Abstract
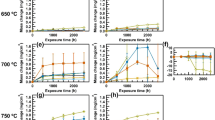
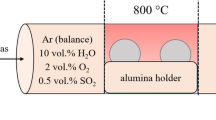
The corrosion behavior of Co alloyed with up to 40 wt.% Mo alloys was studied in H2-H2O-H2S gas mixtures over the temperature range between 600‡C and 900‡C. The parabolic rate constants for corrosion decreased with increasing amounts of Mo. The compositions of all gas atmospheres fall in the sulfide(s stability region of the ternary M-O-S phase diagrams at all temperatures investigated. All the corrosion scales were composed of sulfides, while no oxide was detected. The sulfide scales formed were duplex at all temperatures except at 900‡C. The outer layer consisted primarily of cobalt sulfide, while the inner layer was complex and heterophasic, the phases formed being highly composition dependent. MoS2 predominated in the inner layer for all alloys. However, a metallic Mo layer was formed in the innermost layer of Co-40 Mo. Activation energies were different for all alloys, increasing with increasing Mo content. Identical kinetics were observed for Co-30Mo corroded at 700–800‡C. A Chevrel-phase Co1.62Mo6S8 was present in scales formed on the samples exhibiting the temperature-independent kinetics. A possible model in which Co1.62Mo6S8 forms preferentially in H2-containing mixed gas is suggested. Alloys corroded at 900‡C formed a lamellar-structure scale which contained Co and CoMo2S4 layers perpendicular to the alloy surface. A eutectoid decomposition of an unknown Co-Mo sulfide may be responsible for the presence of the lamellar structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Natesan and M. B. Delaplane, inCorrosion-Erosion Behavior of Materials, K. Natesan, ed. (Metallurgical Society of AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1980), p. 1.
M. Loudjani, J. C. Pivin, C. Roques-Carmes, P. Lacombe, and J. H. Davidson,Metall. Trans. A 13A, 1299 (1982).
M. F. Chen and D. L. Douglass,Oxid. Met. 31, 237 (1989).
R. V. Carter, D. L. Douglass, and F. Gesmundo,Oxid. Met. 31, 341 (1989).
K. N. Strafford and P. K. Datta,Mater. Sci. Tech. 5, 765 (1989).
B. Gleeson, D. L. Douglass, and F. Gesmundo,Oxid. Met. 31, 209 (1989).
G. Wang, R. V. Carter, and D. L. Douglass,Oxid. Met. 32, 273 (1989).
M. F. Chen, D. L. Douglass, and F. Gesmundo,Oxid. Met. 32, 185 (1989).
B. Gleeson, D. L. Douglass, and F. Gesmundo,Oxid. Met. 33, 425 (1990).
P. Singh and N. Birks,Oxid. Met. 12, 23 (1978).
F. Gesmundo andC. De Asmundis, inProceedings of the International Conference on Behavior of High Temperature Alloys in Aggressive Environments, I. Kirmanet al., eds. (Metal Society, London, 1980), p. 435.
K. Holthe and P. Kofstad,Corros. Sci. 20, 919 (1980).
N. S. Jacobson and W. L. Worrell,J. Electrochem. Soc. 131, 1182 (1984).
A. Rahmel, M. Schorr, A. Velasco-Tellez, and A. Pelton,Oxid. Met. 27, 199 (1987).
G. J. Yurek and M. H. LaBranche, inProceedings of the Conference on Corrosion-Erosion-Wear of Materials in Emerging Fossil Energy Systems, A. V. Levy, ed. (NACE, Houston, 1982), p. 933.
Wu Kai, D. L. Douglass, and F. Gesmundo,Oxid. Met. 37, 389 (1992).
S. Mrowec, S. Rusiecki, and A. Wojtowicz,Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Chem. 34, 411 (1986).
A. Davin,Cobalt 30, 19 (1966).
Bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams 1, 93 (1980).
R. Chevral, M. Sergent, and J. Prigent,Mater. Res. Bull. 9, 1487 (1974).
A. M. Umarji, G. V. Subba Rao, M. P. Janawadkar, and T. S. Radhakrishnan,J. Phys. Chem. Solids 41, 421 (1980).
T. Flatley and N. Birks,J. Iron Steel Inst. 209, 523 (1971).
K. Kurokawa, T. Narita, and K. Nishida, inProceedings of the 3rd JIM International Symposium on High Temperature Corrosion of Metals and Alloys (JIM, Sendai, 1983), p. 465.
S. Mrowec and K. Przybylski,Oxid. Met. 23, 107 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shing, C.C., Douglass, D.L. & Gesmundo, F. The corrosion behavior of Co-Mo alloys in H2-H2O-H2S environments. Oxid Met 37, 441–461 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00666629
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00666629