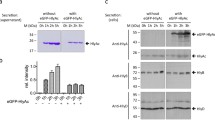
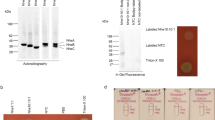
Abstract
Extensive attempts were made to overexpress the Escherichia coli haemolysin translocator protein HlyB, and HlyB fragments, utilising high copy number plasmids or hlyB expressed from strong promoters including λPR, ptrp and the T7 promoter. Analysis of both cytoplasmic and membrane fractions failed to detect any overexpression of the protein, although all the constructs showed biological activity and there was no evidence of HlyB-induced toxicity. In some constructs, the effect of removing a stem-loop structure, immediately upstream of the start codon and implicated in rho-independent termination of transcription, was tested but this did not lead to over-expression. Nevertheless, analysis of hlyB specific mRNA synthesis revealed that some constructs showed at least a 50-fold increase in mRNA levels, indicating that expression of HlyB may be limited at the translational level. When HlyB was expressed as a hybrid, downstream of LacZ, extremely high level overproduction was then detected in total cell extracts. When the expression of HlyB or HlyB fragments expressed from a T7 promoter was examined, the C-terminal ATPase domain was dramatically overexpressed but the production of fragments encompassing the N-terminal membrane domain, was reduced at least 1000-fold. These results indicate that mRNA structures corresponding to the membrane domain of HlyB greatly limit the post-transcriptional expression of HlyB. When such structures are deleted, or disrupted when part of a larger mRNA, HlyB or the HlyB ATPase domain can be overproduced in milligram quantities and this has facilitated the production of high titre antibodies to HlyB.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames GF (1974) Resolution of bacterial proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on slabs. J Biol Chem 249:643–644
Amkraut AA, Garvey JS, Campbell DH (1966) Competition on haptens. J Exp Med 124:293–298.
Bailey MIA, Koronakis V, Schmoll T, Hughes C (1992) Escherichia coli HlyT portein, a transcriptional activator of haemolysin synthesis and secretion, is encoded by the rfaH (sfrB) locus required for expression of sex factor and lipopolysaccharide genes. Mol Microbiol 6:1003–1012
Blight MA (1990) PhD Thesis, University of Leicester, UK
Blight MA, Holland IB (1990) Structure and function of haemolysin B, P-glycoprotein and other members of a novel family of membrane translocators. Mol Microbiol 4:873–880
Blight MA, Pimenta AL, Lazzaroni J-C, Dando C, Kotelevets L, Séror SJ, Holland IB (1994) Identification and preliminary characterisation of temperature-sensitive mutations affecting HlyB, the translocator required for the secretion of haemolysin (HlyA) from Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet 245:431–440
Carmona M, Balsalobre C, Mûnoa F, Mouriñio M, Jubete Y, de la Cruz F, Juárez A (1993) E. coli hha mutants, DNA supercoiling and expression of the haemolysin genes from the recombinant plasmid, pANN 202-312. Mol Microbiol 9:1011–1018
Cross MA, Koronakis V, Stanley PLD, Hughes C (1990) HlyB dependent secretion of haemolysin by uropathogenic E. coli requires conserved sequences flanking the chromosomal hly determinant. J Bacteriol 172:1217–1224
Delepelaire P, Wandersman C (1991) Characterization, localisation and transmembrane organisation of the three proteins PrtD, PrtE and Prtf necessary for protease secretion by the Gramnegative bacterium Erwinia chrysanthemi. Mot Microbiol 5:2427–2435
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabelling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Felmlee T, Welch RA (1988) Alterations of amino acid repeats in the E. coli hemolysin affect cytolytic activity and secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:5269–5273
Felmlee T, Pellet S, Lee EY, Welch RA (1985a) E. coli hemolysin is released extracellularly without cleavage of a signal peptide. J Bacteriol 163:88–93
Felmlee T, Pellet S, Welch RA (1985b) Nucleotide sequence of an E. coli chromosomal hemolysin. J Bacteriol 163:94–105
Gentschev I, Goebel W (1992) Topological and functional studies on HlyB of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet 232:40–48
Gentschev I, Hess J, Goebel W (1990) Change in the cellular localisation of alkaline phosphatase by alteration of its carboxyterminal sequence. Mol Gen Genet 222:211–216
Gibbs RA, Caskey CT (1987) Identification and localisation of mutations at the Lesch-Nyhan locus by ribonuclease A cleavage. Science 236:303–305
Goebel W, Hedgpeth J (1982) Cloning and functional characterization of the plasmid-encoded hemolysin determinant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 151:1290–1298
Gray L, Mackman N, Nicaud J-M, Holland IB (1986) A novel C-terminal signal sequence targets E. coli haemolysin directly to the medium. Mot Gen Genet 205:127–133
Gray L, Baker K, Kenny B, Mackman N, Haigh R, Holland IB (1989) The carboxy-terminal region of haemolysin 2001 is required for secretion of thle toxin from E. coli. John Innes Symposium on Protein Targeting, Chater K (ed). J Cell Sci (Suppl) 11:45–57
Harlow E, Lane D (1988) Antibodies: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Hartlein M, Schiessel S, Wagner W, Rdest U, Kreft J, Goebel W (1983) Transport of hemolysin by E. coli. J Cell Biochem 22:87–97
Holland IB, Kenny B, Blight MA (1990) Haemolysin secretion from E. coli Biochimie 72:131–141
Issartel J-P, Koronakis V, Hughes C (1991) Activation of E. coli prohaemolysin to the mature toxin by acyl carrier protein dependent fatty acylation. Nature 351:759–761
Ito K, Bassford PJ, Beckwith J (1981) Protein localization in E. coli: is there a common step in the secretion of periplasmic and outer membrane proteins? Cell 24:707–717
Juranka P, Zhang F, Kulpa J, Endicott J, Blight MA, Holland IB, Ling V (1992) Characterization of the hemolysin transporter, HlyB, using an epitope insertion. J Biol Chem 267:3764–3770
Kenny B, Haigh R, Holland IB (1991) Analysis of the haemolysin transport process through the secretion from E. coli of PCM, CAT or β-galactosidase fused to the Hly C-terminal signal domain. Mol Microbiol 5:2557–2568
Kenny B, Taylor S, Holland IB (1992) Identification of individual amino acids requred for secretion within the haemolysin (HlyA) C-terminal targeting region. Mot Microbiol 6:1477–1489
Kenny B, Chervaux C, Holland IB (1994) Evidence that residues − 15 to − 46 of the haemolysin secretion signal are involved in early steps in secretion, leading to recognition of the translocator. Mol microbiol (in press)
Koronakis V, Hughes C (1988) Identification at the promoters directing in vivo expression of hemolysin genes in Proteus vulgaris and Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet 213:99–104
Koronakis V, Cross M, Senior B, Koronakis E, Hughes C (1987) The secreted hemolysins of Proteus mirabilis, Prteus vulgaris and Morganella morganii are genetically related to each other and to the alpha-hemolysin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 169:1509–1515
Koronakis V, Cross M, Hughes C (1988) Expression of the E. coli haemolysin secretion gene hlyB involves transcript anti-termination within the hly operon. Nucleic Acids Res 16:4789–4800
Koronakis V, Koronakis E, Hughes C (1989) Isolation of the C-terminal signal directing export of E. coli haemolysin protein across both membranes. EMBO J 8: 595–605
Koronakis V, Hughes C, Koronakis E (1993) ATPase activity and ATP/ADP-induced conformational change in the soluble domain of the bacterial protein translocator HlyB. Mot Microbiol 8:1163–1175
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–683
Lillie SH, Brown SS (1987) Artifactual immunofluorescent labelling in yeast, demonstrated by affinity purification of antibody. Yeast 3:63–70
Mackman N, Holland IB (1984) Functional characterization of a cloned haemolysin determinant from E. coli of human origin, encoding information for the secretion of a 107 kDa polypeptide. Mot Gen Genet 196:129–134
Mackman N, Nicaud J-M, Gray L, Holland IB (1985b) Identification of polypeptides required for the export of haemolysin 2001 from Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet 201:529–536
Mackman N, Nicaud J-M, Gray L, Holland IB (1985b) Genetical and functional organisation of the Escherichia coli haemolysin determinant 2001. Mot Gen Genet 201:282–288
Mackman N, Baker K, Gray L, Haigh R, Nicaud J-M, Holland IB (1987) Release of a chimeric protein into the medium from E. coli using the C-terminal secretion signal of haemolysin. EMBO J 6:2835–2841
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Markham BE, Harper JE, Mount DW, Sancar GB, Sancar A, Rupp WD, kenyon CJ, Walker GC (1984) Analysis of mRNA synthesis following induction of the E. coli SOS system. J Mot Biol 178:237–248
Nicaud J-M, Mackman N, Gray L, Holland IB (1985a) Characterization of HlyC and the mechanism of activation and secretion of the haemolysin from E. coli 2001. FEBS Lett 187:339–344
Nicaud J-M, Mackman N, Gray L, Holland IB (1985b) Regulation of haemolysin synthesis in Escherichia coli determined by HLY genes of human origin. Mol Gen Genet 199:111–116
Nicaud J-M, Mackman N, Gray L, Holland IB (1986) The C-terminal, 23kD peptide of E. coli haemolysin 2001 contains all the information necessary for its secretion by the haemolysin (Hly) export machinery. FEBS Lett 204:331–335
Rosenberg AH, Lade BN, Chui D, Lin SW, Dunn JJ, Studier FW (1987) Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNA's by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene 56:125–135
Stanley KK, Luzio JP (1984) Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J 3:1429–1434
Stanley P, Koronakis V, Hughes C (1991) Mutational analysis supports a role for multiple structural features in the C-terminal secretion signal of Escherichia coli haemolysin. Mol Microbiol 5:2391–2403
Stewart GSAB, Lubinsky-Minsk S, Kuhn J (1986) pHG276: a multiple cloning site pBR322 copy number vector expresing a functional lac-peptide from the bacteriophage lambda PR promoter. Plasmid 15:182–190
Studier FW, Rosenberg AH, Dunn JJ, Dubendorff JW (1990) Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol 185:60–89
Thomas WD Jr, Wagner SP, Welch RA (1992) A heterologous membrane protein domain fused to the C-terminal ATP-binding domain of HlyB can export Escherichia coli hemolysin. J Bacteriol 174:6771–6779
Vogel M, Hess J, Then I, Juarez A, Goebel W (1988) Characterization of a sequence (hlyR) which enhances synthesis and secretion of hemolysin in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet 212:76–84
Wagner W, Vogel M, Goebel W (1983) Transport of hemolysin across the outer membrane of Escherichia coli requires two functions. J Bacteriol 154:200–210
Wandersman C, Delepelaire P (1990) TolC an E. coli outer membrane protein required for hemolysin secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:4776–4780
Wandersman C, Létoffé S (1993) Involvement of lipopolysaccharide in the secretion of E. coli haemolysin and Erwinia chrysanthemi proteases. Mol Microbiol 7:141–150
Wang R, Seror SJ, Blight MA, Pratt JM, Broome-Smith JK, Holland IB (1991) Analysis of the membrane organisation of an E. coli protein translocator, HlyB, a member of a large family of prokaryote and eukaryote surface transport proteins. J Mol Biol 217:441–454
Welch RA, Pellet S (1988) Transcriptional organisation of the Escherichia coli haemolysin genes. J Bacteriol 170:1622–1630
Welch RA, Hull R, Falkow S (1983) Molecular cloning and physical characterisation of a chromosomal haemolysin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun 42:178–186
Wright EM, Humphreys GO, Yarranton GT (1986) Dual-origin plasmids containing an amplifiable Co1E1 ori; temperature-controlled expression of cloned genes. Gene 49:311–321
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by W. Goebel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blight, M.A., Menichi, B. & Holland, I.B. Evidence for post-transcriptional regulation of the synthesis of the Escherichia coli HlyB haemolysin translocator and production of polyclonal anti-HlyB antibody. Molec. Gen. Genet. 247, 73–85 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00425823
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00425823