Abstract
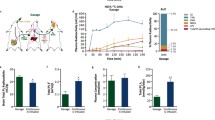
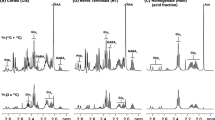
Following intravenous injection of [U-14C]palmitate in awake adult rats, whole brain radioactivity reached a broad maximum between 15–60 min, then declined rapidly to reach a relatively stable level between 4 hr and 20 hr. At 44 hr total radioactivity was 57% of the 4 hr value (p<0.05). About 50% of palmitate which entered the brain from the blood was oxidized rapidly, producing14C-labeled water-soluble components which later left the cytosol. Radioactivity in the cytosolic fraction peaked at 45 min and then declined, coincident with the decline in total brain radioactivity. Membrane fractions were rapidly labeled to levels which remained relatively stable from 1 to 44 hr. Increases in the relative distributions of radioactivity were seen between 1 and 4 hr for the microsomal and mitochondrial fractions, and beyond 4 hr for the synaptic and myelin membrane fractions (p<0.05). Radioactivity in membrane fractions was 80–90% lipid, 5–13% water-soluble components and 3–17% protein. The proportion of label in membrane-associated protein increased with time. Proportions of radioactivity in the combined membrane fractions increased from 65% to 76% to 80% at 4, 20 and 44 hr, respectively. The results show that plasma-derived palmitate enters oxidative and synthetic pathways to an equal extent, immediately after entry into the brain. At and after 4 hr, the radiolabel resides predominantly in stable membrane lipids and protein. Brain radioactivity at 4 hr can be used therefore, to examine incorporation of palmitate into lipids in vivo, in different experimental conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dhopeshwarkar, G. A., and Mead, J. F. 1969. Fatty acid uptake by the brain. II. Incorporation of [1-14C] palmitic acid into the adult rat brain. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 187:461–467.
Dhopeshwarkar, G. A., and Mead, J. F. 1973. Uptake and transport of fatty acids into the brain and the role of the blood-brain-barrier system. Pages 104–142,in Paoletti, R., and Kritchevsky D. (eds.), Advances in Lipid Research, Academic Press, New York.
Dhopeshwarkar, G. A., and Mead, J. F. 1975. Age and lipids of the central nervous system: lipid metabolism in the developing brain. Pages 119–132,in Brody, H., Harman, D., and Ordy, J. M. (eds.), Aging, Vol. 1, Raven Press, New York.
Bourre, J. M., Gozlan-Devillierre, N., Daudu, O., and Baumann, N. 1978. Is there a blood-brain relationship for saturated fatty acids during development?, Biol. Neonate 34:182–186.
Gozlan-Devillierre, N., Baumann, N. A., and Bourre, J. M. 1976. Mouse brain uptake and metabolism of stearic acid, Biochimie 58:1129–1133.
Gozlan-Devillierre, N., Baumann, N. A., and Bourre, J. M. 1978. Distribution of radioactivity in myelin lipids following subcutaneous injection of [1-14C]stearate, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 528:490–496.
Gozlan-Devillierre, N., Baumann, N. A., and Bourre, J. M. 1978. Incorporation of stearic acid into brain lipids in the developing brain: blood-brain relationships during development. Dev. Neurosci. 1:153–158.
Dhopeshwarkar, G. A., Subramanian, C., and Mead, J. F. 1971. Fatty acid uptake by the brain. IV. Incorporation of [1-14C]linoleic acid into the adult rat brain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 231:8–14.
Dhopeshwarkar, G. A., Subramanian, C., and Mead, J. F. 1971. Fatty acid uptake by the brain V. Incorporation of [1-14C] linolenic acid into adult rat brain, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 239:162–167.
Vignais, P. M., Gallagher, C. H., and Zabin, I. 1958. Activation and oxidation of long chain fatty acids by rat brain, J. Neurochem. 2:283–287.
Beattie, D. S., and Basford, R. E. 1965. Brain mitochondria-III Fatty acid oxidation by bovine brain mitochondria. J. Neurochem. 12:103–111.
Kawamura, N., and Kishimoto, Y. 1981. Characterization of water-soluble products of palmitic acid β-oxidation by a rat brain preparation. J. Neurochem. 36:1786–1791.
Sun, G. Y., and Horrocks, L. A. 1973. Metabolism of palmitic acid in the subcellular fractions of mouse brain. J. Lipid Res. 14:206–214.
Kimes, A. S., Sweeney, D., London, E. D., and Rapoport, S. I. 1983. Palmitate incorporation into different brain regions in the awake rat, Brain Res. 274:291–301.
Tabata, H., Kimes, A. S., Robinson, P. J., and Rapoport, S. I. 1986. Homeostasis of cerebral incorporation of plasma palmitate during aging of the rat, (submitted).
Miller, J. C., Gnaedinger, J. M., and Rapoport, S. I. 1986. Metabolism of plasma-derived fatty acid in rat brain. Trans. Amer. Soc. Neurochem. 17:195.
Miller, J. C., Gnaedinger, J. M., and Rapoport, S. I. 1986. Utilization of plasma fatty acid in rat brain: distribution of [14C]palmitate between oxidative and synthetic pathways, J. Neurochem (in press).
Gnaedinger, J., Miller, J. C., and Rapoport, S. I. 1986. Subcellular distribution of iv injected14C-palmitate in rat brain, Trans. Amer. Soc. Neurochem. 17:302.
Cotman, C. W., Banker, G., Churchill, L., and Taylor, D. 1974. Isolation of postsynaptic densities from rat brain, J. Cell Biol. 63:441–455.
Nieto-Sampedro, M., Bussineau, C. M., and Cotman, C. W. 1981. Optimal concentration of iodonitrotetrazolium for the isolation of junctional fractions from rat brain, Neurochem. Res. 6:307–320.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J. 1951. Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent, J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–275.
Cotman, C. W., and Matthews, D. A. 1971. Synaptic plasma membranes from rat brain synaptosomes: Isolation and partial characterization, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 249:380–395.
Miller, R. G., Jr. 1966. Simultaneous Statistical Inference. Pages 76–81, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Dhopeshwarkar, G. A., Subramanian, C., McConnell, D. H., and Mead, J. F. 1972. Fatty acid transport into the brain, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 255:572–579.
Sun, G. Y. 1977. Effect of chronic electrical stimulation on incorporation of [1-14C]oleate into glycerolipids of mouse brain, J. Neurochem. 28:1385–1387.
Allweis, C., Landau, T., Abeles, M., and Magnes, J. 1966. The oxidation of albumin-bound palmitic acid to CO2 by the perfused cat brain. J. Neurochem. 13:795–804.
Spitzer, J. J. 1973. CNS and fatty acid metabolism, Physiologist 16:55–68.
Sun, G. Y., and Su, K. L. 1979. Metabolism of arachidonoyl phosphoglycerides in mouse brain subcellular fractions, J. Neurochem. 32:1053–1059.
Lees, M. B., and Sakura, J. D. 1978. Preparation of proteolipids. Pages 345–370.In Marks, N., and Rodnight, R. (eds), in Research Methods of Neurochemistry, Volume 4, Plenum Press, New York.
Towsend, L. E., Agrawal, D., Benjamins, J. A., and Agrawal, H. C. 1982. In vitro acylation of rat brain myelin proteolipid protein, J. Biol. Chem. 257:9745–9750.
Lajtha, A. L., Maker, H. S., and Clarke, D. D. 1981. Metabolism and transport of carbohydrates and amino acids. Pages 339–341,in Siegel, G. J., Albers, R. W., Agranoff, B. W., and Katzman, R. (eds), in Basic Neurochemistry, Little, Brown and Co., Boston.
Norton, W. T. 1981. Formation, structure, and biochemistry of myelin. Pages 83–87.In Siegel, G. J., Albers, R. W., Agranoff, B. W., and Katzman, R. (eds.), in Basic Neurochemistry, Little, Brown and Co., Boston.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gnaedinger, J.M., Miller, J.C., Latker, C.H. et al. Cerebral metabolism of plasma [14C]palmitate in awake, adult rat: Subcellular localization. Neurochem Res 13, 21–29 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00971850
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00971850