Summary
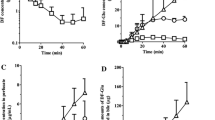
The metabolism of 3α-[(10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo-[a,d]cyclohepten-5-yl)oxy]-8-methyltropanium iodide (deptropine methiodide; N-methyldeptropine), a potential agent for the treatment of peptic ulcers and gastrointestinal spasms, was studied by passing the N-14CH3-labelled compound through the isolated perfused rat liver. The substance was rapidly taken up by the liver. This process followed first-order kinetics with a half-life of 5 min. It was calculated that 94% of the drug was removed by the liver during one passage. About 70% of the initial radioactivity was excreted in the bile during a perfusion period of 2 h. This elimination process exhibited first-order kinetics with a half-life of about 25 min.
N-Methyldeptropine was found to be broken down in the liver into N-methyltropine, and a non radioactive fragment. N-methyltropine and N-methyldeptropine were eliminated in the bile. The former also diffused back into the perfusion fluid. In addition, the bile contained an uncharacterised radioactive product related to N-methyltropine, possibly a complex of N-methyltropine with bile components.
Both the rapid uptake of N-methyldeptropine in the liver and the biotransformation into products with a much lower pharmacological and toxicological potency, should lessen the likelihood of side effects outside the gastrointestinal tract after oral dosage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray, G. A.: A simple efficient liquid scintillator for the counting of aqueous solutions in a liquid scintillation counter. Analyt. Biochem. 1, 279–287 (1960).
Hespe, W., de Roos, A. M., Nauta, W. Th.: Aspects of the metabolic fate of deptropine citrate. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 164, 397–411 (1966).
Hespe, W., Prins, H.: A comparative autoradiographic study on the distribution of deptropine citrate and deptropine methiodide in mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 18, 53–57 (1969).
Kalser, S. H., Kelvington, E. J., Randolph, M. M., Santomenna, D. M.: Drug metabolism in hypothermia, II. C14-atropine uptake metabolism and excretion by the isolated perfused rat liver. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 147, 260–269 (1964).
McMahon, R. E., Culp, H. W., Mills, J., Marshall, F. J.: Demethylation studies. IV. The in vitro and in vivo cleavage of alkyl- and arylalkyl-p-nitrophenyl ethers J. med. Chem. 6, 343–346 (1963).
Meijer, D. K. F., Arends, J. W., Weitering, J. G.: The cardiac glycoside sensitive step in the hepatic transport of the bis quaternary Ammonium compound, Hexafluorenium. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 15, 245–251 (1971).
Meijer, D. K. F., Bos, E. S., van der Laan, K. J.: Hepatic transport of mono and bisquaternary ammonium compounds. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 11, 371–377 (1970).
Meijer, D. K. F., Scaf, A. H. J.: Inhibition of the transport of d-tubocurarine from blood to bile by k-strophantoside in the isolated perfused rat liver. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 4, 343–346 (1968).
Meijer, D. K. F., Weitering, J. G.: Curare-like agents: Relation between lipid solubility and transport into bile in perfused rat liver. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 10, 283–289 (1970).
Millburn, P., Smith, R. L., Williams, R. T.: Biliary excretion of foreign compounds, biphenyl, stilboestrol and phenolphthalein in the rat: molcular weight, polarity and metabolism as factors in biliary excretion. Biochem. J. 105, 1275–1281 (1967).
Roos, A. M. de: Investigation into the stability of the ether bond in a series of benzhydryl ethers. Part V. The rate of hydrolysis of tricyclic analogues of benzhydryl ethers. Pharm. Weekblad 102, 851–855 (1967).
Schanker, L. S.: Hepatic transport of organic cations. The biliary system, pp. 469–480. Oxford: Blackwell Sci. Publ. 1965.
Schanker, L. S., Solomon, H. M.: Active transport of quaternary ammonium compounds into bile. Amer. J. Physiol. 204, 829–832 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Deptropine methiodide will be referred to as MDT.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lavy, U.I., Hespe, W. & Meijer, D.K.F. Uptake and excretion of the quaternary ammonium compound deptropine methiodide in the isolated perfused rat liver. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 275, 183–192 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00508906
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00508906