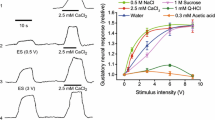
Summary
Rabbit livers were perfused with Krebs solution via the portal vein and small bundles of the hepatic nerve were monitored for spontaneous afferent impulses arising in the liver. The concentration of the Krebs solution was varied by altering the amount of water in which the salts were dissolved. An alteration from 5% more concentrated to 5% more dilute andvice versa did not affect this spontantous discharge. Addition to the Krebs solution of up to 60 mM sucrose, of up to 22 mM mannitol or of 0.8 mM polyethylenglycol 6000 mol. wt. did not alter the frequency of impulses.
Perfusion with bovine serum, or Krebs solution containing approx. 0.6 mM polyvinylpyrrolidone, mol. wt. 44000, or dextran mol. wt. 110 000 increased the frequency of discharge in some nerve bundles. An alteration of 0.06 mM in the concentration of dextran produced a significant change of frequency.
It is concluded that spontaneous discharge in some afferent hepatic nerves is influenced by colloidal osmotic pressure but not by changes of ionic osmotic pressure. The nerves affected differ from ‘sodium-sensitive’ nerves and from the ‘osmoreceptors’ of Niijima.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews, W. H. H., Orbach, J.: Sensitivity of nerve endings to changes of osmolarity in the perfused rabbit liver. J. Physiol. (Lond.)231, 115–116P (1973a)
Andrews, W. H. H., Orbach, J.: A study of compounds which initiate and block nerve impulses in the perfused rabbit liver. Brit. J. Pharmacol.49, 192–204 (1973b)
Adrews, W. H. H., Orbach, J.: Sodium receptors activating some nerves of perfused rabbit livers. Amer. J. Physiol.227, 1273–1275 (1974)
Brauer, R. W., Holloway, R. H., Leong, G. F.: Changes in liver functions and structure due to experimental passive congestion under controlled hepatic vein pressures. Amer. J. Physiol.197, 681–692 (1959)
Daly, J. J., Roe, J. W., Horrock, P.: A comparison of sodium excretion following the infusion of saline into systemic and portal veins in the dog: evidence for a hepatic role in the control of sodium excretion. Clin. Sci.33, 481–487 (1967)
Dennhardt, R., Ohm, W. W., Haberich, F. J.: Die Ausschaltung der Leberäste des N. vagus an der wachen Ratte und ihr Einfluß auf die hepatogene Diurese — indirekter Beweis für die afferente Leitung der Leber-Osmoreceptoren über den N. vagus. Pflügers Arch.328, 51–56 (1971)
Forker, E. L.: Bile formation in guinea pigs: analysis with inert solutions of graded molecular radius. Amer. J. Physiol.215, 56–62 (1968)
Goresky, C. A.: A linear methods for determining liver sinusoidal and extravascular volumes. Amer. J. Physiol.204, 626–640 (1963)
Greenway, C. V., Stark, R. D.: Hepatic vascular bed. Physiol. Rev.51, 23–65 (1971)
Haberich, F. J.: Osmoreception in the portal circulation. Fed. Proc.27, 1137–1141 (1968)
Haberich, F. J., Aziz, O., Nowacki, P. E.: Über einen osmoreceptorisch tätigen Mechanismus in der Leber. Pflügers Arch.285, 73–89 (1965)
Hint, H.: The relationship between the molecular weight of dextran and its effects. Report of Symposium on Rheomacrodex, held at Cardiff, sponsored by Pharmacia (Great Britain) Ltd., London 1964
Niijima, A.: Afferent discharge from osmoreceptors in the liver of the guinea pig. Science166, 1519–1520 (1969)
Passo, S. S., Thornborough, J. R., Rothballer, A. B.: Hepatic receptors in control of sodium excretion in anaesthetised cats. Amer. J. Physiol.224, 373–375 (1973)
Rothschild, M. A., Oratz, M., Evans, C. D., Schreiber, S. S.: Role of hepatic interstitial albumin in regulating albumin synthesis. Amer. J. Physiol.210, 57–62 (1966).
Schneider, E. G., Davis, J. O., Robb, C. A., Baumber, J. S., Johnson, J. A., Wright, F. S.: Lack of evidence for a hepatic osmoreceptor mechanism in conscious dogs. Amer. J. Physiol.218, 42–45 (1970)
Strandhoy, J. W., Williamson, H. E.: Evidence for an hepatic role in the control of sodium excretion. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.)133, 419–422 (1970)
Tsai, Te Lin: A histological study of sensory nerves in the liver. Acta neuroveg. (Wien)17, 354–385 (1958)
Verney, E. B.: The antidiuretic hormone and the factors which determine its release. Proc. roy. Soc. B135, 25–105 (1947)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andrews, W.H.H., Orbach, J. Effect of osmotic pressure on spontaneous afferent discharge in the nerves of the perfused rabbit liver. Pflugers Arch. 361, 89–94 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587346
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587346