Summary
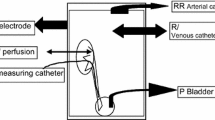
The effects of indomethacin on changes in renal blood flow induced by adenosine, NECA (adenosine-5′-N-ethyl-carboxamide) and 2′,3′-dinitro-NECA were investigated in 6 chronically instrumented conscious dogs. Adenosine (187.5, 375 and 750 nmol/kg, i.v.) induced a dose-dependent initial decrease, followed by a reactive increase in renal blood flow. NECA (1.5 nmol/kg, i.v.) also induced an initial decrease, which was, however, followed by a prolonged reactive increase in renal blood fow. 2′,3′-dinitro-NECA (50 nmol/kg, orally) induced only an increase in renal blood flow. Indomethacin (27.9 μmol/kg, i.v.) caused no relevant change of the initial decrease and a significant attenuation of the reactive increase in renal blood flow induced by adenosine. NECA-induced changes in blood flow were affected by indomethacin in the same direction but to a greater extent than were adenosine-induced changes in blood flow. Indomethacin reversed the increase to a decrease in renal blood flow induced by 2′,3′-dinitro-NECA. Thus, prostaglandins seem to be involved in mediating the response of renal blood flow to adenosine, NECA and 2′,3′-dinitro-NECA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiken JW, Vane JR (1973) Intrarenal prostaglandin release attenuates the renal vasoconstrictor activity of angiotensin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 184:678–687
Baer PG (1981) The contribution of prostaglandins to renal blood flow maintenance is determined by the level of activity of the renin-angiotensin system. Life Sci 28:587–593
Ellis P, Ungar A (1982) Effects of indomethacin on blood pressure, catecholamine release and adrenal blood flow in the anaesthetized, laparatomized dog. Br J Pharmacol 74:824P-825P
Faloona GR, Unger RH (1974) Radioimmunoassay of glucagon. In: Jaffe BM, Behrmannn HR (eds) Methods of hormone radioimmunoassay. Academic Press, New York London
Haas JA, Osswald H (1981) Adenosine induced fall in glomerular capillary pressure. Effect of ureteral obstruction and aortic constriction in the Munich-Wistar rat kidney. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 317:86–89
Hashimoto K, Kumakura S (1965) The pharmacological features of the coronary, renal mesenteric and femoral arteries. Jpn J Physiol 15:540–551
Herbaczynska-Cedro K, Vane JR (1974) Prostaglandins as mediators of reactive hyperaemia in kidney. Nature 247:492
Hinshaw LB, Page BB, Brake CM, Emerson TE Jr (1963) Mechanisms of intrarenal hemodynamic changes following acute arterial occlusion. Am J Physiol 205:1033–1041
Honda N, Aizawa C, Yoshitoshi Y (1968) Postocclusive reactive hyperemia in the rabbit kidney. Am J Physiol 215:190–196
Osswald H (1975) Renal effects of adenosine and their inhibition by theophylline in dogs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 288:79–86
Osswald H, Schmitz H-J, Heidenreich O (1975) Adenosine response of the rat kidney after saline loading, sodium restriction and hemorrhagia. Pflügers Arch 357:323–333
Osswald H, Schmitz HJ, Kemper R (1978a) Renal action of adenosine: effect of renin secretion in the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 303:95–99
Osswald H, Spielman WS, Knox FG (1978b) Mechanism of adenosine-mediated decreases in glomerular filtration rate of dogs. Circ Res 43:465–469
Owen T, Ehrhart IC, Weidner WJ, Scott JB, Haddy FJ (1975) Effects of indomethacin on local blood flow regulation in canine heart and kidney (38916). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 149:871–876
Satoh S, Ohyama Y, Hayashi M (1981) Effects of renal nerve stimulation, norepinephrine and angiotensin II on renal blood flow in relation to release of PG-like substances in anesthetized dogs. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 254:304–316
Schütz W, Raberger G, Kraupp O (1978) Evidence for glucagonreleasing activity of vasoactive adenosine analogues in the conscious dog. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 304: 249–254
Spielman WS, Osswald H (1978) Characterization of the postocclusive response of renal blood flow in the rat. Am J Physiol 235:F286-F290
Swain JA, Heyndrickx GR, Boettcher DH, Vatner SF (1975) Prostaglandin control of renal circulation in the unanesthetized dog and baboon. Am J Physiol 229:826–830
Tagawa H, Vander AJ (1970) Effects of adenosine compounds on renal function and renin secretion in dogs. Circ Res 26:327–332
Thurau K (1964) Renal hemodynamics. Am J Med 36:698–719
Vatner SF (1974) Effects of hemorrhage on regional blood flow distribution in dogs and primates. J Clin Invest 54:225–235
Wiener H, Krivanek P, Kolassa N (1983) Metabolism and disposition of 2′,3′-Di-O-nitro-adenosine-5′-(N-ethylcarboxamide) in dogs. Biochem Pharmacol 32:1899–1906
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beck, A., Seitelberger, R. & Raberger, G. Effects of indomethacin on changes in renal blood flow induced by adenosine and its analogues in conscious dogs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 326, 75–79 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00518782
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00518782