Abstract
-
1.
Membrane current responses produced by intracellular ionophoretic injection of Ca2+ ions into voltage clampedHelix neurones were investigated.
-
2.
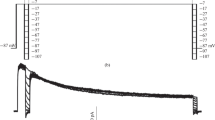
The Ca2+ activated current depends on the intensity and duration of the Ca2+ injection as well as on the membrane potential. The current-voltage relation is nonlinear and shows strong outward rectification.
-
3.
The Ca2+ activated current reverses near the equilibrium potential for K+ ions and the associated current fluctuations disappear at the K+ reversal potential, which indicates a single current source, probably activation of K+ channels.
-
4.
The Ca2+ activated K+ conductance is voltage dependent and changes e-fold per 31 mV membrane depolariation.
-
5.
Extracellular tetraethylammonium, gallamine and quinidine block the Ca2+ activated K+ current. Extracellular 4-aminopyridine aminopyridine has no blocking effect.
-
6.
Sustained injection of high amounts of Ca2+ irreversibly suppresses the outward current.
-
7.
The K+ outward current evoked by repeated Ca2+ injection exhibits summation and facilitation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armando-Hardy M, Ellory JC, Ferreira HG, Fleminger S, Lew VL (1975) Inhibition of the calcium-induced increase in the potassium permeability of human red blood cells by quinine. J Physiol 250:32P-33P
Constanti A, Adams PR, Brown DA (1981) Calcium activated outward currents (Ic) in voltage-clamped bullfrog sympathetic neurones. Soc Neurosci Abstr 7:14
Dionne VE, Ruff RL (1977) Endplate current fluctuations reveal only one channel type at frog neuromuscular junction. Nature 266:263–265
Eckert R, Lux HD (1977) Calcium-dependent depression of a late outward current in snail neurons. Science 197:472–475
Eckert R, Tillotson DL (1981) Calcium-mediated inactivation of the calcium conductance in caesium-loaded giant neurones of Aplysia california. J Physiol 314:265–280
Goldman DE (1943) Potential, impedance, and rectification in membranes. J Gen Physiol 27:37–60
Gorman ALF, Hermann A (1979) Internal effects of divalent cations on potassium permeability in molluscan neurones. J Physiol 296:393–410
Gorman ALF, Thomas MV (1980) Potassium conductance and internal calcium accumulation in a molluscan neurone. J Physiol 308:287–313
Hermann A (1978) Different contribution of Ca-dependent K+ current in Aplysia neurones and the effect of TEA. J Gen Physiol 72:51–6a
Hermann A, Gorman ALF (1979) External and internal effects of tetraethylammonium on voltage-dependent and Ca-dependent K+ currents components in molluscan pacemaker neurones. Neurosci Lett 12:87–92
Hermann A, Gorman ALF (1981a) Effects of 4-aminopyridine on potassium currents in a molluscan neuron. J Gen Physiol 78:63–86
Hermann A, Gorman ALF (1981b) Effects of tetraethylammonium on potassium currents in a molluscan neuron. J Gen Physiol 78:87–110
Hermann A, Hartung K (1981) Specificity of the calcium activated potassium conductance in Helix neurones. Pflügers Arch 389:R22
Hermann A, Hartung K (1982) Noise and relaxation measurements of the Ca2+ activated K+ current in Helix neurones. Pflügers Arch 393:254–261
Heyer CB, Lux HD (1976) Control of the delayed outward potassium currents in bursting pace-maker neurones of the snail, Helix pomatia. J Physiol 262:349–382
Hofmeier G, Lux HD (1981) Three distinct effects mediated by calcium ions on electrical membrane porperties of helix neurones. Proc. XXVIII Intern Congress Physiol Sci, Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest
Kerkut GA, Lambert JDC, Gayton JF, Loker JE, Walker RJ (1975) Mapping of nerve cells in the suboesophageal ganglia of Helix aspersa. Comp Biochem Physiol 50A:1–25
Kostyuk PG, Sorokina ZA, Kholodova YD (1969) Measurement of activity of hydrogen, potassium and sodium ions in striated muscle fibers and nerve cells. In: Lavallee M, Schanne OF, Hebert NC (eds) Glass microelectrodes. Wiley, New York, pp 322–348
Kostyuk PG, Doroshenko PA, Tsyndrenko AY (1980) Calciumdependent potassium conductance studied on internally dialysed nerve cells. Neuroscience 5:2187–2192
Lux HD (1980) Voltage dependence of Ca2+-activated K+ conductance. In: Koester J, Byrne JH (eds) Molluscan Nerve Cells: From biophysics to behavior. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory 1: 105–114
Meech RW (1974) The sensitivity of Helix aspersa neurones to injected calcium ions. J Physiol 237:259–277
Meech RW (1978) Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Ann Rev Biophys Bioeng 7:1–18
Meech RW, Standen NB (1975) Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol 249:211–239
Meech RW, Thomas RC (1977) The effect of calcium injection on the intracellular sodium and pH of snail neurones. J Physiol 265:867–879
Schauf CL, Smith KJ (1981) Electrophysiological effects of gallamine triethiodide on mammalian and amphibian myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol 312:40P-41P
Thompson SH (1977) Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol 265:465–488
Woolum JC, Gorman ALF (1981) Time dependence of the calcium-activated current. Biophys J 36:297–302
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hermann, A., Hartung, K. Properties of a Ca2+ activated K+ conductance in /Helix neurones investigated by intracellular Ca2+ ionophoresis. Pflugers Arch. 393, 248–253 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584078
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584078