Abstract
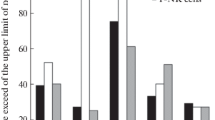
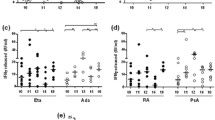
Relative proportions and numbers of helper [OKT4(+)] and suppressor [OKT8(+)] peripheral blood lymphocytes were examined in 32 young patients during the acute phase of rheumatic fever. No significant decrease in percentage T cells during acute rheumatic fever was noted in comparison to normal children controls from the same population. A decrease in absolute numbers of OKT4(+) T cells was also noted in acute rheumatic subjects not receiving corticosteroids (P<0.05). In addition, a significant decrease was documented in both proportions and total numbers of OKT8(+) putative suppressor cells during acute rheumatic attacks. C-reactive protein binding to T-lymphocyte subsets showed no preferential reactivityin vivo for suppressor or helper T cells. Antigen-reactive T lymphocytes identified with the T29 mouse hybridoma reagent showed similar proportions and numbers in rheumatic children as were noted in controls. The present data indicate profound alterations in both helper- and suppressor-cell types in the peripheral blood profile of children with acute rheumatic fever.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krishman C, Kaplan MH: Immunopathologic studies of systemic lupus erythematosus. II. Anti-nuclear reaction of γ-globulin eluted from homogenates and isolated glomeruli of kidneys from patients with lupus nephritis. J Clin Invest 46:569–579, 1967
Tan EM, Schur PH, Carr RI, Kunkel HG: Deoxyribonucleic (DNA) and antibodies to DNA in the serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest 45:1732–1740, 1966
Koffler D, Schur PH, Kunkel HG: Immunological studies concerning the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med 126:607–624, 1967
Katanzaro FJ, Stetson CA, Morris AJ, Chamovitz R, Rammelkamp CH Jr, Stolzer BL, Perry WD: The role of the streptococcus in the pathogenesis of rheumatic fever. Am J Med 17:749–756, 1954
Rammelkamp CH, Wannamaker LW, Denny FW: The epidemiology and presentation of rheumatic fever. Bull NY Acad Med 28:321–334, 1952
McCarty M: Nature of rheumatic fever. Circulation 14:1138–1143, 1956
Reinherz EL, Kung PC, Goldstein G, Schlossman SF: A monoclonal antibody with selective reactivity with functionally mature human thymocytes and all peripheral human T cells. J Immunol 123:1312–1317, 1979
Reinherz EL, Kung PC, Goldstein G, Schlossman SF: Separation of functional subsets of human T cells by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4061–4065, 1979
Reinherz EL, Kung PC, Goldstein G, Levey RH, Schlossman SF: Discrete stages of human intrathymic differentiation: analysis of normal thymocytes and leukemic lymphoblasts of T lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:1588–1592, 1980
American Heart Association: Jones criteria (revised) for guidance in the diagnosis of rheumatic fever. Circulation 32:664–668, 1956
Boyum A: Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood: Isolation of mononuclear cells by one centrifugation and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation of Ig. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 21(Suppl. 97):77–89, 1968
Bankhurst AD, Williams RC Jr: Identification of DNA-binding lymphocytes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest 56:1378–1385, 1975
Williams RC Jr, Kilpatrick KA, Kassaby M, Abdin ZH: Lymphocytes binding C-reactive protein during acute rheumatic fever. J Clin Invest 61:1384–1393, 1978
Reinherz EL, Kung PC, Goldstein G, Schlossman SF: Further characterization of the human inducer T cell subset defined by monoclonal antibody. J Immunol 123:2894–2896, 1979
Reinherz EL, Kung PC, Goldstein G, Schlossman SF: A monoclonal antibody reactive with the human cytotoxic/suppressor cell subset previously defined by a heteroantiserum termed TH2. J Immunol 124:1301–1307, 1980
Hausman PB, Raff HV, Gilbert RC, Picker LJ, Stobo JD: T cells and macrophages involved in the autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction are required for the response to conventional antigen. J Immunol 125:1374–1379, 1980
Breard J, Reinherz EL, Kung PC, Goldstein G, Schlossman SF: A monoclonal antibody reactive with human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol 124:1943–1948, 1980
Williams RC Jr, Kilpatrick K: Rabbit antisera to human cord T cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 18:431, 1981
Pepys MB, Dash AC, Ashley MJ: Isolation of C-reactive protein by affinity chromatography. Clin Exp Immunol 30:32–37, 1977
Williams RC Jr, Van de Rijn I, Mahros F, Abdin ZH, Reid H, Poon-King T: Lymphocytes binding C-reactive protein and streptococcal membranes in acute rheumatic fever. J Lab Clin Med 96:803–814, 1980
Williams RC Jr, Zabriskie JB, Mahros F, Hassaballa F, Abdin ZH: Lymphocyte surface markers in acute rheumatic fever and post-streptococcal acute glomerulonephritis. Clin Exp Immunol 27:135–142, 1977
Wagner V, Rejholec V: Agglutinins and incomplete antibodies after a single antigenic inoculation in normal and rheumatic individuals. Ann Rheum Dis 14:243–250, 1955
Creger WP, Choy SH, Rantz LA: Experimental determination of the hypersensitive diathesis in man. J Immunol 66:445–450, 1951
Kuhns WJ, McCarty M: Studies of diphtheria antitoxin in rheumatic fever subjects: Analysis of reactions to the Schick test and of antitoxin responses following hyperimmunization with diphtheria toxoid. J Clin Invest 33:759–767, 1954
Zabriskie JB, Hsu KC, Seegal BC: Heart-reactive antibody associated with rheumatic fever: Characterization and diagnostic significance. Clin Exp Immunol 7:147–159, 1970
Read SE, Fischetti VA, Utermohlen V, Falk RE, Zabriskie JB: Cellular reactivity studies to streptococcal antigens. Migration inhibition studies in patients with streptococcal infections and rheumatic fever. J Clin Invest 54:439–450, 1974
Kaplan MH, Myerserian M: An immunological cross-reaction between group A streptococcal cells and human heart tissue. Lancet 1:706–710, 1962
Zabriskie JB, Freimer EH: An immunological relationship between the group A streptococcus and mammalian muscle. J Exp Med 124:661–678, 1966
Goldstein I, Rebeyrotte P, Parlebas J, Halpern B: Isolation from heart valves of glycopeptides which share immunological properties with streptococcus haemolyticus group A polysaccharides. Nature 219:866–868, 1968
Kasp-Grochowska E, Kingston D: Streptococcal cross-reacting antigen and the bundle of His. Clin Exp Immunol 27:63–65, 1977
Husby G, Van de Rijn I, Zabriskie JB, Abdin ZH, Williams RC Jr: Antibodies reacting with cytoplasm of subthalamic and caudate nuclei neurons in chorea and acute rheumatic fever. J Exp Med 144:1094–1110, 1976
Cromartie WJ, Craddock JG: Rheumatic-like lesions in mice. Science 154:285–287, 1966
Cromartie WJ, Craddock JG, Schwab JH, Anderle SK, Yang CH: Arthritis in rats after systemic injection of streptococcal cells or cell walls. J Exp Med 146:1585–1602, 1977
Murphy GE, Becker CG: Occurrence of caterpillar nuclei within normal immature and normal appearing and altered mature heart muscle cells and the evolution of Anitschkow cells from the latter. Am J Pathol 48:931–957, 1966
Becker CG, Murphy GE: Demonstration of contractile protein in endothelium and cells of the heart valves, endocardium, intima, arteriosclerotic plaques and Aschoff bodies of rheumatic heart disease. Am J Pathol 55:1–37, 1969
Gray ED, Wannamaker LW, Ayoub EM, El Kholy A, Abdin Z: Cellular immune responses to extracellular streptococcal products in rheumatic heart disease. J Clin Invest 68:665–671, 1981
Sakane T, Steinberg AD, Green I: Studies of immune functions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Complement-dependent immunoglobulin M anti-thymus-derived cell antibodies preferentially inactivate suppressor cells. J Clin Invest 63:954–965, 1979
Morimoto C, Reinherz EL, Schlossman SF, Schur PH, Mills JA, Steinberg AD: Alterations in immunoregulatory T cell subsets in active systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest 66:1171–1174, 1980
Fox RI, Thompson LF, Huddlestone JR: T cells express T lymphocyte-associated antigens. J Clin Invest 126:2062–2063, 1981
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, R.C., Raizada, V., Prakash, K. et al. Changes in T-lymphocyte subsets during acute rheumatic fever. J Clin Immunol 2, 166–172 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00915218
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00915218