Summary
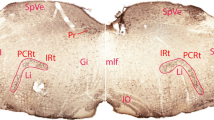
The occurrence and distribution of neurotensin-immunoreactive (NT-IR) perikarya was studied in the central nervous system of the guinea pig using a newly raised antibody (KN 1). Numerous NT-IR perikarya were found in the nuclei amygdaloidei, nuclei septi interventriculare, hypothalamus, nucleus parafascicularis thalami, substantia grisea centralis mesencephali, ventral medulla oblongata, nucleus solitarius and spinal cord. The distribution of NT-IR perikarya was similar to that previously described in the rat and monkey. In the gyrus cinguli, hippocampus and nucleus olfactorius, though, no NT-IR neurons were detected in this investigation. Additional immunoreactive perikarya, however, were observed in areas of the ventral medulla oblongata, namely in the nucleus paragigantocellularis, nucleus retrofacialis and nucleus raphe obscurus.
The relevance of the NT-IR perikarya within the ventral medulla oblongata is discussed with respect to other neuropeptides, which are found in this area, and to cardiovascular regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- abl:
-
nucleus amygdaloideus basalis lateralis
- abm:
-
nucleus amygdaloideus basalis medialis
- acc:
-
nucleus amygdaloideus centralis
- aco:
-
nucleus amygdaloideus corticalis
- ahp:
-
area posterior hypothalami
- ala:
-
nucleus amygdaloideus lateralis anterior
- alp:
-
nucleus amygdaloideus lateralis posterior
- ame:
-
nucleus amygdaloideus medialis
- atv:
-
area tegmentalis ventralis
- bst:
-
nucleus proprius striae terminalis
- CA:
-
commissura anterior
- CC:
-
corpus callosum
- cgld:
-
corpus geniculatum laterale dorsale
- cglv:
-
corpus geniculatum laterale ventrale
- cgm:
-
corpus geniculatum mediale
- CHO:
-
chiasma opticum
- CI:
-
capsula interna
- co:
-
nucleus commissuralis
- cod:
-
nucleus cochlearis dorsalis
- cp:
-
nucleus caudatus/Putamen
- cs:
-
colliculus superior
- cu:
-
nucleus cuneatus
- dmh:
-
nucleus dorsomedialis hypothalami
- DP:
-
decussatio pyramidum
- em:
-
eminentia mediana
- ent:
-
cortex entorhinalis
- epi:
-
epiphysis
- FLM:
-
fasciculus longitudinalis medialis
- fm:
-
nucleus paraventricularis hypothalami pars filiformis
- FX:
-
fornix
- gd:
-
gyrus dentatus
- gp:
-
globus pallidus
- gr:
-
nucleus gracilis
- hl:
-
nucleus habenulae lateralis
- hm:
-
nucleus habenulae medialis
- hpe:
-
hippocampus
- ift:
-
nucleus infratrigeminalis
- io:
-
oliva inferior
- ip:
-
nucleus interpeduncularis
- LM:
-
lemniscus medialis
- MT:
-
tractus mamillo-thalamicus
- na:
-
nucleus arcuatus
- nls:
-
nucleus lateralis septi
- nms:
-
nucleus medialis septi
- npca:
-
nucleus proprius commissurae anterioris
- ns:
-
nucleus solitarius
- n III:
-
nucleus nervi oculomotorii
- nt V:
-
nucleus tractus spinalis nervi trigemini
- ntm:
-
nucleus mesencephalicus nervi trigemini
- osc:
-
organum subcommissurale
- P:
-
tractus cortico-spinalis
- PC:
-
pedunculus cerebri
- PCI:
-
pedunculus cerebellaris inferior
- pir:
-
cortex piriformis
- pol:
-
area praeoptica lateralis
- pom:
-
area praeoptica medialis
- prt:
-
area praetectalis
- pt:
-
nucleus parataenialis
- pvh:
-
nucleus paraventricularis hypothalami
- pvt:
-
nucleus paraventricularis thalami
- r:
-
nucleus ruber
- re:
-
nucleus reuniens
- rgi:
-
nucleus reticularis gigantocellularis
- rl:
-
nucleus reticularis lateralis
- rm:
-
nucleus raphe magnus
- ro:
-
nucleus raphe obscurus
- rp:
-
nucleus raphe pallidus
- rpc:
-
nucleus reticularis parvocellularis
- rpgc:
-
nucleus reticularis paragigantocellularis
- sch:
-
nucleus suprachiasmaticus
- SM:
-
stria medullaris thalami
- snc:
-
substantia nigra compacta
- snl:
-
substantia nigra lateralis
- snr:
-
substantia nigra reticularis
- ST:
-
stria terminalis
- tad:
-
nucleus anterior dorsalis thalami
- tam:
-
nucleus anterior medialis thalami
- tav:
-
nucleus anterior ventralis thalami
- tbl:
-
nucleus tuberolateralis
- tc:
-
nucleus centralis thalami
- tl:
-
nucleus lateralis thalami
- tmd:
-
nucleus medialis dorsalis thalami
- TO:
-
tractus opticus
- TOL:
-
tractus olfactorium lateralis
- tpo:
-
nucleus posterior thalami
- tr:
-
nucleus reticularis thalami
- trs:
-
nucleus triangularis septi
- TS:
-
tractus solitarius
- TS V:
-
tractus spinalis nervi trigemini
- tvl:
-
nucleus ventrolateralis thalami
- vmh:
-
nucleus ventromedialis hypothalami
- vh:
-
ventral horn, Columna anterior
- zi:
-
zona incerta
References
Adair JR, Hamilton BL, Scappaticci KA, Helke CJ, Gillis RA (1977) Cardiovascular responses to electrical stimulation of the medullary raphe area of the cat. Brain Res 128:141–145
Andrezik JA, Chan-Palay V, Palay SL (1981) The nucleus paragigantocellularis lateralis in the rat. Anat Embryol 161:373–390
Beitz AJ (1982) The sites of origin of brain stem neurotensin and serotonin projections to the rodent nucleus raphe magnus. J Neurosci 2:829–842
Beitz AJ, Shepard RD, Wells WE (1983) The periaqueductal grayraphe magnus projection contains somatostatin, neurotensin and serotonin but not cholecystokinin. Brain Res 261:132–137
Carraway R, Leeman S (1973) The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J Biol Chem 248:6854–6861
Carraway R, Leeman SE (1975) The amino acid sequence of a hypothalamic peptide, neurotensin. J Biol Chem 250: 1907–1911
Caverson MM, Ciriello J, Calaresu FR (1983) Direct pathway from cardiovascular neurons in the ventrolateral medulla to the region of the intermediolateral nucleus of the upper thoracic cord: an anatomical and electrophysiological investigation in the cat. J Auton Nerv Syst 9:451–475
Cechetto D, Ciriello J, Calaresu FR (1983) Afferent connections to cardiovascular sites in the amygdala: a horseradish peroxidase study in the cat. J Auton Nerv Syst 8:97–110
Clineschmidt BV, McGuffin JC (1977) Neurotensin administered intracisternally inhibits responsiveness of mice to noxious stimuli. Eur J Pharmacol 46:395–396
DeGroat WC, Nadelhaft J, Morgan C, Schauble T (1979) The central origin of efferent pathways in the carotid sinus nerve of the cat. Science 205:1017–1019
Dev NB, Loeschke HH (1979) Topography of the respiratory and circulatory responses to acetylcholine and nicotine on the ventral surface of the medulla oblongata. Pflügers Arch 379:19–27
Errington ML, Dashwood MR (1979) Projections to the ventral surface of the cat brainstem demonstrated by horseradish peroxidase. Neurosci Lett 12:153–158
Ervin GN, Birkemo LS, Nemeroff CB, Prange AJ Jr (1981) Neurotensin blocks certain amphetamine-induced behaviours. Nature 291:73–76
Flórez J, Mediavilla A (1977) Respiratory and cardiovascular effects of metenkephalin applied to the ventral surface of the brain stem. Brain Res 138:585–590
Forssmann WG, Pickel VM, Reinecke M, Hock D, Metz J (1981) Immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry of nervous tissue. In: Heym Ch, Forssmann WG (eds) Techniques in neuroanatomical research. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 171–205
Gorgas K, Reinecke M, Weihe E, Forssmann WG (1983) Neurotensin and substance P immunoreactive nerve endings in the guinea pig carotid sinus and their ultrastructural counterparts. Anat Embryol 167:347–354
Hamilton RB, Ellenberger H, Liskowsky D, Schniedermann N (1981) Parabrachial area as mediator of bradycardia in rabbits. J Auton Nerv Syst 4:261–281
Hara Y, Shiosaka S, Senba E, Sakanaka M, Inagaki S, Takagi H, Kawai Y, Takatsuki K, Matsuzaki T, Tohyama M (1982) Ontogeny of the neurotensin-containing neuron system of the rat: immunohistochemical analysis. I. Forebrain and diencephalon. J Comp Neurol 208:177–195
Hökfelt T, Ljungdahl A, Steinbusch H, Verhofstad A, Nilsson G, Brodin E, Pernow B, Goldstein M (1978) Immunohistochemical evidence of substance P-like immunoreactivity in some 5-hydroxy-tryptamine-containing neurons in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 3:517–538
Ibata Y, Fukui K, Okamura H, Kawakami T, Tanaka M, Obata HL, Tsuto T, Terubayashi H, Yanaihara C, Yanaihara N (1983) Coexistence of dopamine and neurotensin in hypothalamic arcuate and periventricular neurons. Brain Res 269: 177–179
Inagaki S, Shinoda K, Kubota Y, Shiosaka S, Matsuzaki T, Tohyama M (1983) Evidence for the existence of a neurotensin-containing pathway from the endopiriform nucleus and the anterior olfactory nucleus and nucleus of diagonal band (Broca) of the rat. Neuroscience 8:487–493
Iversen LL, Iversen SD, Bloom F, Douglas C, Brown M, Vale W (1978) Calcium-dependent release of somatostatin and neurotensin from rat brain in vitro. Nature 273:161–163
Jennes L, Stumpf WE, Kalivas PW (1982) Neurotensin: topographical distribution in rat brain by immunohistochemistry. J Comp Neurol 210:211–224
Kahn D, Abrams GM, Zimmermann EA, Carraway R, Leeman SE (1980) Neurotensin neurons in the rat hypothalamus: an immunocytochemical study. Endocrinology 107:47–54
Kalivas PW, Burgess SK, Nemeroff CB, Prange AJ (1983) Behavioral and neurochemical effects of neurotensin microinjection into the ventral tegmentel area of the rat. Neuroscience 8:495–505
Kataoka K, Mizuno N, Frohmann LA (1979) Regional distribution of immunoreactive neurotensin in monkey brain. Brain Res Bull 4:57–60
Kobayashi RM, Brown M, Vale W (1977) Regional distribution of neurotensin and somatostatin in rat brain. Brain Res 126:584–588
Langhorst P, Schulz B, Schulz G, Lambertz M (1983) Reticular formation of the lower brainstem. A common system for cardiorespiratory and somatomotor functions: discharge patterns of neighboring neurons influenced by cardiovascular and respiratory afferents. J Auton Nerv Syst 9:411–432
Levine AS, Kneip J, Grace M, Morley JE (1983) Effects of centrally administered neurotensin on multiple feeding paradigms. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 18:19–23
Loewy AD, McKellar S (1980) The neuroanatomical basis of cardiovascular control. Fed Proc 39:2495–2503
Loewy AD, Sawyer WB (1982) Substance P antagonist inhibits vasomotor responses elicited from ventral medulla in rat. Brain Res 245:379–383
Loewy AD, Wallach JH, McKellar S (1981) Efferent connections of the central medulla oblongata in the rat. Brain Res Rev 3:63–80
Lovick TA, Hunt SP (1983) Substance P-immunoreactive and serotonin-containing neurones in the ventral brainstem of the cat. Neurosci Lett 36:223–228
McCarthy PS, Walker RJ, Yajimat H, Kitagawa K, Woodruff GN (1979) The action of neurotensin on neurones in the nucleus accumbens and cerebellum of the rat. Gen Pharmacol 10:331–333
Miletić V, Rancić M (1979) Neurotensin excites cat spinal neurones located in laminae I–III. Brain Res 169:600–604
Minagawa H, Shiosaka S, Inagaki S, Sakanaka M, Taktsuki K, Ishimoto I, Senba E, Kawai Y, Hara Y, Matsuzaki T, Tohyama M (1983) Ontogeny of neurotensin-containing neuron system of the rat: immunohistochemical analysis. II. Lower brain stem. Neuroscience 8:467–486
Morley JE, Levine AS, Oken MM, Grace M, Kneip J (1982) Neuropeptides and thermoregulation: the interactions of bombesin, neurotensin, TRH, somatostatin, naloxone and prostaglandins. Peptides 3:1–6
Nemeroff CB, Bissette G, Prange AJ Jr, Loosen PT, Lipton MA (1977) Neurotensin: central nervous system effects of a hypothalamic peptide. Brain Res 128:485–496
Oishi M, Inagaki Ch, Takaori S, Yajima H, Akazawa Y (1982) Attenuation of triphasic blood pressure responses induced by shortening of amino acid sequences of neurotensin. Neuropeptides 2:279–286
Osbahr AJ III, Nemeroff CB, Luttinger D, Mason GA, Prange AJ Jr (1981) Neurotensin-induced antinociception in mice: antagonism by thyrotropin-releasing hormone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 217:645–651
Osumi Y, Nagasaka Y, Wang LH Fu, Fujiwara M (1978) Inhibition of gastric acid secretion and mucosal blood flow induced by intraventriculary applied neurotensin in rat. Life Sci 23: 2275–2280
Quirion R (1983) Interactions between neurotensin and dopamine in the brain: an overview. Peptides 4:609–615
Reches A, Burke RE, Jiang D, Wagner HR, Fahn S (1983) Neurotensin interacts with dopaminergic neurons in rat brain. Peptides 4:43–48
Reinecke M, Forssmann WG, Thiekötter G, Triepel J (1983) Localization of neurotensin-immunoreactivity in the spinal cord and peripheral nervous system of the guinea pig. Neurosci Lett 37:37–42
Schlaefke ME, See WR (1980) Ventral medullary surface stimulus responses in relation to ventilatory and cardiovascular effects. In: Koepchen HP, Hilton SM, Trzebski A (eds) Central interaction between respiratory and cardiovascular control systems. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 55–64
Schläfke ME, Kille JF, Loeschke HH (1979) Elimination of central chemosensitivity by coagulation of a bilateral area on the ventral medullary surface in awake cats. Pflügers Arch 378: 231–241
Schulz B, Lambertz M, Schulz G, Langhorst P (1983) Reticular formation of the lower brainstem. A common system for cardiorespiratory and somatomotor functions: discharge patterns of neighboring neurons influenced by somatosensory afferents. J Auton Nerv Syst 9:433–449
Senba E, Shiosaka S, Hara Y, Inagaki S, Kawai Y, Tatatsuki K, Sakanaka M, Iida H, Takagi H, Minagawa H, Tohyama M (1982) Ontogeny of the Leucine-Enkephalin neuron system of the rat: immunohistochemical analysis. I. Lower brainstem. J Comp Neurol 205:341–359
Seybold VS, Elde RP (1982) Neurotensin immunoreactivity in the superficial laminae of the dorsal horn of the rat: I. Light microscopic studies of cell bodies and proximal dendrites. J Comp Neurol 205:89–100
Stanley BG, Hoebel BG, Leibowitz SF (1983) Neurotensin: effects of hypothalamic and intravenous injections on eating and drinking. Peptides 4:493–500
Stanzione P, Zieglgänsberger W (1983) Action of neurotensin on spinal cord neurons in the rat. Brain Res 268:111–118
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunocytochemistry, 2nd ed. Wiley, New York
Stock G, Schmelz M, Knuepfer MM, Forssmann WG (1983) Functional and anatomic aspects of central nervous cardiovascular regulation. In: Ganten D, Pfaff D (eds) Central cardiovascular control. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 1–30
Thiekötter G (1984) Neurotensin im Zentralnervensystem des Meerschweinchens. Eine Mapping-Studie. Dissertation Heidelberg
Triepel J, Thiekötter G, Elger K-H, Mader J, Kiemle I, Forssmann WG (1981) Immunohistochemical localization of glucagon, glicentin, VIP, somatostatin, and neurotensin in guinea pig brain. Neurosci Lett (Suppl) 7:S266
Triepel J, Kiemle I, Mader J, Elger K-H, Thiekötter G, Weindl A, Forssmann WG (1982) Neuropeptide mapping of the brain stem in normal and colchicine-treated guinea pig. Neurosci Lett (Suppl) 10:S488
Triepel J, Elger KH, Kiemle I, Mader J, Reinecke M, Thiekötter G, Weindl A, Forssmann WG (1984a) Neuropeptide in cardiovaskulären Zentren. Verh Anat Ges (in press)
Triepel J, Elger K-H, Kiemle I, Mader J, Shehab T, Thiekötter G, Forssmann WG (1984b) Somatostatin-like immunoreactive neurons and axons in the central nervous system of guinea pig, tupaia, and cat. University Press
Uhl GR, Snyder SH (1976) Regional and subcellular distribution of brain neurotensin. Life Sci 19:1827–1832
Uhl GR, Snyder SH (1977) Neurotensin receptor binding, regional and subcellular distributions favour transmitter role. Eur J Pharmacol 41:89–91
Uhl GR, Kuhar MJ, Snyder SH (1977) Neurotensin: Immunohistochemical localization in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:4059–4063
Uhl GR, Goodman RR, Snyder SH (1979) Neurotensin-containing cell bodies, fibers and nerve terminals in the brainstem of the rat: Immunohistochemical mapping. Brain Res 167:77–91
Williams RG, Dockray GJ (1983) Distribution of Enkephalin-related peptides in rat brain: immunohistochemical studies using antisera to Met-Enkephalin and Met-Enkephalin Arg6Phe7. Neuroscience 9:563–586
Williams JT, Katayama Y, North RA (1979) The action of neurotensin on single myenteric neurones. Eur J Pharmacol 59: 181–186
Young WS III, Uhl GR, Kuhar MJ (1978) Iontophoresis of neurotensin in the area of the locus coeruleus. Brain Res 150:431–435
Zieglgänsberger W, Siggins G, Brown M, Vale W, Bloom F (1978) Actions of neurotensin upon single neurone activity in different regions of the rat brain. Proc VII Int Congr Pharmacol 126
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgesellschaft (DFG) SFB 90, Carvas
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Triepel, J., Mader, J., Weindl, A. et al. Distribution of NT-IR perikarya in the brain of the guinea pig with special reference to cardiovascular centers in the medulla oblongata. Histochemistry 81, 509–516 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00489528
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00489528