Summary
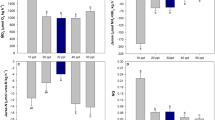
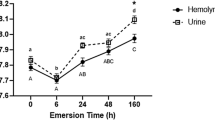
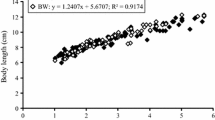
The efflux of sodium ions from the loggerhead turtle,Caretta caretta, was investigated when animals were acclimated to seawater, freshwater, and during the acclimation period after transfer from seawater to freshwater. The rate of sodium loss in animals acclimated to seawater was found to be 3 μM Na · g−1 · hr−1. Cannulation of the cloaca showed that only 5% of the gross efflux of sodium was via the cloaca and it was calculated that 60% of the gross efflux was via nasal gland secretion and 35 % via integumentary diffusional loss. Cannulation experiments indicated that a significant amount of sodium may enter the body via the cloaca. Transfer of animals from seawater to freshwater resulted in a decline of sodium efflux by 90–99 % within 6 hr, and a further decline to only approximately 0 01 μM Na · g−1· hr−1 after 1–2 days in freshwater. Cannulation experiments of individuals acclimated to freshwater indicated that the role of the cloaca in sodium loss in freshwater was minimal. It was calculated that sodium loss in freshwater is so small that survival in freshwater for at least 20 days is possible without active extraction of sodium from the medium. No evidence could be found for active uptake of sodium ions from freshwater baths byCaretta.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bentley, P. J.: Endocrines and osmoregulation. Berlin-Heidelberg-NewYork: Springer 1971.
Bentley, P. J., Bretz, W. L., Schmidt-Nielsen, K.: Osmoregulation in the diamondback terrapin,Malaclemys terrapin centrata. J. exp. Biol.46, 161–167 (1967).
Bentley, P. J., Schmidt-Nielsen, K.: Comparison of water exchange in two aquatic turtles,Trionyx spinifer andPseudemys scripta. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.32, 363–365 (1970).
Dunson, W. A.: Sodium fluxes in fresh-water turtles. J. exp. Zool.165, 171–182 (1967).
Dunson, W. A.: Some aspects of electrolyte and water balance in three estuarine reptiles, the diamondback terrapin, American and “ Salt water ” crocodiles. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.32, 161–174 (1970).
Evans, D. H.: Sodium, chloride and water balance of the intertidal teleost,Pholis gunnellus. J. exp. Biol.50, 179–190 (1969).
Holmes, W. N., McBean, R. L.: Some aspects of the electrolyte excretion in the green turtle,Chelonia mydas mydas. J. exp. Biol.41, 81–90 (1964).
Matz, J.: Fish gills: mechanisms of salt transfer in fresh water and sea water. Phil. Trans. B262, 209–249 (1971).
Motais, R.: Les mécanismes d'échanges ioniques branchiaux chez les téléostéens. Leur role l'osmorégulation. Ann. Inst. Oceanogr.45, 1–83 (1967).
Potts, W. T. W., Parry, G.: Osmotic and ionic regulation in animals.423 pgs. Pergamon Press, NewYork: Macmillan 1964.
Schmidt-Nielsen, K., Fange, R.: Salt glands in marine reptiles. Nature (Lond.)182, 783–785 (1958).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by NSF grant GB 16839.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Evans, D.H. The sodium balance of the euryhaline marine loggerhead turtle,Caretta caretta . J. Comp. Physiol. 83, 179–185 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00696894
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00696894