Summary
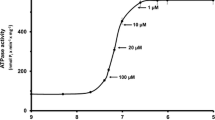
Relatively pure mitochondrial-free Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) was isolated from crab and cockroach skeletal muscle, and the SR calcium uptake was studied in control and insecticide-treated conditions by incubation in Ca45 media followed by millipore filtration and counting by liquid scintillation methods. All insecticides used (parathion, DDT, γBHC and tri-cresyl phosphate) at 1 mM concentrations caused a slight fall in the intrinsic Ca2+ content of the SR, but this Ca2+ loss was insufficient to explain the contracture induction effect of these agents.
All insecticides used (at 1 mM) caused a massive inhibition of SR Ca2+ uptake, and all were able to release Ca2+ previously bound to the SR during incubation in the presence of ATP. It is concluded that the contracture-induction effect of these insecticides is due to their inhibition of SR Ca2+ uptake, resulting in a massive rise in myoplasmic free Ca2+.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baskin, R. J., Deamer, D. W.: Comparative ultrastructure and calcium transport in heart and skeletal muscle microscomes. J. Cell Biol.43, 610–617 (1969)
Bittar, E. E., Hift, H., Huddart, H., Tong, E. Y.: The effects of caffeine on sodium transport, membrane potential, mechanical tension and ultrastructure in barnacle muscle fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.) (in press) (1974)
Bradbury, S. J.: The effect of parathion on crustacean skeletal muscle. I. The mechanical threshold and dependence on Ca2+ ions. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.44A, 1021–1032 (1973a)
Bradbury, S. J.: The effect of parathion on crustacean skeletal muscle. II. Disruption of excitation-contraction coupling. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.44A, 1033–1046 (1973b)
Carvalho, A. P.: Effects of potentiators of muscular contraction on binding of cations by sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. gen. Physiol.51, 427–442 (1968a)
Carvalho, A. P.: Calcium-binding properties of sarcoplasmic reticulum as influenced by ATP, caffeine, quinine and local anaesthetics. J. gen. Physiol.52, 622–642 (1968b)
Fuchs, F., Gertz, E. W., Briggs, F. N.: The effect of quinine on calcium accumulation by isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum of skeletal and cardiac muscle. J. gen. Physiol.52, 955–968 (1968)
Greenwood, M., Huddart, H.: The effect of an organochlorine and an organophosphorous insecticide on the fine structure of cockroach flight muscle in relation to the maintenance of contractility. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. (in press) (1974)
Huddart, H.: The subcellular distribution of potassium and sodium in some skeletal muscles. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.38A, 715–721 (1971)
Huddart, H., Oates, K.: Localization of the intracellular site of action of caffeine on skeletal muscle. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.36, 677–682 (1970)
Lehninger, A. L.: Mitochondria and calcium ion transport. Biochem. J.119, 129–138 (1970)
Lorand, L. H., Schuel, R., Demovsky, A., Meisler, J.: Distribution and some properties of muscle relaxing particles. In: Molecular biology of muscular contraction (Ebashi, S., Oosawa, F., Sekine, T., Tonomura, Y., eds.). Tokyo: Igaku Shoin Ltd. 1965
Molnar, J., Lorand, L.: A phosphoryl group acceptor attached to the microsomal fraction of muscle. Arch. Biochem. Biophys.98, 356–364 (1962)
Nakamaru, Y., Schwartz, A.: The influence of hydrogen ion concentration on calcium binding and release by skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. gen. Physiol.59, 22–32 (1972)
Narahashi, T., Haas, H. G.: DDT: Interaction with nerve membrane conductance changes. Science (N.Y.)157, 1438–1440 (1967)
Narahashi, T., Haas, H. G.: Interaction of DDT with the components of lobster nerve membrane conductance. J. gen. Physiol.51, 177–198 (1968)
Narahashi, T., Moore, J. W.: Neuroactive agents and nerve membrane conductances. J. gen. Physiol.51, 93s-101s (1968)
Sandow, A.: Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Pharmac. Rev.17, 265–320 (1965)
Sandow, A.: Skeletal muscle. Ann. Rev. Physiol.32, 87–138 (1970)
Weber, A., Herz, R.: The relationship between caffeine contracture of intact muscle and the effect of caffeine on reticulum. J. gen. Physiol.52, 750–759 (1968)
Wilcox, W. D., Fuchs, F.: The effect of some local anaesthetic compounds on sarcotubular calcium transport. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)180, 210–212 (1969)
Yu, B. P., DeMartinis, F. D., Masoro, E. J.: Isolation of Ca++-sequestering sarcotubular membranes from rat skeletal muscle. Analyt. Biochem.24, 523–530 (1968)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huddart, H., Greenwood, M. & Williams, A.J. The effect of some organophosphorous and organochlorine compounds on calcium uptake by Sarcoplasmic reticulum isolated from insect and crustacean skeletal muscle. J Comp Physiol B 93, 139–150 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00696268
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00696268