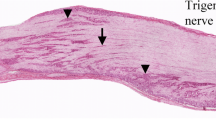
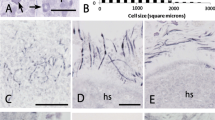
Summary
Immunocytochemistry has been used to examine the trigeminal ganglion cell populations in the rat which express calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and the oligosaccharide antigen recognized by the monoclonal antibody LA4. Calcitonin gene-related peptide and LA4 identify two large but mainly separate populations of trigeminal ganglion cells. Depending on the method of assessment used, CGRP-immunoreactive cells represent 29–37% of trigeminal ganglion cells while LA4 labels 26–40% of the cells, but with only 8% overlap between the two populations. Both CGRP and LA4 label predominantly small diameter cells (mean diameters 23 μm and 25 μm respectively) but with CGRP cells exhibiting a greater range of diameters than LA4 cells. The cell sizes indicate that small diameter CGRP-immunoreactive cells and most LA4-immunoreactive cells are likely to have unmyelinated axons, and together the two populations can account for the great majority of unmyelinated trigeminal primary afferent neurons. Centrally, CGRP and LA4 show distinct patterns of staining. Thus although both antigens are found in lamina II of subnucleus caudalis of the spinal trigeminal nucleus, CGRP is most abundant in lamina I and lamina II outer while LA4 irnmunoreactivity is most dense in lamina II inner. In addition CGRP-, but not LA4-, immunoreactive fibres occur in the magnocellular portion of caudalis. Previous studies have show that in rat dorsal root ganglion cells CGRP coexists with most other known neuropeptides and can therefore be used as a general marker for peptide-containing primary afferents. In contrast LA4 labels a cell population which is probably largely identical to that identified by the presence of fluoride resistant acid phosphatase or by the binding of lectins such as Griffonia simplidfolia isolectin B4 and this population does not contain neuropeptides. Our results thus provide further evidence that unmyelinated primary afferents can be divided into peptide and non-peptide containing subpopulations and that these populations innervate distinct regions of laminae I and II.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez, F. J. &Priestley, J. V. (1990) Anatomy of somatostatin-immunoreactive fibres and cell bodies in the rat trigeminal subnucleus caudalis.Neuroscience 38, 343–57.
Alvarez, F. J., Rodrigo, J., Jessell, T. M., Dodd, J. &Priestley, J. V. (1989a) Morphology and distribution of primary afferent fibres expressing α-glactose extended oligosaccharides in the spinal cord and brainstem of the rat. Light microscopy.Journal of Neurocytology 18, 611–29.
Alvarez, F. J., Rodrigo, J., Jessell, T. M., Dodd, J. &Priestley, J. V. (1989b) Ultrastructure of primary afferent fibres and terminals expressing α-glactose extended oligosaccharides in the spinal cord and brainstem of the rat.Journal of Neurocytology 18, 631–45.
Alvarez, F. J., Rodrigo, J. &Priestley, J. V. (1990) Distribution of small diameter primary afferents containing oligosaccharide residues recognized by monoclonal antibody LA4 in the dorsal horn of the cat.Brain Research 524, 175–9.
Cameron, A. A., Leah, J. D. &Snow, P. J. (1989) The coexistence of neuropeptides in feline sensory neurons.Neuroscience 27, 969–80.
Carr, P. A., Yamamoto, T. &Nagy, J. I. (1990) Cakitonin gene-related peptide in primary afferent neurons of the rat: co-existence with fluoride-resistant acid phosphatase and depletion of neonatal capsaicin.Neuroscience 36, 751–60.
Chou, D. K., Dodd, J., Jessell, T. M., Costello, C. E. &Jungalwala, F. B. (1989) Identification of α-galactose (α-fucose)-asialo-GMl glycolipid expressed by subsets of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons.Journal of Biological Chemistry 264, 3409–15.
Chung, K., Lee, W. T. &Carlton, S. M. (1988) The effects of dorsal rhizotomy and spinal cord isolation on calcitonin gene-related peptide-labeled terminals in the rat lumbar dorsal horn.Neuroscience Letters 90, 27–32.
Conrath, M., Taquet, H., Pohl, M. &Carayon, A. (1989) Immunocytochemical evidence for calcitonin generelated peptide-like neurons in the dorsal horn and lateral spinal nucleus of the rat cervical spinal cord,Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy 2, 335–47.
Dalsgaard, C. -J., Ygge, J., Vincent, S. R., Ohrling, M., Dockray, G. J. &Elde, R. (1984) Peripheral projections and neuropeptide coexistence in a subpopulation of fluoride-resistant acid phosphatase reactive spinal primary sensory neurons.Neuroscience Letters 51, 139–44.
Dodd, J. &Jessell, T. M. (1985) Lactoseries carbohydrates specify subsets of dorsal root ganglion neurons projecting to superficial dorsal horn of rat spinal cord,Journal of Neuroscience 5, 3278–94.
Fischer, J. &Cs1llik, B. (1985) Lectin binding: a genuine marker for transganglionic regulation of human primary sensory neurons.Neuroscience Letters 54, 263–7.
Fried, K., Arvidsson, J., Robertson, B., Brodin, E. &Theodorsson, E. (1989) Combined retrograde tracing and enzyme/immunohistochemistry of trigeminal ganglion cell bodies innervating tooth pulps in the rat.Neuroscience 33, 101–9.
Garry, M. G., Miller, K. E. &Seybold, V. S. (1989) Lumbar dorsal root ganglia of the cat: a quantitative study of peptide immunoreactivity and cell size.Journal of Comparative Neurology 284, 36–47.
Gibbins, I. L., Furness, J. B. &Costa, M. (1987) Pathway-specific patterns of the co-existence of substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide, cholecystokinin and dynorphin in neurons of the dorsal root ganglia of the guinea-pig.Cell and Tissue Research 248, 417–37.
Gibson, S. J. &Polak, J. M. (1986) Neurochemistry of the spinal cord. InImmunocytochemistry: Modern Methods and Applications (edited byPolak, J. M. &Vannoorden, S.) pp. 360–89. Bristol: Wright.
Gibson, S. J., Polak, J. M., Bloom, S. R., Sabate, I. M., Mulderry, P. K., Ghatei, M. A., Morrison, J. F. B., Kelly, J. S., Rosenfeld, M. G. &Evans, R. (1984) Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-immunoreactivity in the spinal cord of man and eight other species.Journal of Neuroscience 4, 3101–11.
Görcs, T. J., Leranth, C. &Maclusky, N. J. (1986) The use of gold-substituted silver-intensified diaminobenzidine (DAB) and non-intensified DAB for simultaneous electron microscopic immunoperoxidase labeling of tyrosine hydroxylase and glutamic acid decarboxylase immunoreactivity in the rat medial preoptic area.Journal of Histochemisty and Cytochemistry 54, 1439–47.
Harper, A. A. &Lawson, S. N. (1985) Conduction velocity is related to morphological cell type in rat dorsal root ganglion neurones.Journal of Physiology 359, 31–46.
Holzer, P. (1988) Local effector functions of capsaicin-sensitive nerve endings: involvement of tachykinins, calcitonin gene-related peptide and other neuropeptides.Neuroscience 24, 739–68.
Hunt, S. P. &Rossi, J. (1985) Peptide- and non-peptide-containing primary afferents: the parallel processing of nociceptive information.Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London (B) 308, 283–9.
Jessell, T. M. &Dodd, J. (1986) Neurotransmitters and differentiation antigens on subsets of sensory neurons projecting to the spinal dorsal horn. InNeuropeptides in Neurological and Psychiatric Disease (edited byMartin, J. B. &Barchas, J. D. (pp. 111–33. New York: Raven Press.
Ju, G., Hökfelt, T., Brodin, E., Fahrenkrug, J., Fisher, J. A., Frey, P., Elde, R. P. &Brown, J. C. (1987) Primary sensory neurons of the rat showing calcitonin generelated peptide immunoreactivity and their relation to substance P-, somatostatin-, galanin-, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-, and cholecystokinin-immunoreactive ganglion cells.Cell and Tissue Research 247, 417–31.
Knyhiár-Csillik, E. &Csillik, B. (1981) FRAP: histochemistry of the primary nociceptive neuron.Progress in Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 14, 1–133.
Kruger, L., Sternini, C., Brecha, N. C. &Mantyh, P. W. (1988) Distribution of calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in relation to the rat central somatosensory projection.Journal of Comparative Neurology 273, 147–62.
Lawson, S. N. (1979) The postnatal development of large light and small dark neurons in mouse dorsal root ganglia: a statistical analysis of cell numbers and size.Journal of Neurocytology 8, 275–94.
Lawson, S. N., Harper, E. I., Harper, A. A., Garson, J. A., Coakham, H. B. &Randles, B. J. (1985) Monoclonal antibody 2C5: a marker for a subpopulation of small neurons in rat dorsal root ganglia.Neuroscience 16, 365–74.
Lawson, S., Mccarthy, P. &Waddell, P. (1989) Immunoreactivity of rat primary afferent neurons with C- and A-fibres. InProcessing of Sensory Information in the Superficial Dorsal Horn of the Spinal Cord (edited byCervero, F., Bennett, G. J. &Headley, P. M.) pp. 71–4. New York: Plenum.
Leah, J. D., Cameron, A. A. &Snow, P. J. (1985) Neuro-peptides in physiologically identified mammalian sensory neurons.Neuroscience Letters 56, 257–64.
Lee, Y., Kawai, Y., Shiosaka, S., Takami, K., Kiyama, H., Hillyard, C. J., Girgis, S. I., Macintyre, I., Emson, P. C. &Tohyama, M. (1985) Coexistence of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P-like peptide in single cells of the trigeminal ganglion of the rat: immunohistochemical analysis.Brain Research 330, 194–6.
Light, A. R., Trevino, D. L. &Perl, E. R. (1979) Morphological features of functionally defined neurons in the marginal zone and substantia gelatinosa of the spinal dorsal horn.Journal of Comparative Neurology 186, 117–32.
Lynn, B. &Carpenter, S. E. (1982) Primary afferent units from the hairy skin of the rat hind limb.Brain Research 238, 29–43.
Matsuyama, T., Wanaka, A., Yoneda, S., Kimura, K., Kamada, T., Girgis, S., Macintyre, I., Emson, P. &Tohyama, M. (1986) Two distinct calcitonin gene-related peptide-containing peripheral nervous systems: distribution and quantitative differences between the iris and cerebral artery with special reference to substance P.Brain Research 373, 205–12.
Mccarthy, P. W. &Lawson, S. N. (1990) Cell type and conduction velocity of rat primary sensory neurons with calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity.Neuroscience 34, 623–32.
Mcneill, D. L., Coggeshall, R. E. &Carlton, S. M. (1988) A light and electron microscopic study of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the spinal cord of the rat.Experimental Neurology 99, 699–708.
Mcneill, D. L., Westlund, K. N. &Coggeshall, R. E. (1989) Peptide immunoreactivity of unmyelinated primary afferent axons in rat lumbar dorsal roots.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 37, 1047–52.
Merighi, A., Polak, J. M., Gibson, S. J., Gulbenkian, S., Valentino, K. L. &Peirone, S. M. (1988) Ultrastructural studies on calcitonin gene-related peptide-, tachykinins- and somatostatin-immunoreactive neurons in rat dorsal root ganglia: evidence for the colocalization of different peptides in single secretory granules.Cell and Tissue Research 254, 101–9.
Miletic, V. &Tan, H. (1988) Iontophoretic application of calcitonin gene-related peptide produces slow and prolonged depolarization of neurons in cat lumbar dorsal horn.Brain Research 446, 169–72.
Molander, C., Ygge, J. &Dalsgaard, C. J. (1987) Substance P-, somatostatin- and calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity and fluoride resistant acid phosphatase-activity in relation to retrogradely labeled cutaneous, vascular and visceral primary sensory neurons in the rat.Neuroscience Letters 74, 37–42.
Mori, K. (1986) Lectin Ulex europaeus agglutinin I specifically labels a subset of primary afferent fibres which project to the superficial dorsal horn of the spinal cord.Brain Research 365, 404–8.
Murase, K., Ryu, P. D. &Randic, M. (1989) Excitatory and inhibitory amino acids and peptide-induced responses in acutely isolated rat spinal dorsal horn neurons.Neuroscience Letters 103, 56–63.
Nagy, J. I. &Hunt, S. P. (1982) Fluoride-resistant acid phosphatase-containing neurons in dorsal root ganglia are separate from those containing substance P or somatostatin.Neuroscience 7, 89–97.
O'Brien, C., Woolf, C. J., Fitzgerald, M., Lindsay, R. M. M. &Molander, C. (1989) Differences in the chemical expression of rat primary afferent neurons which innervate skin, muscle or joint.Neuroscience 32, 493–502.
O'Conner, T. F. &Van Der Kooy, D. (1988) Enrichment of a vasoactive neuropeptide (calcitonin gene related peptide) in the trigeminal sensory projection to the intracranial arteries.Journal of Neuroscience 8, 2468–76.
Plenderleith, M. B., Cameron, A. A., Key, B. &Snow, P. J. (1989) The plant lectin soybean agglutinin binds to the soma, axon and central terminals of a subpopulation of small-diameter primary sensory neurons in the rat and cat.Neuroscience 31, 683–95.
Price, J. (1985) An immunohistochemical and quantitative examination of dorsal root ganglion neuronal subpopulations.Journal of Neuroscience 5, 2051–9.
Priestley, J. V. &Cuello, A. C. (1989) Ultrastructural and neurochemical analysis of synaptic input to trigeminothalamic projection neurons in lamina I of the rat: a combined immunocytochemical and retrograde labelling study.Journal of Comparative Neurology 285, 467–86.
Quartu, M., Alvarez, F. J., Morris, H. R., Del Fiacco, M. &Priestley, J. V. (1989) Light and electron microscopic analysis of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) immunostaining in the spinal trigeminal nucleus and trigeminal ganglion of the rat (abstract).European Journal of Neuroscience Suppl 2, 267.
Rose, R. D. &Rohrlich, D. (1987) Counting sectioned cells via mathematical reconstruction.Journal of Comparative Neurology 263, 365–86.
Silverman, J. D. &Kruger, L. (1988a) Acid phosphatase as a selective marker for a class of small sensory ganglion cells in several mammals: spinal cord distribution, histochemical properties and relation to fluoride-resistant acid phosphatase (FRAP) of rodents.Somatosensory Research 5, 219–46.
Silverman, J. D. &Kruger, L. (1988b) Lectin and neuropeptide labeling of separate populations of dorsal root ganglion neurons and associated “nociceptor” thin axons in rat testis and cornea whole-mount preparations.Somatosensory Research 5, 259–67.
Silverman, J. D. &Kruger, L. (1990a) Analysis of taste bud innervation based on glycoconjugate and peptide neuronal markers.Journal of Comparative Neurology 292, 575–84.
Silverman, J. D. &Kruger, L. (1990b) Selective neuronal glycoconjugate expression in sensory and autonomie ganglia: relation of lectin reactivity to peptide and enzyme markers.Journal of Neurocytology 19, 789–801.
Streit, W. J., Schulte, B. A., Balentine, J. D. &Spicer, S. S. (1986) Evidence for glycoconjugates in nociceptive primary sensory neurons and its origin from the golgi complex.Brain Research 377, 1–17.
Sugiura, Y., Lee, C. L. &Perl, E. R. (1987) Central projections of identified, unmyelinated (C) afferent fibres innervating mammalian, skin.Science 234, 358–61.
Traub, R. J., Solodkin, A. &Ruda, M. A. (1989) Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in the cat lumbosacral spinal cord and the effects of multiple dorsal rhizotomies.Journal of Comparative Neurology 287, 225–37.
Tsai, S. H., Tew, J. M., Mclean, J. H. &Shipley, M. T. (1988) Cerebral arterial innervation by nerve fibres containing calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP): I. Distribution and origin of CGRP perivascular innervation in the rat.Journal of Comparative Neurology 271, 435–44.
White, F. A., Bennett-Clarke, C. A., Macdonald, G. J., Enfiejian, H. L., Chiaia, N. L. &Rhoades, R. W. (1990) Neonatal infraorbital nerve transection in the rat: comparison of effects on substance P immunoreactive primary afferents and those recognized by the lectin Bandiera simplicifolia-I.Journal of Comparative Neurology 300, 249–62.
Woolf, C. J. (1987) Afferent C fibre function in the dorsal horn: brief and.prolonged excitation. InFine Afferent Nerve Fibres and Pain (edited bySchmidt, R. F., Schaible, M. G. &Vahle-Hinz, C. H.) pp. 300–11. VCH Pubs.
Yaksh, T. L. (1986) The central pharmacology of primary afferents with emphasis on the disposition and role of primary afferent substance P. InSpinal Afferent Processing (edited byYaksh, T. L.) pp. 165–95. New York: Plenum.
Young, R. (1977) Fiber spectrum of the trigeminal sensory root of frog, cat and man determined by electron microscopy. InPain in the Trigeminal Region (edited byAnderson, D. &Matthews, B.) pp. 137–48. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alvarez, F.J., Morris, H.R. & Priestley, J.V. Sub-populations of smaller diameter trigeminal primary afferent neurons defined by expression of calcitonin gene-related peptide and the cell surface oligosaccharide recognized by monoclonal antibody LA4.. J Neurocytol 20, 716–731 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01187846
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01187846