Summary
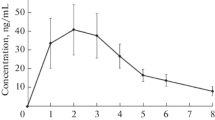
In healthy normal subjects following the administration of labetalol the pharmacological effects were measured and compared with the plasma concentrations achieved. The inhibition of exercise induced tachycardia and inhibition of exercise induced increases in systolic pressure were significantly related to the administered dose of labetalol. Labetalol was rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and peak plasma concentrations occurred two hours after oral administration. There was a linear correlation (r=0.84) between the logarithm of the plasma concentration and the maximum inhibition of exercise tachycardia at two hours. After intravenous administration there was an immediate reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure with a concomitant small increase in heart rate. There was a rapid decline in the associated plasma concentration but the pharmacological effects were maintained in excess of two hours. Our findings are consistent with those of others who have studied the relationship between pharmacological events and plasma concentrations after single doses of other adrenoceptor blocking drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ablad, B., Ervik, M., Hallgren, J., Johnson, G., Solvell, L.: Pharmacological effects and serum levels of orally administered alprenolol in man. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.5, 44–52 (1972)
Hicks, D. C., Arbab, A. G., Turner, P., Hills, M.: A comparison of intravenous pindolol and propranolol in man. J. clin. Pharmacol.12, 212–226 (1972)
Fitzgerald, J. D., Scales, B.: Effects of a new adrenergic beta blocking agent (ICI 50172) on heart rate in relation to its blood levels. Int. J. clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Tox.6, 467–474 (1968)
Brown, R. C., Carruthers, S. G., Kelly, J. G., McDevitt, D. G., Shanks, R. G.: Observations on the efficacy and pharmacokinetics of sotalol after oral administration. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.9, 367–372 (1967)
Faulkner, J. K., Stopher, D. A., Walden, R., Singleton, W., Taylor, S. H.: Pharmacokinetic and pharmacological studies with tolamolol in man. Brit. J. clin. Pharmacol.2, 423–428 (1975)
Prichard, B. N. C., Thompson, F. D., Boakes, A. J., Joekes, A. M.: Some haemodynamic effects of compound AH 5158 compared with propranolol, propranolol plus hydralazine and diazoxide: The use of AH 5158 in the treatment of hypertension. Clin. Sci.48, 97s-100s (1975)
Rosei, E. A., Brown, S. S., Trust, P. M., Lever, A. F., Robertson, J. I. S.: Intravenous labetalol in severe hypertension. Lancet1975 II, 1093
Richards, D. A., Tuckman, J., Prichard, B. N. C.: Assessment of alpha and beta adrenoceptor blocking actions of labetalol. Brit. J. clin. Pharmacol.3, 849–855 (1976)
Richards, D. A., Woodings, E. P., Stephens, M. D. B., Maconochie, J. G.: The effects of oral AH 5158, a combined alpha and beta adrenoceptor antagonist, in healthy volunteers. Brit. J. clin. Pharmacol.1, 505–510 (1974)
Rose, G. A., Holland, W. W., Crawley, E. A.: A sphygmomanometer for epidermiologists. Lancet1964 I, 296–300
Britton, H. T. S., Robinson, R. A.: The use of antimony — antimonous oxide electrode in the determination of the concentration of hydrogen ions and in potentiometric titrations. The Prideaux-Ward universal buffer mixture. J. chem. Soc., 458–473 (1931)
Robinson, B. F., Epstein, S. E., Beiser, G. D., Braunwald, E.: Control of heart rate by the autonomic nervous system: studies in man between baro-receptor mechanisms and exercise. Circulat. Res.19, 400 (1966)
Shand, D. G., Nuckolls, E. M., Oates, J. A.: Plasma propranolol levels in adults with observations in four children. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.11, 112–120 (1970)
Coltart, D. J., Shand, D. G.: Plasma propranolol levels in the quantitative assessment of beta adrenergic blockade in man. Brit. med. J.1970 III, 731
Carruthers, S. G., Kelly, J. G., McDevitt, D. G., Shanks, R. G.: Blood levels of practolol after oral and parenteral administration and their relationship to exercise heart rate. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.15, 497 (1974)
Kumana, C. R., Kaye, C. M.: An investigation of the relationship between beta adrenoceptor blockade and plasma practolol concentration in man. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.7, 243–248 (1974)
Martin, L. E., Hopkins, R., Bland, R.: Metabolism of labetalol by animals and man. Brit. J. clin. Pharmacol.3, 695–710 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richards, D.A., Maconochie, J.G., Bland, R.E. et al. Relationship between plasma concentrations and pharmacological effects of labetalol. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 11, 85–90 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00562897
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00562897