Abstract
Background
Short-term treatment with non-peptide agonists of delta-opioid receptors, such as agonist SNC80, induced behavioral effects in rodents, which could be modulated via changes in central neurotransmission. The present experiments aimed at testing the hypothesis that chronic treatment with SNC80 induces anxiolytic effects associated with changes in hippocampal glutamate and brainstem monoamine pathways.
Methods
Adult male Wistar rats were used in experiments. Rats were treated with SNC80 (3 mg/kg/day) for fourteen days. Neuronal excitability was assessed using extracellular in vivo single-unit electrophysiology. The behavioral parameters were examined using the elevated plus maze and open field tests.
Results
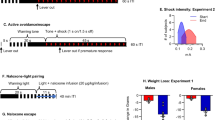
Chronic SNC80 treatment increased the excitability of hippocampal glutamate and ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons and had no effect on the firing activity of dorsal raphe nucleus serotonin cells. Chronic SNC80 treatment induced anxiolytic effects, which were, however, confounded by increased locomotor activity clearly confirmed in an open field test. The ability to cope with stressful situations and habituation processes in a novel environment was not influenced by chronic treatment with SNC80.
Conclusion
Our study suggests that the psychoactive effects of SNC80 might be explained by its ability to stimulate hippocampal glutamate and mesolimbic dopamine transmission.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Original experimental data are available upon request.
Abbreviations
- SNC80:
-
( +)-4-[(Alpha R)-alpha-((2S,5R)-4-allyl-2,5-dimethyl-1-piperazinyl)-3-methoxybenzyl]-N,N-diethyl-benzamide
- DPDPE:
-
(D-Pen2,5)-enkephalin
- RM ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance for repeated measures
- CA1/3:
-
Cornu Ammonis 1/3
- DOR:
-
Delta-opioid receptor
- DRN:
-
Dorsal raphe nucleus
- EPM:
-
Elevated plus maze
- HD:
-
Head dipping
- HCl:
-
Hydrochloric acid
- 5-HT:
-
Serotonin
- NaCl:
-
Sodium chloride
- NaOH:
-
Sodium hydroxide
- SAP:
-
Stretch attend postures
- VTA:
-
Ventral tegmental area
References
Veening JG, Gerrits PO, Barendregt HP. Volume transmission of beta-endorphin via the cerebrospinal fluid; a review. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2012;9:16.
Bodnar RJ. Endogenous opiates and behavior: 2016. Peptides. 2018;101:167–212.
Chu Sin Chung P, Kieffer BL. Delta opioid receptors in brain function and diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2013;140:112–20.
Calderon SN, Rothman RB, Porreca F, Flippen-Anderson JL, McNutt RW, Xu H, et al. Probes for narcotic receptor mediated phenomena. 19. Synthesis of (+)-4-[(alpha R)-alpha-((2S,5R)-4-allyl-2,5-dimethyl-1-piperazinyl)-3- methoxybenzyl]-N,N-diethylbenzamide (SNC 80): a highly selective, nonpeptide delta opioid receptor agonist. J Med Chem. 1994;37:2125–8.
Saitoh A, Kimura Y, Suzuki T, Kawai K, Nagase H, Kamei J. Potential anxiolytic and antidepressant-like activities of SNC80, a selective delta-opioid agonist, in behavioral models in rodents. J Pharmacol Sci. 2004;95:374–80.
Saitoh A, Yoshikawa Y, Onodera K, Kamei J. Role of delta-opioid receptor subtypes in anxiety-related behaviors in the elevated plus-maze in rats. Psychopharmacology. 2005;182:327–34.
Jutkiewicz EM, Rice KC, Woods JH, Winsauer PJ. Effects of the delta-opioid receptor agonist SNC80 on learning relative to its antidepressant-like effects in rats. Behav Pharmacol. 2003;14:509–16.
Jutkiewicz EM, Rice KC, Traynor JR, Woods JH. Separation of the convulsions and antidepressant-like effects produced by the delta-opioid agonist SNC80 in rats. Psychopharmacology. 2005;182:588–96.
Saitoh A, Yamada M, Yamada M, Takahashi K, Yamaguchi K, Murasawa H, et al. Antidepressant-like effects of the delta-opioid receptor agonist SNC80 ([(+)-4-[(alphaR)-alpha-[(2S,5R)-2,5-dimethyl-4-(2-propenyl)-1-piperazinyl]-(3-me thoxyphenyl)methyl]-N, N-diethylbenzamide) in an olfactory bulbectomized rat model. Brain Res. 2008;1208:160–9.
Moravcikova L, Moravcik R, Jezova D, Lacinova L, Dremencov E. Delta-opioid receptor-mediated modulation of excitability of individual hippocampal neurons: mechanisms involved. Pharmacol Rep. 2021;73:85–101.
Hlavacova N, Li Y, Pehrson A, Sanchez C, Bermudez I, Csanova A, et al. Effects of vortioxetine on biomarkers associated with glutamatergic activity in an SSRI insensitive model of depression in female rats. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2018;82:332–8.
Sakamoto K, Yamada D, Yamanaka N, Nishida M, Iio K, Nagase H, et al. A selective delta opioid receptor agonist SNC80, but not KNT-127, induced tremor-like behaviors via hippocampal glutamatergic system in mice. Brain Res. 2021;1757: 147297.
Dremencov E, Gur E, Lerer B, Newman ME. Effects of chronic antidepressants and electroconvulsive shock on serotonergic neurotransmission in the rat hippocampus. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2003;27:729–39.
Grinchii D, Dremencov E. Mechanism of action of atypical antipsychotic drugs in mood disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:9532.
Douma EH, de Kloet ER. Stress-induced plasticity and functioning of ventral tegmental dopamine neurons. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020;108:48–77.
Bosse KE, Jutkiewicz EM, Gnegy ME, Traynor JR. The selective delta opioid agonist SNC80 enhances amphetamine-mediated efflux of dopamine from rat striatum. Neuropharmacology. 2008;55:755–62.
Homberg JR, Adan RAH, Alenina N, Asiminas A, Bader M, Beckers T, et al. The continued need for animals to advance brain research. Neuron. 2021;109:2374–9.
Koprdova R, Csatlosova K, Durisova B, Bogi E, Majekova M, Dremencov E, et al. Electrophysiology and behavioral assessment of the new molecule SMe1EC2M3 as a representative of the future class of triple reuptake inhibitors. Molecules. 2019;24:4218.
Dremencov E, Csatlosova K, Durisova B, Moravcikova L, Lacinova L, Jezova D. Effect of physical exercise and acute escitalopram on the excitability of brain monoamine neurons: in vivo electrophysiological study in rats. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017;20:585–92.
Dremencov E, Lacinova L, Flik G, Folgering JHA, Cremers T, Westerink BHC. Purinergic regulation of brain catecholamine neurotransmission: in vivo electrophysiology and microdialysis study in rats. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2017;36:431–41.
Csatlosova K, Bogi E, Durisova B, Grinchii D, Paliokha R, Moravcikova L, et al. Maternal immune activation in rats attenuates the excitability of monoamine-secreting neurons in adult offspring in a sex-specific way. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021;43:82–91.
Grinchii D, Paliokha R, Tseilikman V, Dremencov E. Inhibition of cytochrome P450 by proadifen diminishes the excitability of brain serotonin neurons in rats. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2018;37:711–3.
Paxinos G, Watson C. Paxino's and Watson's The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 7th ed. Amsterdam; Boston: Elsevier/AP, Academic Press is an imprint of Elsevier; 2014.
El Mansari M, Ebrahimzadeh M, Hamati R, Iro CM, Farkas B, Kiss B, et al. Long-term administration of cariprazine increases locus coeruleus noradrenergic neurons activity and serotonin(1A) receptor neurotransmission in the hippocampus. J Psychopharmacol. 2020;34:1143–54.
Kandel ER, Spencer WA. Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons. II. After-potentials and repetitive firing. J Neurophysiol. 1961;24:243–59.
Vandermaelen CP, Aghajanian GK. Electrophysiological and pharmacological characterization of serotonergic dorsal raphe neurons recorded extracellularly and intracellularly in rat brain slices. Brain Res. 1983;289:109–19.
Grace AA, Bunney BS. Intracellular and extracellular electrophysiology of nigral dopaminergic neurons–1. Identification and characterization. Neuroscience. 1983;10:301–15.
Adeniyi PA, Shrestha A, Ogundele OM. Distribution of VTA glutamate and dopamine terminals, and their significance in CA1 neural network activity. Neuroscience. 2020;446:171–98.
Hajós M, Allers KA, Jennings K, Sharp T, Charette G, Sík A, et al. Neurochemical identification of stereotypic burst-firing neurons in the rat dorsal raphe nucleus using juxtacellular labelling methods. Eur J Neurosci. 2007;25:119–26.
Grace A, Bunney B. The control of firing pattern in nigral dopamine neurons: burst firing. J Neurosci. 1984;4:2877–90.
Dawe GS, Huff KD, Vandergriff JL, Sharp T, O’Neill MJ, Rasmussen K. Olanzapine activates the rat locus coeruleus: in vivo electrophysiology and c-Fos immunoreactivity. Biol Psychiat. 2001;50:510–20.
Karailiev P, Hlavacova N, Chmelova M, Homer NZM, Jezova D. Tight junction proteins in the small intestine and prefrontal cortex of female rats exposed to stress of chronic isolation starting early in life. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021;33:e14084.
Hlavacova N, Bakos J, Jezova D. Eplerenone, a selective mineralocorticoid receptor blocker, exerts anxiolytic effects accompanied by changes in stress hormone release. J Psychopharmacol. 2010;24:779–86.
Dubovický M, Skultétyová I, Jezová D. Neonatal stress alters habituation of exploratory behavior in adult male but not female rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1999;64:681–6.
Dubovicky M, Jezova D. Effect of chronic emotional stress on habituation processes in open field in adult rats. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2004;1018:199–206.
Tao R, Auerbach SB. Opioid receptor subtypes differentially modulate serotonin efflux in the rat central nervous system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002;303:549–56.
Wozny C, Maier N, Fidzinski P, Breustedt J, Behr J, Schmitz D. Differential cAMP signaling at hippocampal output synapses. J Neurosci. 2008;28:14358–62.
Easter A, Sharp TH, Valentin JP, Pollard CE. Pharmacological validation of a semi-automated in vitro hippocampal brain slice assay for assessment of seizure liability. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2007;56:223–33.
Watson GB, Lanthorn TH. Electrophysiological actions of delta opioids in CA1 of the rat hippocampal slice are mediated by one delta receptor subtype. Brain Res. 1993;601:129–35.
Chung PC, Boehrer A, Stephan A, Matifas A, Scherrer G, Darcq E, et al. Delta opioid receptors expressed in forebrain GABAergic neurons are responsible for SNC80-induced seizures. Behav Brain Res. 2015;278:429–34.
Bausch SB, Garland JP, Yamada J. The delta opioid receptor agonist, SNC80, has complex, dose-dependent effects on pilocarpine-induced seizures in Sprague-Dawley rats. Brain Res. 2005;1045:38–44.
Devine DP, Leone P, Carlezon WA, Wise RA. Ventral mesencephalic ∂ opioid receptors are involved in modulation of basal mesolimbic dopamine neurotransmission: an anatomical localization study. Brain Res. 1993;622:348–52.
Perrine SA, Hoshaw BA, Unterwald EM. Delta opioid receptor ligands modulate anxiety-like behaviors in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 2006;147:864–72.
Vergura R, Balboni G, Spagnolo B, Gavioli E, Lambert DG, McDonald J, et al. Anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like activities of H-Dmt-Tic-NH-CH(CH2-COOH)-Bid (UFP-512), a novel selective delta opioid receptor agonist. Peptides. 2008;29:93–103.
Hudzik TJ, Maciag C, Smith MA, Caccese R, Pietras MR, Bui KH, et al. Preclinical pharmacology of AZD2327: a highly selective agonist of the δ-opioid receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011;338:195–204.
Solati J, Zarrindast MR, Salari AA. Dorsal hippocampal opioidergic system modulates anxiety-like behaviors in adult male Wistar rats. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2010;64:634–41.
Randall-Thompson JF, Pescatore KA, Unterwald EM. A role for delta opioid receptors in the central nucleus of the amygdala in anxiety-like behaviors. Psychopharmacology. 2010;212:585–95.
Jutkiewicz EM, Baladi MG, Folk JE, Rice KC, Woods JH. The delta-opioid receptor agonist SNC80 [(+)-4-[alpha(R)-alpha-[(2S,5R)-4-allyl-2,5-dimethyl-1-piperazinyl]-(3-methoxybenzyl)-N, N-diethylbenzamide] synergistically enhances the locomotor-activating effects of some psychomotor stimulants, but not direct dopamine agonists, in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;324:714–24.
Nozaki C, Le Bourdonnec B, Reiss D, Windh RT, Little PJ, Dolle RE, et al. δ-Opioid mechanisms for ADL5747 and ADL5859 effects in mice: analgesia, locomotion, and receptor internalization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012;342:799–807.
Jutkiewicz EM, Kaminsky ST, Rice KC, Traynor JR, Woods JH. Differential behavioral tolerance to the delta-opioid agonist SNC80 ([(+)-4-[(alphaR)-alpha-[(2S,5R)-2,5-dimethyl-4-(2-propenyl)-1-piperazinyl]-(3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-N, N-diethylbenzamide) in Sprague-Dawley rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005;315:414–22.
Pradhan AA, Walwyn W, Nozaki C, Filliol D, Erbs E, Matifas A, et al. Ligand-directed trafficking of the δ-opioid receptor in vivo: two paths toward analgesic tolerance. J Neurosci. 2010;30:16459–68.
Vicente-Sanchez A, Dripps IJ, Tipton AF, Akbari H, Akbari A, Jutkiewicz EM, et al. Tolerance to high-internalizing δ opioid receptor agonist is critically mediated by arrestin 2. Br J Pharmacol. 2018;175:3050–9.
Pham TH, Gardier AM. Fast-acting antidepressant activity of ketamine: highlights on brain serotonin, glutamate, and GABA neurotransmission in preclinical studies. Pharmacol Ther. 2019;199:58–90.
Zafiri D, Duvarci S. Dopaminergic circuits underlying associative aversive learning. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022;16:1041929.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Scientific Grant Agency of the Ministry of Education of the Slovak Republic and Slovak Academy of Sciences (grant No 2/0057/22; ED) Slovak Research and Development Agency (APVV-18-0283; DJ and partly APVV-19-0435; LL and APVV-20-0202; ED) and the Neuron Era Net UNMET project (NEURON-051; DJ). The funding agencies had no further role in study design; in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to submit the manuscript for publication. The authors thank Dr Michal Dubovický for his valuable advice with respect to the measurements of habituation processes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ED, LL, and DJ planned the study and formulated the working hypothesis. DG, ZR, and PC conducted the experiments. ED, DG, ZR, and PC analyzed the results. ED, ZR, and DJ wrote the manuscript. All authors critically proofread the manuscript and approved it for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
Experiments with Animals: All experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Health and Animal Welfare Division of the State Veterinary and Food Administration of the Slovak Republic (Permit number Ro 3592/15-221) and confirmed to the Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Protection of Animals Used for Scientific Purposes.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dremencov, E., Grinchii, D., Romanova, Z. et al. Effects of chronic delta-opioid receptor agonist on the excitability of hippocampal glutamate and brainstem monoamine neurons, anxiety, locomotion, and habituation in rats. Pharmacol. Rep 75, 585–595 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-023-00485-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-023-00485-1