Abstract
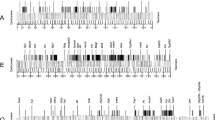
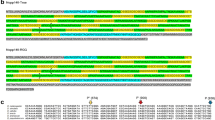
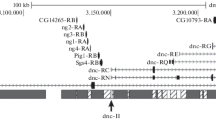
The Pre-intermoult gene-1 (Pig-1) of Drosophila melanogaster maps on the X chromosome, at polytene bands 3C11–12, and is nested within the 79 kb intron of the dunce gene. Pig-1 has so far been characterized only preliminarily and its function is still unknown. We analysed the molecular organization of the gene by cDNA clone isolation and sequencing as well as S1 mapping and primer extension analyses. The results obtained reveal that the gene is colinear with its genomic sequence and define the usage of both 5′ and 3′ alternative sites for Pig-1 transcription; two continuous open reading frames (ORFs) are fully contained within the Pig-1 transcribed region, although several lines of evidence suggest that only the longer ORF is likely to be translated. We also report that the level of Pig-1 transcript is nearly fourfold reduced in a variant strain carrying a deletion within the Pig-1 upstream sequence, thus identifying a regulatory element required for high level gene expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashburner M (1975) Puffing patterns in Drosophila. In: Ashburner M, Wright TRF (eds) The genetics and biology of Drosophila, vol 3. Academic Press, London, pp 793–811
Birnstiel ML, Busslinger N, Strub K (1985) Transcription termination and 3′ processing: the end is in site! Cell 41: 349–359
Cavener DR (1987) Comparison of the consensus sequence flanking transcriptional start site in Drosophila and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res 15: 1353–1361
Chen C, Malone T, Beckendorf SK, Davis RL (1987) At least two genes reside within a large intron of the dunce gene of Drosophila. Nature 329: 721–724
Chirgwin JJ, Przbyla AE, MacDonald RJ, Rutter WJ (1979) Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry 18: 5294–5299
Furia M, Digilio FA, Artiaco D, Giordano E, Polito LC (1990) A new gene nested within the dunce genetic unit of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res 18: 5837–5841
Gil A, Proudfoot NJ (1987) Position-dependent sequence elements downstream the AAUAAA are required for rabbit β-globin mRNA 3′ end formation. Nature 312: 473–474
Hofmann A, Korge G (1987) Upstream sequences of dosage-compensated and non-compensated alleles of the larval secretion protein gene Sgs-4 in Drosophila. Chromosoma 96: 1–7
Kaiser K, Furia M, Glover DM (1986) Dosage compensation at the Sgs-4 locus of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol 187: 529–536
Kozak M (1984) Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 12: 857–872
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
McGinnis W, Shermoen AW, Heemskerk J, Beckendorf SK (1983) DNA sequence changes in an upstream DNAase1-hypersensitive region are correlated with reduced gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80: 1063–1067
Meyerowitz EM, Raghavan KV, Mathers PH, Roark M (1987) How Drosophila make glue: control of Sgs-3 gene expression. Trend Genetics 3: 288–293
Muskavitch MAT, Hogness DS (1980) Molecular analysis of a gene in a developmentally regulated puff of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77: 7362–7366
Muskavitch MAT, Hogness DS (1982) An expendable gene that encodes a Drosophila glue protein is not expressed in variant strains lacking remote upstream sequences. Cell 29: 1041–1051
O'Connell P, Rosbash M (1984) Sequence, structure and codon preference of the Drosophila ribosomal protein 49 gene. Nucleic Acids Res 12: 5495–5513
Shermoen AW, Jongens J, Bornett SW, Flynn K, Beckendorf SK (1987) Developmental regulation by an enhancer from the Sgs-4 gene of Drosophila. EMBO J 6: 207–214
Staden R (1984) Measurements of the effects that coding a protein has on a DNA sequence and their use for finding genes. Nucleic Acids Res 12: 551–567
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
by F. Amaldi
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furia, M., Digilio, F.A., Artiaco, D. et al. Molecular organization of the Drosophila melanogaster Pig-1 gene. Chromosoma 101, 49–54 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00360686
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00360686