Summary
In a double-blind, interindividual comparative study 30 healthy volunteers were randomly allocated to oral treatment with 5 or 10 mg of dihydroergotamine (DHE) or placebo once daily for 16 days. Regional basic venous blood volume (BBV), pressure dependent venous capacitance (Cv) of the calf, resting heart rate and blood pressure were determined on Days 1 and 15 of treatment. Plasma concentrations of DHE were monitored on Days 2 and 16.
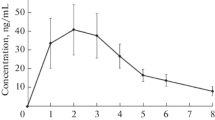
Due to spontaneous vasodilation BBV varied considerably, showing that it is an inappropriate parameter for investigating the venoconstrictor activity of DHE. Cv remained unchanged after the first dose of DHE but it had declined significantly on both dosage regimens at the end of the treatment phase. In contrast, the blood concentration profiles of DHE were comparable at the beginning and the end of the trial. The discrepancy can best be explained by the existence of an effect compartment, e.g. smooth vascular musculature, which slowly becomes filled with DHE and/or its active metabolites. The venoconstrictor activity of DHE exhibited a significant dose-response relationship.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mellander S, Nordenfelt I (1971) Comparative effects of dihydroergotamine and noradrenaline on resistance, exchange and capacitance functions in the peripheral circulation. Clin Sci 39: 183–201
Rieckert H, Pauschinger P (1967) Die Beeinflussung des peripheren Venentonus durch Dihydergot. Ärztl Forsch 21: 99–101
Niehues B, von Smekal P, Thoma R, Piehl W, Chriske HW, Schulten HK (1975) Therapeutische Möglichkeiten zur Behandlung der idiopathischen Positionshypotonie. Med Welt 26: 1403–1405
Juchems R, Netter H, Gross W (1968) Zentrale Hämodynamik des orthostatischen Syndroms. Z Kreisl Forsch 57: 1198–1204
Lohmann FW, Gotzen R, Ungewiß U (1975) Der Einfluß von Dihydroergotamin (Dihydergot) auf die Kreislaufveränderungen und die Funktion des sympathischen Nervensystems in Orthostase. Med Welt 26: 1416–1420
Krüger K, Neff K (1973) Dihydroergotamine in the treatment of orthostatic circulatory disorders: A double-blind comparison with placebo. J Med 4: 106–117
Lang L, Jansen W, Pfaff W (1975) Orthostatische Hypotonie bei älteren Menschen. Med Klin 70: 1976–1981
Lübke KO (1972) Orthostatische Dysregulation — Eine Doppelblindstudie mit Dihydergot und Placebo. Therapiewoche 22: 2935–2943
Mishra BR (1979) Dihydergot in der Behandlung der orthostatischen Dysregulation. Fortschr Med 97: 1436–1440
Warning A, Pfaff W (1978) Zur Therapie der orthostatischen Dysregulation in der Geriatrie. Therapiewoche 28: 7488–7497
de Marées H, Jarmatz H (1977) Blutvolumenverlagerung während orthostatischer Belastung unter oral appliziertem Dihydroergotamin. Münchn Med Wochenschr 40: 1301–1304
Bobik A, Jennings G, Skews H, Esler M, McLean A (1981) Low oral bioavailability of dihydroergotamine and first-pass extraction in patients with orthostatic hypotension. Clin Pharmacol Ther 30: 673–679
Little J, Jennings G, Skews H, Bobik A (1982) Bioavailability of dihydroergotamine in man. J Clin Pharmacol 13: 785–790
Aellig WH (1984) Investigation of the venoconstrictor effect of 8'hydroxydihydroergotamine, the main metabolite of dihydroergotamine in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 26: 239–242
Maurer G, Frick W (1984) Structure elucidation and receptor binding studies of the primary and major metabolites of dihydroergotamine in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 26: 463–470
Müller-Schweinitzer E (1984) Pharmacological actions of the main metabolites of dihydroergotamine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 26: 699–705
Aellig WH, Kiechel JR (1984) unpublished document, cited in: Stürmer E: Pharmakologische und pharmakokinetische Betrachtungen über Dihydroergotamin unter besonderer Berücksichtigung neuerer Aspekte. In: Fitscha P (ed) Neuester Stand der Dihydroergotamin-Forschung. Workshop Wien. Thieme, Stuttgart
Müller-Schweinitzer E (1984) What is known about the action of dihydroergotamine on the vasculature in man? Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol 22: 677–682
Jennings G, Bobik A (1982) Letter to the Editor. Medicinsk Veckobulletin Vecka 11: 15–20 mars
Barbey K, Adam W (1965) Die Messung von Druckvolumendiagrammen am Bein. Arch Klin Exp Dermatol 222: 423–429
de Marées H, de Caleya C, Hemplemann G, Sippel R (1976) Der Einfluß der Spinalanästhesie auf die periphere Hämodynamik. Z Kardiol 65: 478–489
de Marées H, Barbey K, Feuerhake J, Dowidat H (1970) Bestimmung des Blutvolumens des Unterschenkels mit der Venenverschlußplethysmographie und mit einer Isotopenmethode. In: Ehringer H, Deutsch E (eds) Durchblutungsstörungen — Meßmethoden und Pharmakotherapie. Schattauer, Stuttgart, pp 248–253
Rosenthaler J, Munzer H (1976) 9, 10-Dihydroergotamin: Production of antibodies and radioimmunoassay. Experientia (Basel) 32: 234–236
Jansen W, Enghofer E, Seibel K (1983) Einmalige Gabe von Dihydroergotamin pro Tag ausreichend? Münch Med Wochenschr 125: 498–502
Mäntylä R, Kleimola T, Kanto J (1978) The pharmacokinetics of dihydroergotamine in the beagle. Int J Clin Pharmacol 16: 124–128
Kanto J, Allonen H, Koski K, Koulu M, Lammintausta R, Mäntylä R, Kleimona T, Siirtola T (1981) Pharmacokinetics of dihydroergotamine in healthy volunteers and in neurological patients after a single intravenous injection. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol 19: 127–130
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Marées, H., Welzel, D., de Marées, A. et al. Relationship between the venoconstrictor activity of dihydroergotamine and its pharmacokinetics during acute and chronic oral dosing. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 30, 685–689 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00608216
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00608216