Summary
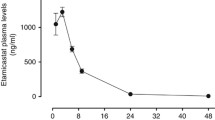
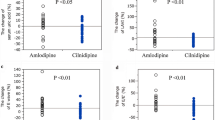
The antihypertensive effects of the hydralazine-related compound cadralazine (2-{3-[6-(2-hydroxypropyl)ethylamino]pyridazinyl}ethyl carbazate, ISF 2469), were investigated in 16 patients with primary hypertension concurrently treated with β-blockers and diuretics. The protocol included a double-blind placebo controlled haemodynamic evaluation after the first tablet and two 4-week double-blind placebo controlled cross-over periods followed by an open evaluation during 2 months. Cadralazine induced a moderate, prolonged fall in blood pressure that was associated with vasodilatation and slight increases in cardiac output (dye-dilution) and heart rate. Renal plasma flow (PAH) and glomerular filtration rate (51Cr-EDTA) were not significantly influenced, but the filtration fraction was reduced. Plasma concentrations of noradrenaline and adrenaline rose, whereas plasma renin activity was unchanged. The haemodynamic parameters were not correlated with the plasma concentrations of cadralazine. During chronic cadralazine treatment the supine blood pressure was significantly lower than during the double-blind placebo phase (160/93 vs 174/102 mmHg). The compound was generally well tolerated but the body weight increased slightly (1.1 kg), probably because of fluid retention. Several patients who had previously experienced side effects with hydralazine, including one with hydralazine-syndrome, tolerated cadralazine well. This suggests that cadralazine does not cross-react with hydralazine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Semeraro C, Dorigotti L, Banfi C, Carpi C (1981) Pharmacological studies on cadralazine: A new antihypertensive vasodilator. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 3: 455–467
Catalano M, Parini J, Libretti A (1983) Cadralazine (ISF 2469) dose-related antihypertensive activity after single oral administration to patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 24: 157–161
Catalano M, Parini J, Romano M, Libretti A (1985) Controlled clinical trial of cadralazine as a second-step drug in the treatment of hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 28: 135–138
Pirelli A, Nardecchia A, Pieri R, Motolese M (1984) Cadralazine in the treatment of mild and moderate hypertension. Cur Ther Res 36: 712–719
Van Brummelen P, Bühler FR, Kiowski W, Bolli P, Bertel O (1979) Antihypertensive efficacy of a new long acting hydralazinelike vasodilator, ISF 2469, in combination with a betablocker and a diuretic. Int J Clin Biopharmacol 17: 380–385
Nilsson NJ (1963) Linearly responding dichromatic curette densitometer for dye-dilution curves. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 15 [Suppl 69]: 181–193
Brun C (1951) A rapid method for the determination of paraaminohippuric acid in kidney function tests. J Lab Clin Med 37: 955–958
Giese J, Jörgensen M, Damkjaer-Nielsen M, Lund JO, Munck O (1970) Plasma renin concentration measured by use of radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 26: 335–367
Hjelmdahl P, Daleskog M, Kahan T (1979) Determination of plasma catecholamines by high performance liquid chromatography with electromagnetic detection: Comparison with a radioenzymatic method. Life Sci 25: 131–136
Hauffe SA, Dubois JP (1984) Determination of cadralazine in human plasma and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 290: 223–230
Esler MD, Nestel PJ (1973) Evaluation of protocol in hypertension. Effects of sympathetic nervous system and renin responsiveness. Br Heart J 35: 469–474
Bühler FR, Laragh JH, Baer L (1972) Propranolol inhibition of renin secretion: A specific approach to diagnosis and treatment of renin-dependent hypertensive disease. N Engl J Med 287: 1209–1221
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Persson, B., Granerus, G., Wysocki, M. et al. Acute systemic and renal haemodynamic effects and long-term antihypertensive action of cadralazine in patients pretreated with β-blockers and diuretics. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 31, 513–518 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00606622
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00606622