Summary
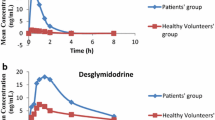
The pharmacokinetics of furosemide was studied in 7 patients with diagnosed liver cirrhosis and in 7 healthy subjects. Furosemide in plasma and ascitic fluid was analyzed spectrofluorometrically. After a single intravenous dose, the cirrhotic patients showed lower initial plasma concentrations of furosemide because of the larger volume of distribution. The mean half-life in cirrhotic patients was significantly greater than in healthy volunteers. The longer half-life was associated with a reduction in the serum clearance of furosemide. Ascitic fluid volume in the patients ranged from 4.6 to 7.71. There was no significant amount of furosemide in the fluid. The diuretic interchange between this fluid and plasma was slow, as peak concentrations ranged from 0.3 to 0.5 µg/ml within 3 to 5 h after bolus administration of furosemide. Diuresis and urinary sodium excretion, 5 h after furosemide injection, were similar in both groups; larger potassium excretion was found in the cirrhotic patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arancibia A, Morales I, Pinto O (1978) Empleo de la computación en la determinación de parámetros farmacocinéticos en un modelo de dos compartimentos. Revista CECOM. Facultad de Medicina, Santiago Norte, Universidad de Chile 4: 17–32
Arroyo V, Rodes J (1975) A rational approach to the treatment of ascites. Postgrad Med J 51 558–562
Beerman B, Dalén E, Lindström B, Rosén A (1975) On the Fate of furosemide in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 9: 57–61
Benet LZ, Greither A, Meister W (1976) Gastrointestinal absorption of drugs in patients with cardiac failure. In: Benet LZ (ed) The effect of disease states on drug pharmacokinetics. APhA, Academy of Pharmaceutical Sciences, American Pharmaceutical Association, Washington DC, pp 44–45
Epstein M, Schneider N, Befeler B (1977) Relationship of systemic and intrarenal haemodynamics in cirrhosis. J Lab Clin Med 89: 1175–1187
Gabuzda GJ (1970) Cirrhosis, ascites and edema. Clinical course related to management. Gastroenterology 58: 546–553
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1975) Pharmacokinetics, Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 48–49
González G, Arancibia A, Marinovic G, Moya JC, Antezana C, Ruiz I (1980) Etude pharmacocinétique du furosémide chez l'homme sain. Thérapie 35: 525–532
Henley LS (1971) Ascites and renal failure in liver disease. Principles of management. Am J Dig Dis 16: 363–367
Kelly MR, Cutler RE, Forrey AW, Kimpel BM (1974) Pharmacokinetics of orally administered furosemide. Clin Pharmacol Ther 15: 178–186
Klotz U, Avant GR, Hoyumpa A, Schenker S, Wilkinson GR (1975) The effects of age and liver diseases on the disposition and elimination of diazepam in adult man. J Clin Invest 55: 347–359
Lancestremere RG, Davidson PL, Earley LE, O'Brien FJ, Papper S (1962) Renal failure in Laennec's cirrhosis. II. — Simultaneous determination of cardiac output and renal hemodynamics. J Clin Invest 41: 1922–1927
Lewis GP, Jusko WJ (1975) Pharmacokinetics of ampicillin in cirrhosis. Clin Pharmacol Ther 18: 475–484
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Naranjo CA, Busto U, Cassis L (1978) Furosemide-induced adverse reactions during hospitalization. Am J Hosp Pharm 35: 794–798
Naranjo CA, Pontigo E, Valdenegro C, González G, Ruiz I, Busto U (1979) Furosemide-induced adverse reactions in cirrhosis of the liver. Clin Pharmacol Ther 25: 154–160
Prandota J, Pruitt AW (1975) Furosemide binding to human albumin and plasma of nephrotic children. Clin Pharmacol Ther 17: 159–166
Rupp W (1974) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of Lasix. Scot Med J 19: 5–13
Shear L, Ching S, Gabuzda GJ (1970) Compartmentalization of ascites and edema in patient with hepatic cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 282: 1391–1396
Sherlock S (1970) Ascites formation and its management. Scand J Gastroenterol 5 (Suppl): 9–15
Sherlock S (1975) Disease of the liver and biliary systems, 5th ed. Blackwell Oxford London Edinburgh Melbourne, pp 142–147
Siersback-Nielsen K, Hansen JM, Kampmann J, Kristensen M (1973) Rapid evaluation of creatinine clearance. Lancet 1: 123–136
Thompson PD, Melmon KL, Richardson JA, Cohn K, Steinbrunn W, Cudiher R, Rowland M (1973) Lidocaine pharmacokinetics in advanced heart failure, liver disease and renal failure in humans. Ann Intern Med 78: 499–508
Wagner JC (1975) Fundamentals of clinical pharmacokinetics. Drug Intelligence Publishing, Hamilton, IL, pp 82–90
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
González, G., Arancibia, A., Rivas, M.I. et al. Pharmacokinetics of furosemide in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 22, 315–320 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00548399
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00548399