Summary
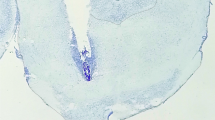
Systemic administrations of opioids are known to induce “catatonia” or “lead pipe rigidity” in rats. The relevance of the caudate nucleus in inducing rigidity was tested. For this purpose, several opioids (or saline) were injected into the head of the caudate nucleus (“intrastriatal” injection) through an implanted cannula, and the electromyographical activity (EMG) was recorded in the gastrocnemius-soleus muscle (GS). Morphine (7.5–30 μg), injected unilaterally, induced a continuous EMG activity in the ipsilateral GS muscle. This effect could be antagonized by systemic administration of naloxone (1 or 2 mg/kg i.p.). D-ala2-met5-enkephalinamide (3 μg) and levorphanol (22.5 μg) induced an EMG activity, too, whereas an equimolar dose of dextrorphan was ineffective, indicating that this effect was stereospecific and mediated via opioid receptors in the caudate nucleus. The EMG activity observed after systemic morphine administration (15 mg/kg i.p.) was antagonized by intrastriatal injection of naloxone (5 μg). From our results, it can be concluded that the striatum — at least the head of the caudate nucleus — plays an important role in mediating the rigidity observed after systemic administration of morphine and other opioids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andén, N.-E., Johnels, B.: Effect of local application of apomorphine to the striatum and to the nucleus accumbens on the reserpine-induced rigidity in rats. Brain Res. 133, 386–398 (1977)
Atweh, S. F., Kuhar, M. J.: Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. III. The telencephalon. Brain Res. 134, 393–405 (1977).
Barbeau, A.: Biology of the striatum. In: Biology of brain dysfunction, Vol. 2, (G. E. Gall, ed.), pp. 333–350. New York: Plenum Press 1973
Bloom, F., Segal, D., Ling, N., Guillemin, R.: Endorphins: Profound behavioral effects in rats suggest new etiological factors in mental illness. Science 194, 630–632 (1976)
Carenzi, A., Frigeni, V., Della Bella, D.: Synaptic localization of opiate receptors in rat striatum. In: Advances in biochemical psychopharmacology, Vol. 18 (E. Costa and M. Trabucchi, eds.), pp. 265–270. New York: Raven Press 1978
Celsen, B., Kuschinsky, K.: Effects of morphine on kinetics of 14C-dopamine in rat striatal slices. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 284, 159–165 (1974)
Childers, S. R., Schwarcz, R., Coyle, J. T., Snyder, S. H.: Radioimmunoassay of enkephalins: Levels of methione- and leucine-enkephalin in morphine-dependent and kainic acid-lesioned rat brains. In: Advances in biochemical psychopharmacology, Vol. 18 (E. Costa and M. Trabucchi, eds.), pp. 161–173. New York: Raven Press 1978
Costall, B., Fortune, D. H., Naylor, R. J.: Involvement of mesolimbic and extrapyramidal nuclei in the motor depressant action of narcotic drugs. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 30, 566–572 (1978)
De Wied, D., Kovács, G. L., Bohus, B., van Ree, J. M., Greven, H. M.: Neuroleptic activity of the neuropeptide β-LPH62-77 (Des-tyr1-endorphin; DTE). Eur. J. Pharmacol. 49, 427–436 (1978)
Di Chiara, G., Gessa, G. L.: Ipsiversive-cataleptogenic neurons of nigra pars reticulata: out-put pathways of striatal dopaminergic responses. In: Advances in pharmacology and therapeutics, Vol. 5: Neuropsychopharmacology (C. Dumont, ed.), pp. 219–229. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1979
Di Chiara, G., Vargin, L., Porceddu, M. L., Longoni, R., Mulas, A., Gessa, G. L.: Indirect activation of the DA system as a possible mechanism for the stimulatory effects of narcotic analgesics. In: Advances in biochemical psychopharmacology, Vol. 16 (E. Costa and G. L. Gessa, eds.), pp. 571–575. New York: Raven Press 1977
Di Chiara, G., Porceddu, M. L., Morelli, M., Mulas, M. L., Gessa, G. L.: Evidence for a gabaergic projection from the substantia nigra to the ventromedial thalamus and to the superior colliculus of the rat. Brain Res. 176, 273–284 (1979)
Fifková, E., Maršala, J.: Stereotaxic atlases for the cat, rabbit and rat. In: Electrophysiological methods in biological research (J. Bureš, M. Petran and J. Zachar, eds.). New York and London: Academic Press 1967
Fonnum, F., Walaas, I.: Localization of neurotransmitter candidates in neostriatum. In: The neostriatum (I. Divac and R. G. E. Öberg, eds.), pp. 53–69. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1979
Gayton, R. J., Bradley, P. B.: Comparison of the effects of morphine and related substances with those of dopamine on single neurones in the rat caudate nucleus. In: Opiates and endogenous opioid peptides (H. W. Kosterlitz, ed.), pp. 213–216. Amsterdam: North Holland Publishing Company 1976
Havemann, U., Winkler, M., Genc, E., Kuschinsky, K.: Opioid actions on motility: Possible actions on GABA-ergic and dopaminergic neurons. Brain Res. Bull. 5 Suppl. 2 (in press 1980)
Iwatsubo, K., Kondo, Y.: Inhibitory effect of morphine on the release of preloaded 3H-GABA from rat substantia nigra in response to the stimulation of caudate nucleus and globus pallidus. In: Characteristics and functions of opioids (J. M. van Ree and L. Terenius, eds.), pp. 357–358. Amsterdam: Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press 1978
Kuschinsky, K., Hornykiewicz, O.: Morphine catalepsy in the rat: relation to striatal dopamine metabolism. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 19, 119–122 (1972)
Mavrojannis, M.: L'action cataleptique de la morphine chez les rats. Contribution à la théorie toxique de la catalepsie. Société de Biologie, Comptes Rendus 55, 1092–1094 (1903)
Moroni, F., Cheney, D. L., Peralta, E., Costa, E.: Opiate receptor agonists as modulators of γ-aminobutyric acid turnover in the nucleus caudatus, globus pallidus and substantia nigra of the rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 207, 870–877 (1978)
Moroni, F., Peralta, E., Cheney, D. L., Costa, E.: Regulation of gammaaminobutyric acid neurons in caudatus, pallidus and nigra-effects of opioids and dopamine agonists. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 208, 190–194 (1979)
Pert, A.: Central sites involved in opiate actions. In: The bases of addiction (J. Fishman, ed.), pp. 299–332. Berlin: Dahlem Konferenzen 1978
Pert, A., De Wald, L. A., Liao, H., Sivit, C.: Effects of opiates and opioid peptides on motor behaviors: sites and mechanisms of action: In: Endorphins in mental health research (E. Usdin, W. E. Bunney, Jr., and N. S. Kline, eds.), pp. 45–61. London: Macmillan 1979
Pollard, H., Llorens-Cortes, C., Schwartz, J. C.: Enkephalin receptors on dopaminergic neurons in rat striatum. Nature (Lond.) 268, 745–747 (1977)
Schwartz, J. C., Pollard, H., Llorens, C., Malfroy, B., Cros, C., Pradelles, P., Dray, F.: Endorphins and endorphin receptors in striatum: relationships with dopaminergic neurons. In: Advances in biochemical psychopharmacology, Vol. 18 (E. Costa and M. Trabucchi, eds.), pp. 245–264. New York: Raven Press 1978
Wand, P., Kuschinsky, K., Sontag, K.-H.: Morphine-induced muscular rigidity in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 24, 189–193 (1973)
Wilcox, R. E., Levitt, R. A.: Naloxone reversal of morphine catatonia: Role of caudate nucleus and periaqueductal gray. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 9, 425–428 (1978)
Zieglgänsberger, W., Fry, J. P.: Actions of enkephalin on cortical and striatal neurones of naive and morphine tolerant/dependent rats. In: Opiates and endogenous opioid peptides (H. W. Kosterlitz, ed.), pp. 231–238. Amsterdam: North Holland Publishing Company 1976
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
with technical assistance of Ch. Bode and H. Kügler
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Havemann, U., Winkler, M. & Kuschinsky, K. Opioid receptors in the caudate nucleus can mediate EMG-recorded rigidity in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 313, 139–144 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498570
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498570