Summary
Isolated rat papillary muscles were stimulated electrically in a 50 ml. Tyrode bath at 37°C. Potentiation of contractile force following a period of rest and post-stimulation potentiation were studied.
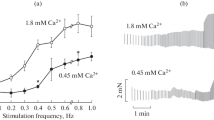
A potentiation of contractile force increased with an increase in the period of rest up to 32 secs. Post-stimulation potentiation was observed following short periods of high frequency stimulation. The changes in the duration of stimulation (from 7,5 up to 60 secs.) had no significant influence on the degree of post-stimulation potentiation. An increase in frequency of stimulation (from 10 to 40 per sec.) caused an increase in post-stimulation potentiation.
The possibility of a release of a “post-stimulation substance” is discussed. It is suggested that such a hypothetical substance may be pharmacologically similar to sympathomimetic amines.
The “Treppe” phenomenon in isolated papillary muscles of cats and rats is different, when the potentiation of contractile force following a period of rest and post-stimulation potentiation are similar in both species. It is therefore suggested that different mechanisms may be responsible for these phenomena.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Benforado, J. M.: Frequency-dependent pharmacological and physiological effects of the rat ventricle strip. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 122, 86 (1958).
Cattell, McK., and H. Gold: The influence of digitalis glucosides on the force of contraction of mammalian cardiac muscle. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 62, 116 (1938).
Relation of rhythm to force of contraction of mammalian cardiac muscle. Amer. J. Physiol. 182, 307 (1955).
Garb, S., and M. Penna: Some quantitative aspects of the relation of rhythm to the contractile force of mammalian ventricular muscle. Amer. J. Physiol. 182, 601 (1955).
Garb, S., M. Penna and A. Scriabine: Species differences in the utilisation of glucose for contractile force by isolated perfused hearts. Amer. J. Physiol. 180, 103 (1955).
Hollander, P. B., and J. L. Webb: Cellular membrane potentials and contractility of normal rat atrium and the effects of temperature tension and stimulus frequency. Circulat. Res. 3, 604 (1955).
Kuschinsky, G., u. E. Muscholl: Die Wirkung von Theophyllin, Coffein und Theobromin auf Kontraktionskraft, Erregbarkeit, Refraktärzeit und Spontanfrequenz des isolierten Herzmuskel der Katze. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 229, 348 (1956).
Lüllmann, H.: Die Wirkung von Coffein und Theophyllin auf den Herzmuskel. Arch. Kreisl.-Forsch. 23, 11 (1955).
Penna, M., and S. Garb: Relationship of changes in ionic concentrations to the augmentation produced by extra contractions in isolated mammalian ventricular muscle. Amer. J. Physiol. 184, 572 (1956).
Rosin, H., and A. Farah: Post-stimulation potentiation of contractility in the isolated auricle of the rabbit. Amer. J. Physiol. 180, 75 (1955).
Whalen, W. J., N. Fishman and R. Erickson: Nature of the potentiating substance in cardiac muscle. Amer. J. Physiol. 194, 573 (1958).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit 2 Textabbildungen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scriabine, A. Über die Änderung der Kontraktionsamplitude des elektrisch gereizten Rattenpapillarmuskels nach einer Reizpause oder einer Periode hochfrequenter Reizung. Pflügers Archiv 269, 311–318 (1959). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00362201
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00362201