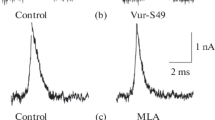
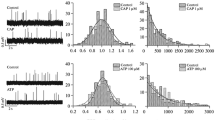
Summary
In the isolated nerve-muscle preparation of the cat nictitating membrane exposure to 0.04 μM of the scorpion venom tityustoxin (TsTX) increased significantly the overflow of 3H-noradrenaline and the responses elicited by postganglionic nerve stimulation (1200 pulses, 0.5 ms duration, supramaximal voltage). Concentration effect curves to exogenous (-)-noradrenaline were not affected in the presence of this concentration of TsTX.
The enhanced release of 3H-noradrenaline obtained during nerve stimulation as well as the increase of the postsynaptic responses observed during exposure to TsTX were more pronounced at 4 Hz than at 20 Hz. The increase in the overflow of noradrenaline observed with the toxin was selective for nerve stimulation since the release evoked by tyramine was not affected by TsTX.
TsTX did not increase further the enhancement of 3H-noradrenaline release obtained in the presence of 18 mM tetraethylammonium (TEA). On the other hand, both TsTX and TEA were able to increase further the overflow of 3H-noradrenaline after block of the presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors with phenoxybenzamine 0.29 or 2.9 μM.
In slices of rat cerebral cortex, TsTX 0.04 μM increased 3H-noradrenaline release induced by 10 mM and by 20 mM KCl. The increased release evoked by the toxin was more pronounced for the lower concentration of K+.
An increased release of 3H-noradrenaline in the presence of the toxin was also observed in rat hypothalamic slices stimulated with 20 mM K+. The K+ stimulated induced release of 3H-noradrenaline was also increased by 1.8 mM TEA. As shown for the peripheral nervous, system the simultaneous addition of TEA and TsTX did not result in additive effects when compared with the effects of the two agents added separately. Tityustoxin did not modify the metabolic pattern of the neurotransmitter released by K+ from rat hypothalamic slices.
It is concluded that TsTX increases the stimulation-induced release of 3H-noradrenaline from both peripheral and central noradrenergic nerve terminals. Tityustoxin appears to act on the nerve terminal by a mechanism similar to that of TEA, an agent known to enhance the amount of noradrenaline released by nerve stimulation by increasing the duration of the action potentials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler-Graschinsky, E., Langer, S. Z., Rubio, M. C.: Metabolism of norepinephrine released by phenoxybenzamine in isolated guinea-pig atria. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 180, 286–301 (1972)
Blaustein, M. P.: Effects of potassium, veratridine and scorpion venom on calcium accumulation and transmitter release by nerve terminals in vitro. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 247, 617–655 (1975)
Chubb, I. W., De Potter, W. P., De Schaepdryver, A. F.: Tyramine does not release noradrenaline from splenic nerves by exocytosis. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 274, 281–286 (1972)
Coutinho Netto, J., Diniz, C. R.: Properties of Tityustoxin obtained by a new method of purification. An. Acad. Bras. Cien. 46, 698 (1974)
Enero, M. A., Langer, S. Z.: Influence of reserpine induced depletion of noradrenaline on the negative feed-back mechanism for transmitter release during nerve stimulation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 49, 214–225 (1973)
Enero, M. A., Langer, S. Z., Rothlin, R. P., Stefano, F. J. E.: Role of the α-adrenoceptor in regulating noradrenaline overflow by nerve stimulation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 44, 672–688 (1972)
Farah, M. B., Alder-Graschinsky, E., Langer, S. Z.: Possible physiological significance of the initial step in the catabolism of noradrenaline in the central nervous system of the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 297, 119–131 (1977)
Gomez, M. V., Diniz, C. R.: Separation of toxic components from Brazilian Scorpion Tityus Serrulatus venom. Mem. Inst. Butantan 33, 899 (1966)
Graefe, K. H., Stefano, F. J. E., Langer, S. Z.: Preferential metabolism of (-)-3H-norepinephrine through the deaminated glycol in the rat vas deferens. Biochem. Pharmacol. 22, 1147–1160 (1973)
Hedqvist, P.: Further evidence that prostaglandins inhibit the release of noradrenaline from adrenergic nerve terminals by restriction of availability of calcium. Br. J. Pharmacol. 58, 599–603 (1976)
Hubbard, J. I.: Mechanism of transmitter release. Progr Biophys. Mol. Biol. 21, 33–124 (1970)
Katz, B., Miledi, R.: The release of acetylcholine from nerve endings by graded electric pulses. Proc. R. Soc. (Biol.) 167, 23–28 (1967a)
Katz, B., Miledi, R.: A study of synaptic transmission in the absence of nerve impulses. J. Physiol (Lond.) 192, 407–436 (1967b)
Keesey, J. C., Wallgren, H., Mc Ilwain, H.: The sodium, potassium and chloride of cerebral tissues: maintenance, change on stimulation and subsequent recovery. Biochem. J. 95, 289–300 (1965)
Kirpekar, S. M., Prat, J. C., Puig, M., Wakade, A. R.: Modification of the evoked release of noradrenaline from the perfused cat spleen by various ions and agents. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 221, 601–615 (1972)
Koppenhöfer, E., Schmidt, H.: Die Wirkung von Skorpiongift auf die Ionenströme des Ranvierschen Schnürrings. I. Die Permeabilitäten P Na und P K. Pflügers Arch. Ges. Physiol. 303, 133–149 (1968a)
Koppenhöfer, E., Schmidt, H.: Die Wirkung von Skorpiongift auf die Ionenströme des Ranvierschen Schnürrings. II. Unvollständige Natrium-Inaktivierung. Pflügers Arch. Ges. Physiol. 303, 150–161 (1968b)
Langer, S. Z.: Presynaptic regulation of catecholamine release. Biochem. Pharmacol. 23, 1793–1800 (1974)
Langer, S. Z.: Presynaptic receptors and their role in the regulation of transmitter release. Sixth Gaddum Memorial Lecture. Br. J. Pharmacol. 60, 481–497 (1977)
Langer, S. Z., Adler-Graschinsky, E., Almeida, A. P., Diniz, C. R.: Prejunctional effects of a purified toxin from the Scorpion Tityus serrulatus: Release of 3H-noradrenaline and enhancement of transmitter overflow elicited by nerve stimulation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 287, 243–259 (1975)
Langer, S. Z., Adler, E., Enero, M. A., Stefano, F. J. E.: The role of the alpha, receptor in regulating noradrenaline overflow by nerve stimulation. XXVth. Int. Congr. Physiol. Sciences, Munich 1971, p. 335 (1971)
Langer, S. Z., Enero, M. A.: The potentiation of responses to adrenergic nerve stimulation in the presence of cocaine: its relationship to the metabolic fate of released norepinephrine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 191, 431–443 (1974)
Laverty, R., Taylor, K. M.: The fluorimetric assay of catecholamines and related compounds: Improvements and extensions to the hydroxyindole technique. Anal. Biochem. 22, 269–279 (1968)
Lindmar, R., Löffelholz, K., Muscholl, E.: Unterschiede zwischen Tyramin und Dimethylphenylpiperazin in der Ca2+-Abhängigkeit und im zeitlichen Verlauf der Noradrenalin-Freisetzung am isolierten Kaninchenherzen. Experientia 23, 933–934 (1967)
Lipton, P.: Effects of membrane depolarization on light scattering by cerebral cortical slices. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 231, 365–383 (1973)
Moguilevsky, J. A., Rubinstein, L.: Glycolytic and oxidative metabolism of hypothalamic areas in prepuberal androgenized rats. Neuroendocrinology 2, 213–221 (1967)
Moss, J., Thoa, N. B., Kopin, I. J.: On the mechanism of Scorpion toxin-induced release of norepinephrine from peripheral adrenergic neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 190, 39–48 (1974)
Snedecor, G. M., Cochran, W. G.: Statistical methods, 6th Ed. Ames: The Iowa State University Press 1967
Starke, K.: Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 77, 1–124 (1977)
Thoenen, H., Haefely, W., Staehelin, H.: Potentiation by tetraethylammonium of the response of the cat spleen to postganglionic nerve stimulation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 157, 532–540 (1967)
Thompson, J. W.: Studies on the response of isolated nictitating membrane of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 141, 46–72 (1958)
Vargas, O., Doria de Lorenzo, M. del C., Saldate, M. C., Orrego, F.: Potassium induced release of (3H)-GABA and of (3H) noradrenaline from normal and reserpinized rat brain cortex slices. Differences in calcium-dependency, and in sensitivity to potassium ions. J. Neurochemistry 28, 165–170 (1977)
Warnick, J. E., Albuquerque, E. X., Diniz, C. R.: Electrophysiological observations on the action of the purified scorpion venom, tityus toxin, on nerve and skeletal muscle of the rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 198, 155–167 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adler-Graschinsky, E., Langer, S.Z. Mechanism of the enhancement in transmitter release from central and peripheral noradrenergic nerve terminals induced by the purified scorpion venom, tityustoxin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 303, 243–249 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498050
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498050