Abstract
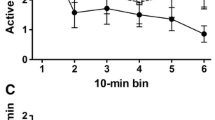
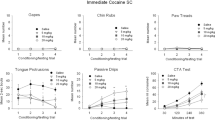
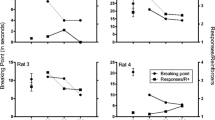
The effect of a dexamphetamine-amylobarbitone mixture (1∶6.5 by weight) on a sensory-contingent bar pressing (SCBP) for different sensory changes was investigated. The aim was to examine the role of (a) reward value of contingent change per se (non drug) and (b) stimulus properties in enhanced SCBP under the drug mixture. The sensory reinforcers used were light Onset, light Offset, and sound offset combined with the light changes contemporaneously. In the first two phases the sensory stimuli were given as continuous reinforcement and in the third phase on an FR2 schedule. The results from the first two phases were consistent with the notion that the drug mixture operates to increase the nondrug reward value of SCBP. That is, the extent to which responding under the drug was enhanced was not significantly related to the kind of sensory change. Instead, responding under the mixture was enhanced in proportion to the level of non drug responding, especially in Phase 1. However, in Phase 3, SCBP was enhanced proportionately more, to a significant extent, in those treatments receiving the combined light and sound change. It was concluded that properties of the sensory stimuli other than their reward value per se (non drug) may also be related to the extent of SCBP enhancement under the drug mixture. In particular, properties of the sound offset reinforcer appear to make it more amenable to enhancement under the drug than the two light reinforcers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glow, P. H., Russell, A.: The effects of dexamphetamine, amylobarbitone sodium and their mixture on sensory contingent bar pressing behaviour in the rat. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 31, 239–251 (1973a)
Glow, P. H., Russell, A.: Drug enhanced sensory contingent bar pressing: Comparing the effects of contingent and non-contingent sensory change. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 32, 285–292 (1973b)
Glow, P. H., Russell, A.: Sensory contingent bar pressing for familiar and novel change under a dexamphetamine-amylobarbitone mixture. Anim. Learning Behav. 2, 27–30 (1974)
Glow, P. H., Russell, A., Kirby, N. H.: Sensory reinforcement using paired stimuli from different modalities. Aust. J. psychol. 23, 133–137 (1971)
Kumar, R.: Extinction of fear. I. Effects of amylobarbitone and dexamphetamine given separately and in combination on fear and exploratory behaviour in rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 19, 163–187 (1971)
Rushton, R., Steinberg, H.: Mutual potentiation of amphetamine and amylobarbitone measured by activity in rats. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 21, 295–305 (1963)
Weijnen, J. A. W. M.: Effects of amphetamine-amylobarbitone mixtures on ambulation of rats in the Y-maze. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 5, 180–184 (1969)
Winer, B. J.: Statistical principles in experimental designs. New York: McGraw-Hill 1970
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glow, P.H., Russell, A. The effects of a dexamphetamine-amylobarbitone sodium mixture on the reward value of different sensory changes. Psychopharmacologia 41, 181–185 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421077
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421077