Abstract
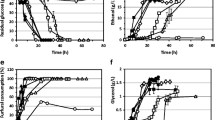
Batch growth of the yeasts Candida utilis, Pachysolen tannophilus and Pichia stipitis on 1% D-xylose was monitored using a commercial fluorosensor with an excitation wavelength of 340 nm and a detection wavelength of 460 nm. Step changes in oxygen concentration were made and in the presence of 0.3 g/l of xylose, step changes from aerobic to anaerobic conditions resulted in an increase of the fluorescence level by about 40% for the non-fermentative yeast C. utilis. However, the increases of the fluorescence levels for P. tannophilus and P. stipitis stayed below 10%. These measurements indicate better control of (or better redox balance for) intracellular NADH concentration in P. tannophilus and P. stipitis than in C. utilis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- F NFU:
-
fluorescence
- F 0 NFU:
-
initial fluorescence
- ΔF NFU:
-
final fluorescence difference
- t s:
-
time
- τ s:
-
time constant
References
Prior, B. A.; Kilian, S. G.; du Preez, J. C.: Fermentation of D-xylose by the yeasts Candida shehatae and Pichia stipitis. Prospects and problems. Proc. Biochem. Febr. (1989) 21–32
Jeffries, T. W.: Utilization of xylose by bacteria, yeasts and fungi. Adv. in Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 27 (1983) 1–32
Slininger, P. J.; Bothast, R. J.; van Cauwenberge, J. E.; Kurtzman, C. P.: Conversion of D-xylose to ethanol by the yeast Pachysolen tannophilus. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 24 (1982) 371–384
Slininger, P. J.; Bothast, R. J.; Okos, M. R.; Ladisch, M. R.: Comparative evaluation of ethanol production by xylose-fermenting yeasts presented high xylose concentrations. Biotechnol. Lett. 7 (1985) 431–436
Nunez, Ma. J.; Sanroman, A.; Lopez, E.; Vazquez, G.; Lema, J. M.: The D-xylose fermenting capacities of immobilized Pichia stipitis and Pachysolen tannophilus. Biotechnol. Lett. 11 (1989) 353–358
Bruinenberg, P. M.; de Bot, P. H. M.; van Dijken, J. P.; Scheffers, W. A.: The role of redox balances in the anaerobic fermentation of xylose by yeasts. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 18 (1983) 287–292
Bruinenberg, P. M.; de Bot, P. H. M.; van Dijken, J. P.; Scheffers, W. A.: NADH-linked aldose reductase: The key to anaerobic alcoholic fermentation of xylose by yeasts. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 19 (1984) 256–260
du Preez, J. C.; van Driessel, B.; Prior, B. A.: Effect of aerobiosis on fermentation and key enzyme levels during growth of Pichia stipitis, Candida shehatae and Candida tenuis on D-xylose. Arch. Microbiol. 152 (1989 b) 143–147
Scheper, Th.; Schügerl, K.: Culture fluorescence studies on aerobic continuous cultures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 23 (1986) 440–444
Scheper, Th.; Lorenz, Th.; Schmidt, W.; Schügerl, K.: On-line measurement of culture fluorescence for process monitoring and control of biotechnological processes. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 506 (1987) 431–445
Harrison, D. E. F.; Chance, B.: Fluorimetric technique for monitoring changes in the level of reduced nicotinamide nucleotides in continuous cultures of microorganisms. Appl. Microbiol. 19 (1970) 446–450
Rieger, M.: Untersuchung zur Regulation von Glykolyse und Atmung in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PhD thesis, ETH Zürich Switzerland 1983
Rao, G.; Mutharasan, R.: NADH levels and solventogenesis in Clostridium acetobutylicum: new insights through culture fluorescence. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 30 (1989) 59–66
Armiger, W. B.; Forro, J. F.; Montalvo, L. M.; Lee, J. F.: The interpretation of on-line measurements of intracellular NADH in fermentation processes. Chem. Eng. Commun. 45 (1986) 197–206
Grosz, R.; Stephanopoulos, G.: Physiological, biochemical, and mathematical studies of micro-aerobic continuous ethanol fermentation by saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Intracellular metabolite and enzyme assays at steady state chemostat cultures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 36 (1990) 1020–1029
Lidén, G.; Larsson, C.; Gustafsson, L.; Niklasson, C.: A calorimetric and fluorescence study of batch cultures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 31 (1989) 355–357
Delgenes, J. P.; Moletta, R.; Navarro, J. M.: Fermentation of D-xylose, D-glucose, L-arabinose mixture by Pichia stipitis: Effect of the oxygen transfer rate on fermentation performance. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 34 (1989) 398–402
du Preez, J. C.; Prior, B. A.; Monteiro, A. M. T.: The effect of aeration on xylose fermentation by Candida shehatae and Pachysolen tannophilus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 19 (1984) 261–266
Coppella, S. J.; Rao, G.: Practical considerations in the measurement of culture fluorescence. Biotechnol. Prog. 6 (1990) 398–401
Bailey, J. E.; Ollis, D. F.: Biochemical engineering fundamentals. 2nd ed., New York: McGraw Hill 1986
Coughanowr, D. R.; Koppel, L. B.: Process systems analysis and control. Tokyo: McGraw-Hill 1965
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lidén, A.G., Niklasson, C. Fluorescence measurements under aerobic and anaerobic conditions on Pichia stipitis, Pachysolen tannophilus and Candida utilis grown on D-xylose. Bioprocess Engineering 7, 219–224 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369549
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369549