Abstract
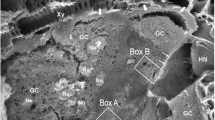
In-vivo differential interference contrast microscopy was used to detect individual Golgi vesicles and a new structure in the tip of fast-growing rhizoids of Chara fragilis Desvaux. This structure is a spherical clear zone which is free of Golgi vesicles, has a diameter of 5 μm and is positioned in the center of the apical Golgi-vesicle accumulation (“Spitzenkörper”). After glutaraldehyde fixation and osmium tetroxide-potassium ferricyanide staining of the rhizoid, followed by serial sectioning and three-dimensional reconstruction, the spherical zone shows a tight accumulation of anastomosing endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membranes. The ER membranes radiate from this aggregate towards the apical plasmalemma and to the membranes of the statolith compartments. Upon gravistimulation the ER aggregate changes its position according to the new growth direction, indicating its participation in growth determination. After treatment of the rhizoid with cytochalasin B or phalloidin the ER aggregate disappears and the statoliths sediment. It is concluded that the integrity of the ER aggregate is actin-dependent and that it is related to the polar organisation of the gravitropically growing cell tip.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CB:
-
cytochalasin B
- DIC:
-
differential interference contrast microscopy
- DMSO:
-
dimethyl sulfoxide
- ER:
-
endoplasmic reticulum
References
Bojovic-Cvetic, D., Vujicie, R. (1980) Membraneous aggregates in hyphal tips of Aspergillus flavus. Arch. Mikrobiol. 126, 245–249
Brunswik, H. (1924) Untersuchungen über die Geschlechts- und Kernverhältnisse bei der Hymenomycetengattung Coprinus. Bot. Abhandlungen 5, 1–152
Buder, J. (1961) Der Geotropismus der Characeenrhizoide. Ber. Dtsch. Bot. Ges. 74, (14)-(23)
Forsberg, C. (1965) Nutritional studies of Chara in axenic cultures. Physiol. Plant. 18, 275–290
Franke, W.W., Herth, W., Vanderwoude, W.J. Morré, D.J. (1972) Tubullar and filamentous structures in pollen tubes: Possible involvement as guide elements in protoplasmic streaming and vectorial migration of secretory vesicles. Planta 105, 317–341
Friedrich, U., Hertel, R. (1973) Abhängigkeit der geotropischen Krümmung der Chara-Rhizoide von der Zentrifugalbe-schleunigung. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 70, 173–184
Girbardt, M. (1965) Lebendnachweis von Einzelelementen des endoplasmatischen Retikulums. J. Cell Biol. 27, 433–440
Girbardt, M. (1969) Die Ultrastruktur der Apikalregion von Pilzhyphen. Protoplasma 67, 413–441
Grove, S.N., Bracker, C.E., Morré, D.J. (1970) An ultrastructural basis for hyphal tip growth in Phytium ultimum. Am. J. Bot. 57, 245–266
Hejnowicz, Z., Heinemann, B., Sievers, A. (1977) Tip growth: Patterns of growth rate and stress in the Chara rhizoid. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 81, 409–424
Hejnowicz, Z., Sievers, A. (1981) Regulation of the position of statoliths in Chara rhizoids Protoplasma 108, 117–137
Hepler, P.K. (1981) The structure of the endoplasmic reticulum revealed by osmium-tetroxide ferricyanide staining. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 26, 102–110
Martin, M., Gay, J.L. (1983) Ultrastructure of conidium development in Erysiphe pisi. Can. J. Bot. 61, 2472–2495
Newcomb, E.H., Bonnett, H.T. (1965) Cytoplasmic microtubule and wall microfibril orientation in root hairs of radish. J. Cell Biol. 27, 575–589
Reiss, H.D., Herth, W. (1979) Calcium ionophore A 23187 affects localized wall secretion in the tip region of pollen tubes of Lilium longiflorum. Planta 145, 225–232
Reynolds, E.S. (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212
Rosen, W.G. (1968) Ultrastructure and physiology of pollen. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 19, 435–462
Sassen, M.M.A. (1964) Fine structure of Petunia pollen grain and pollen tube. Acta Bot. Neerl. 13, 175–181
Schmiedel, G., Schnepf, E. (1980) Polarity and growth of caulonema tip cells of the moss Funaria hygrometrica. Planta 147, 405–413
Schnepf, E. (1986) Cellular polarity. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 37, 23–47
Schroeder, H. (1904) Zur Statolithentheorie des Geotropismus. Beih. Bot. Centralbl. 16, 269–288
Schröter, K., Läuchli, A., Sievers, A. (1975) Mikroanalytische Identifikation von Bariumsulfat-Kristallen in Statolithen der Rhizoide von Chara fragilis Desv. Planta 122, 213–255
Sievers, A. (1963a) Beteiligung des Golgi-Apparates bei der Bildung der Zellwand von Wurzelhaaren. Protoplasma 56, 188–192
Sievers, A. (1963b) Über die Feinstruktur des Plasmas wachsender Wurzelhaare. Z. Naturforsch. 18c, 830–836
Sievers, A. (1965) Elektronenoptische Untersuchungen zur geotropischen Reakton: I. Besonderheiten im Feinbau der Rhizoide von Chara foetida. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 53, 193–213
Sievers, A. (1967a) Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zur geotropischen Reaktion. II. Die polare Organisation des normal wachsenden Rhizoids von Chara foetida. Protoplasma 64, 225–253
Sievers, A. (1967b) Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zur geotropischen Reaktion. III. Die transversale Polarisierung der Rhizoidspitze von Chara foetida nach 5 bis 10 Minuten Horizontallage. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 57, 462–473
Sievers, A., Heinemann, B., Rodriguez-Garcia, M.I. (1979) Nachweis des subapikalen differentiellen Flankenwachstums im Chara-Rhizoid während der Graviresponse. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 91, 435–442
Sievers, A., Schmitz, M. (1982) Röntgen-Mikroanalyse von Barium, Schwefel und Strontium in Statolithen-Kompartimenten von Chara-Rhizoiden. Ber. Dtsch. Bot. Ges. 95, 353–360
Sievers, A., Schnepf, E. (1981) Morphogenesis and polarity of tubular cells with tip growth. In: Cytomorphogenesis in plants, pp. 265–299, Kiermayer, O., ed. Springer, Wien New York
Sievers, A., Schröter, K. (1971) Versuch einer Kausalanalyse der geotropischen Reaktionskette im Chara Rhizoid. Planta 96, 339–353
Spurr, A.R. (1969) A low viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 26, 31–43
Steudle, E., Läuchli, A., Sievers, A. (1978) X-ray microanalysis of barium and calcium in plant material: Significance for the analysis of statoliths. Z. Naturforsch. 33c, 444–446
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bartnik, E., Sievers, A. In-vivo observations of a spherical aggregate of endoplasmic reticulum and of Golgi vesicles in the tip of fast-growing Chara rhizoids. Planta 176, 1–9 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392473
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392473