Abstract
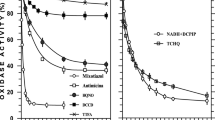
Myxothiazol inhibited the electron transport in the cytochrome b/c segment of membrane particles from Pseudomonas cichorii. A residual NADH-oxidation due to the presence of an alternative pathway via cytochrome o (Em,7=+250 mV) was sensitive to the quinone analog 5-undecyl-6-hydroxy-4,7-dioxobenzothiazole (UHDBT). This latter inhibitor was equally effective in blocking the linear respiratory chain of Pseudomonas aptata, a strain deficient in cytochromes of c type and Rieske iron-sulphur centre. The analysis of the oxido-reduction kinetic patterns of cytochromes indicated that, among the b type haems present in P. aptata, only cyt. o could be reduced by ubiquinol-1 in a reaction insensitive to both antimycin A and myxothiazol but inhibited by UHDBT. This latter finding has been correlated to the fact that P. aptata exhibits a defective b/c complex. In membranes from P. cichorii, in which the absorption maximum of dithionite reduced cytochrome(s) b shifted by 2–3 nm in the presence of antimycin A and/or myxothiazol, the electron flow through the b/c oxidoreductase complex has tentatively been arranged in a proton motive “Q-cycle” like mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- UHDBT:
-
5-undecyl-6-hydroxy-4,7-dioxobenzothiazole
- cyt.:
-
cytochrom
- Em, 7:
-
mid-point potential at pH 7.0
- b/c complex:
-
ubiquinol-cyt. c oxidoreductase
References
Brandon JR, Brocklehurst JR, Lee CP (1972) Effect of antimycin A and 2-heptyl-4-hydroxyquinoline N-oxide on the respiratory chain of submitochondrial particles of beef heart. Biochemistry 11:1150–1154
Chance B (1957) Techniques for the assay of respiratory enzymes. In: Colowick SP, Kaplan NO (eds) Methods in enzymology, vol 4. Academic Press, New York, pp 273–342
Cramer WA, Crofts AR (1982) Electron and proton transport. In: Govindjee (eds) Photosynthesis. Energy conversion by plants and bacteria, vol I, Academic Press, New York, pp 387–467
Crofts AR (1983) The mechanism of the ubiquinol: cytochrome c oxidoreductase of mitochondria and of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. In: Martonosi AN (ed) The enzymes of biological membranes, 2nd edn. Plenum Publ., New York, pp 347–382
Hauska G, Hurt E, Gabellini N, Lokau W (1983) Comparative aspects of quinol-cyt. c/plastocyanin oxidoreductases. Biochim Biophys Acta 726:97–133
Jagow G von, Engel WD (1981) Complete inhibition of electron transfer from ubiquinol to cytochrome b by the combined action of antimycin A and myxothiazol. FEBS Lett 136:19–24
Jagow G von, Ljungdhal PO, Graf P, Ohnishi T (1984) An inhibitor of mitochondrial respiration which binds to cyt. b and displaces quinone from the iron sulphur protein of the b/c complex. J Biol Chem 259:6318–6326
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mitchell P (1975) Proton motive redox mechanism of the cytochrome b/c complex in the respiratory chain: proton motive ubiquinone cycle. FEBS Lett 56:1–6
Rieske JS (1967) Preparation and properties of reduced coenzyme Q-cytochrome c reductase complex III of the respiratory chain. In: Estabrook RW, Pullman ME (eds) Methods in enzymology, vol 10. Academic Press, New York, pp 239–245
Zannoni D (1982) Cytochrome b type oxidases in the respiratory chains of the phytopathogenic bacteria Pseudomonas cichorii and Pseudomonas aptata. Arch Microbiol 133:267–273
Zannoni D, Ingledew JW (1984) A comparative survey of the ironsulphur centres in the cytoplasmic membranes of Pseudomonas cichorii and Pseudomonas aptata. J Gen Microbiol 130:1107–1111
Zannoni D (1984) Respiratory energy transduction by membrane fragments of the phytopathogenic bacteria Pseudomonas cichorii and Pseudomonas aptata. Arch Microbiol 138:195–199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cocchi, S., Zannoni, D. Effects of myxothiazol and 5-undecyl-6-hydroxy-4,7-dioxobenzothiazole on the respiratory pathways of the phytopathogenic fluorescent bacteria Pseudomonas cichorii and Pseudomonas aptata . Arch. Microbiol. 142, 365–369 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00491905
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00491905