Summary
-
1.
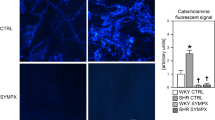
Resting cardiovascular status and the reflex responses to lower body negative pressure (LBNP) were examined in control rabbits and in rabbits sympathectomised with 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA).
-
2.
Resting systemic arterial pressure and total peripheral resistance were significantly higher in control than in 6-OHDA treated animals.
-
3.
Control animals responded to LBNP at −25 mm Hg with a peripheral vasoconstriction and tachycardia. These responses were absent in 6-OHDA-treated animals.
-
4.
Control animals responded to LBNP at −70 mm Hg with a peripheral vasoconstriction and a bradycardia followed by a tachycardia. There was no significant change in heart rate in response to this stimulus in 6-OHDA-treated animals, although a slight vasoconstriction was seen.
-
5.
Bethanidine blocked the tachycardia and vasoconstriction seen in response to LBNP in control and 6-OHDA-treated rabbits. Under these conditions there was no significant difference between the total peripheral resistance of the control and treated animals.
-
6.
The results indicated that neither the maintenance of the resting systemic arterial pressure nor the reflexes elicited by LBNP in control or in chronically sympathectomised rabbits involved hormonal mechanisms, but LBNP was maintained for 1 min only. These findings are discussed in the context of previous observations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aars, H., Akre, S.: Sympathetic nervous response to induced fall and rise of arterial blood pressure in rabbits. Pflügers Arch.326, 223–230 (1971)
Aars, H., Akre, S.: Nervous and humoral control of vascular resistance during acute haemorrhagic hypotension in rabbits. Acta physiol. scand.87, 404–410 (1973)
Bennett, T., Malmfors, T.: Regeneration of the noradrenergic innervation of the cardiovascular system of the chick following treatment with 6-hydroxydopamine. J. Physiol. (Lond.)242, 517–532 (1974)
Chalmers, J. P., Korner, P. I., White, S. W.: The effects of haemorrhage in the unanaesthetised rabbit. J. Physiol. (Lond.)189, 367–391 (1967)
de Champlain, J., van Ameringen, M. R.: Regulation of blood pressure by sympathetic nerve fibres and adrenal medulla in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Circulat. Res.31, 617–628 (1972)
Chien, H.: Role of sympathetic nervous system in haemorrhage. Physiol. Rev.47, 214–288 (1967)
Errington, M. L., Rocha e Silva, M.: On the role of vasopressin and angiotensin in the development of irreversible haemorrhagic shock. J. Physiol. (Lond.)242, 119–142 (1974)
Falck, B., Owman, Ch.: A detailed methodological description of the fluorescence method for cellular demonstration of biogenic amines. Acta. Univ. Lund. II,7, 1–23 (1965)
Gauer, O. H., Henry, J. P.: Circulatory basis of fluid volume control. Physiol. Rev.43, 423–481 (1963)
Gauer, O. H., Henry, J. P., Behn, C.: The regulation of extracellular fluid volume. Ann. Rev. Physiol.32, 547–595 (1970)
Gauthier, P., Nadeau, R., de Champlain, J.: Acute and chronic cardiovascular effects of 6-hydroxydopamine in dogs. Circulat. Res.31, 207–217 (1972)
Greenway, C. V., Stark, R. D.: Vascular response of the spleen to rapid haemorrhage in the anaesthetised cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)204, 169–179 (1969)
Haeusler, G., Haefely, W., Thoenen, H.: Chemical sympathectomy in the cat with 6-hydroxydopamine. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther.170, 50–61 (1969)
Kendrick, E., Öberg, B., Wennergren, G.: Vasoconstrictor fibre discharge to skeletal muscle, kidney, intestine and skin at varying levels of arterial baroreceptor activity in the cat. Acta physiol. scand.85, 464–476 (1972)
Korner, P. I.: Integrative neural cardiovascular control. Physiol. Rev.51, 312–367 (1971)
Korner, P. I., Uther, J. B., White, S. W.: Circulatory effects of chloralose-urethane and sodium pentobarbitone anaesthesia in the rabbit. J. Physiol. (Lond.)199, 253–265 (1968)
Malmfors, T., Thoenen, H.: 6-Hydroxydopamine and catecholamine neurons. Amsterdam: North Holland 1971
Mott, J. C.: Baro- and chemoreceptor mechanisms in haemorrhage. Advanc. exp. Med. Biol.33, 455–461 (1972)
Nadeau, R. A., de Champlain, J., Tremblay, G. M.: Supersensitivity of the isolated rat heart after chemical sympathectomy with 6-hydroxydopamine. Canad. J. Physiol. Pharmacol.49, 36–44 (1971)
Öberg, B., Thorén, P.: Increased activity in left ventricular receptors during haemorrhage or occlusion of caval veins in the cat —a possible cause of the vaso-vagal reaction. Acta physiol. scand.85, 164–173 (1972)
De Quattro, V., Nagatsu, T., Moronde, R., Alexander, N.: Catecholamine synthesis in rabbits with neurogenic hypertension. Circulat. Res.24, 545–555 (1969)
Shibata, S., Kuchii, M., Kurahashi, K.: The supersensitivity of isolated rabbit atria and aortic strips produced by 6-hydroxydopamine. Eur. J. Pharmacol.18, 271–280 (1972)
Thoenen, H., Tranzer, J. P.: Chemical sympathectomy by selective destruction of adrenergic nerve endings with 6-hydroxydopamine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak.261, 271–288 (1968)
Tomlinson, D. R.: Two populations of granular vesicles in constricted postganglionic sympathetic nerves. J. Physiol. (Lond.)245, 727–735 (1975)
Tranzer, J. R., Richards, U. G.: Fine structural aspects of the effects of 6-hydroxydopamine on peripheral adrenergic neurons. In: 6-Hydroxydopamine and catecholamine neurons (T. Malmfors and H. Thoenen, eds.). Amsterdam: North Holland 1971
Ungerstedt, U., Marshall, J.: Nerve degeneration in functional studies: Experiments illustrating the problem of lesion specificity and compensatory supersensitivity. In: Chemical tools in catecholamine research (G. Jonsson, T. Malmfors, and Ch. Sachs, eds.), Vol. I, pp. 311–318. Amsterdam: North Holland 1975
Yates, D., Bennett, T., Fentem, P. H., Tomlinson, D. R.: Cardiovascular responses to lower body negative pressure. (simulated haemorrhage) in anaesthetised rabbits following treatment with 6-hydroxydopamine. In: Chemical tools in catecholamine research (G. Jonsson, T. Malmfors, and Ch. Sachs, eds.), Vol. I, pp. 217–222. Amsterdam: North Holland 1975
Yates, J. M., Fentem, P. H.: The effects of lower body negative pressure on the cardiovascular system of the anaesthetised rabbit. Cardiovasc. Res.9, 190–200 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bennett, T., Fentem, P.H., Tomlinson, D.R. et al. The involvement of noradrenergic nerves in the cardiovascular reflex responses to lower body negative pressure in the anaesthetised rabbit. Pflugers Arch. 365, 89–94 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00583632
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00583632