recovery of thein vitro preparations after washout orin vivo after discontinuation of the infusion was also slower during stimulation with short trains of tetani. The antagonist potency of anticholinesterases or 4-aminopyridine and maximal recovery after the use of the optimal concentrations of these antagonists was less in the preparations stimulated with short trains of tetani than in those stimulated with single impulses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, H. H., Kitz, R. J.: Evaluation of recovery from nondepolarizing neuromuscular block, using a digital neuromuscular transmission analyzer: Preliminary report. Anesth. & Analg.52, 740–745 (1973).
Ali, H. H., Utting, J. E., Gray, T. C.: Quantitative assessment of residual antidepolarizing block (Part 1). Br. J. Anaesth.43, 473–485 (1973).
Ali, H. H., Wilson, R. S., Savarese, J. J., Kitz, R. J.: The effect of tubocurarine on indirectly elicited train-of-four muscle response and respiratory measurements in humans. Br. J. Anaesth.47, 570–574 (1975).
Bowman, W. C., Webb, S. N.: Tetanic fade during partial transmission failure produced by non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking drugs in the cat. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol.3, 545–555 (1976).
Bülbring, E.: Observation on the isolated phrenic nerve diaphragm preparation of the rat. Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother.1, 38–61 (1946).
Elmqvist, D., Quastel, D. M. J.: Presynaptic action of hemicholinium at the neuromuscular junction. J. Physiol. (Lond.)177, 463–482 (1965 a).
Elmqvist, D., Quastel, D. M. J.: A quantitative study of end-plate potentials in human muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)178, 505–529 (1965 b).
Foldes, F. F., Rao, D. B. S., Deery, A., Nagashima, H., Underwood, P. S., Duncalf, D.: Stimulation parameters and reversal of d-Tc in vivo. Anesthesiology51, S286 (1979).
Foldes, F. F., Kuze, S., Vizi, E. S., Deery, A.: The influence of temperature on neuromuscular performance. J. Neural Transm.43, 27–45 (1978).
Krebs, H. A., Henseleit, K.: Untersuchungen über die Harnstoffbildung im Tierkörper. Hoppe-Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem. (Berlin)210, 33–66 (1932).
Marshall, I. G., Agoston, S., Booij, L. H. D., Durant, N. N., Foldes, F. F.: Pharmacology of Org-NC45 compared with other nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking drugs. Br. J. Anaesth.52, S11-S19 (1980).
Necdham, D. M.: Biochemistry of muscle. In: The Structure and Function of Muscle, 2nd ed. (Bourne, G. H., ed.), pp. 363–415. New York-London: Academic Press. 1973.
Paton, W. D. M., Vizi, E. S.: The inhibitory action of noradrenaline and adrenaline on acetylcholine output by guinea-pig longitudinal muscle strip. Br. J. Pharmacol.35, 10–28 (1969).
Paton, W. D. M., Waud, D. R.: The margin of safety of neuromuscular transmission. J. Physiol.191, 59–90 (1967).
Slomic, A., Rosenfalck, A., Buchthal, F.: Electrical and mechanical responces of normal and myasthenic muscle (with particular reference to the staircase phenomenon). Brain Res.10, 1–78 (1968).
Thesleff, S.: The mode of neuromuscular block caused by acetylcholine, nicotine, decamethonium and succinylcholine. Acta Physiol. Scand.34, 218–231 (1955).
Van der Veen, F., Bencini, A.: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of Org-NC45 in man. Br. J. Anaesth.52, S37-S41 (1980).
Vizi, E. S., Foldes, F. F., Theunissen, J.: The effects of protoveratrine and germines on the release of acetylcholine from the Auerbach plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. J. Neural Transm.37, 43–60 (1975).
Vizi, E. S., van Dyk, J., Foldes, F. F.: The effect of 4-aminopyridine on acetylcholine release. J. Neural Transm.41, 265–274 (1977).
Zierler, K. L.: Mechanism of muscle contraction and its energetics. In: Medical Physiology, Vol. 1 (Mountcastle, V. B., ed.), p. 84. St. Louis: Mosby. 1974.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foldes, F.F., Chaudhry, I., Ohta, Y. et al. The influence of stimulation parameters on the potency and reversibility of neuromuscular blocking agents. J. Neural Transmission 52, 227–249 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01249606
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01249606