Abstract
-
1.
Incubation of trichloroethylene, 1,1-dichloroethylene, vinylchloride, tetra-chlorocyclopentadiene, the nitroso derivatives of the pesticides Carbaryl, Prometryn, and Dodin in the presence of metabolically active mouse liver microsomes and bacteria as target cells were mutagenic, whereas tetrachloroethylene, 1,2 cis-and transdichloroethylene, hexachlorocyclopentadiene, carbontetrachloride, chloroform, halothane, trichlorofluoromethane and styrene were not activated to mutagenic species.
-
2.
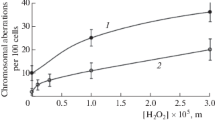
In a similar in vitro test system using freshly isolated human lymphocytes as target cells dimethylnitrosamine induced chromosomal aberrations.
-
3.
It is concluded from the experiments that submammalian or mammalian in vitro cell systems with metabolically active liver microsomes are not only suitable to screen for chemical mutagens but to demonstrate formation of reactive intermediates, which are short lived and cannot be detected by chemical procedures.
Zusammenfassung
-
1.
Trichloräthylen, 1,1-Dichloräthylen, Vinylchlorid, Tetrachlorzyklopentadien sowie die Nitrosoderivate der Pestizide Karbaryl, Prometryn und Dodin wurden von metabolisch aktiven Mäuselebermikrosomen zu reaktiven Zwischenprodukten umgesetzt, die für zugesetzte Testbakterien mutagen waren. Tetrachloräthylen, 1,2 cisund trans-Dichloräthylen, Hexachlorzyklopentadien, Tetrachlorkohlenstoff, Chloroform, Halothan, Trichlorfluormethan und Styrol zeigten im Testsystem keine Mutagenität, während Styrolepoxid ohne metabolische Aktivierung mutagen war.
-
2.
In einem metabolisch aktiven System mit frisch präparierten menschlichen Lymphozyten als Testorganismen induzierte Dimethylnitrosamin Chromosomenaberrationen.
-
3.
Die Untersuchungsergebnisse zeigen, daß sich metabolisierende in vitro Testsysteme mit Bakterien oder Säugetierzellen als Testorganismen nicht nur für Routineuntersuchungen zum Nachweis mutagener Umweltchemikalien eignen sondern auch zum Nachweis reaktiver Metaboliten, die aufgrund ihrer geringen Stabilität mit chemischen Methoden nicht erfaßbar sind.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames, B. N., Gurney, E. G., Miller, J. A., Bartsch, H.: Carcinogens as frameshift mutagens: metabolites and derivatives of 2-acetyl-aminofluorene and other aromatic amine carcinogens. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 69, 3128–3132 (1972)
Ames, B. N., Durston, W. E., Yamasaki, E., Lee, D. F.: Carcinogens are mutagens: a simple test system combining liver homogenates for activation and bacteria for detection. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. 8, 2281–2285 (1973)
Ames, B. N., McCann, J., Yamasaki, E.: Methods for detecting carcinogens and mutagens with the Salmonella/mammalian microsome mutagenicity test. Mutation Res. 31, 347–361 (1975)
Bartsch, H., Camus, A., Malaveille, C.: Comparative mutagenicity of N-nitrosamines in a semisolid and a liquid incubation system in the presence of rat or human tissue fractions. Mutation Res. 37, 149–162 (1976)
Bimboes, D., Greim, H.: Human lymphocytes as target cells in a metabolizing test system in vitro for detecting potential mutagens. Mutation Res. 35, 155–160 (1976)
Bonse, G., Göggelmann, W.: Mutagenicity of chlorinated cyclopentadienes due to metabolic activation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 297, R87 (1977)
Cooper, J. T., Goldstein, S.: Toxicity testing in vitro. II. Use of a microsome-cultured human fibroblast system to study the cytotoxicity of cyclophosphamide. Canad. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 54, 546–550 (1976)
Creech, J. L., Johnson, M. N.: Angiosarcoma of the liver in the manufacture of Polyvinylchloride. J. occup. Med. 16, 150–151 (1974)
Czygan, P., Greim, H., Garro, A. J., Hutterer, F., Rudick, J., Schaffner, F., Popper, H.: Cytochrome P-450 content and the ability of liver microsomes from patients undergoing abdominal surgery to alter the mutagenicity of a primary and a secondary carcinogen. J. nat. Cancer Inst. 51, 1761–1764 (1973a)
Czygan, P., Greim, H., Garro, A. J., Hutterer, F., Schaffner, F., Popper, H., Rosenthal, O., Cooper, D. Y.: Microsomal metabolism of dimethylnitrosamine and the cytochrome P-450 dependency of its activation to a mutagen. Cancer Res. 33, 2983–2986 (1973b)
Czygan, P., Greim, H., Garro, A. J., Schaffner, F., Popper, H.: The effect of dietary protein deficiency on the ability of isolated hepatic microsomes to alter the mutagenicity of a primary and a secondary carcinogen. Cancer Res. 34, 119–123 (1974)
Egert, G., Greim, H.: Formation of mutagenic N-nitroso compounds from the pesticides Prometryne, Dodine and Carbaryl in the presence of nitrite at pH 1. Mutation Res. 37, 179–186 (1976)
Eisenbrand, G., Ungerer, O., Preussmann, R.: The reaction of nitrite with pesticides. II. Formation, chemical properties and carcinogenic activity of the N-nitroso derivative of N-methyl-1-naphthyl carbamate (Carbaryl). Food Cosmet. Toxicol. 13, 365–367 (1975)
Elespuru, R. D., Lijinsky, W.: The formation of carcinogenic nitroso compounds from nitrite and some types of agricultural chemicals. Food Cosmet. Toxicol. 11, 807–817 (1973)
Ellenberger, J., Mohn, G.: Mutagenic activity of cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, and trofosfamide in different genes of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium after biotransformation through extracts of rodent liver. Arch. Toxicol. 33, 225–240 (1975)
Frantz, C. N., Malling, H. V.: Bromodeoxyuridine resistance induced in mouse lymphoma cells by microsomal activation of dimethylnitrosamine. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2, 179–187 (1976)
Gelboin, H. V.: A microsome dependent binding of benzo(a)pyrene to DNA. Cancer Res. 29, 1272–1276 (1969)
Gillette, J. A.: A perspective on the role of chemically reactive metabolites of foreign compounds in toxicity. I. Correlation of changes in covalent binding of reactivity metabolites with changes in the incidence and severity of toxicity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 23, 2785–2791 (1974a)
Gillette, J. A.: A perspective on the role of chemically reactive metabolites of foreign compounds in toxicity. II. Alterations in the kinetics of covalent binding. Biochem. Pharmacol. 23, 2927–2938 (1974b)
Greim, H., Bonse, G., Radwan, Z., Reichert, D., Henschler, D.: Mutagenicity in vitro and potential carcinogenicity of chlorinated ethylenes as a function of metabolic oxirane formation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 24, 2013–2017 (1975)
Heath, C. W., Falk, H., Creech, J. L.: Characteristic cases of angiosarcoma of the liver among vinyl chloride workers in the United States. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 246, 231–236 (1975)
Heidelberger, C.: Chemical carcinogenesis. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 44, 79–119 (1975)
Henschler, D.: Metabolic activation of chlorinated ethylenes: dependence of mutagenic effect on electrophilic reactivity of the metabolically formed epoxides. Arch. Toxicol. 39, 7–12 (1977)
Judah, J. D., McLean, A. E. M., McLean, E. K.: Biochemical mechanisms of liver injury. Amer. J. Med. 49, 609–616 (1970)
Kappus, H., Bolt, H. M., Remmer, H.: Irreversible protein binding of metabolites of ethynylestradiol in vivo and in vitro. Steroids 22, 203–225 (1974)
Kappus, H., Bolt, H. M.: Irreversible binding of norethisterone (Norethindrone) epoxide. Steroids 27, 29–45 (1976)
Leibman, K. C., Ortiz, E.: Oxidation of styrene in liver microsomes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 18, 552–554 (1969)
Leibman, K. C., Ortiz, E.: Epoxide intermediates in microsomal oxidation of olefins to glycols. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 173, 242–246 (1970)
Leibman, K. C.: Metabolism and toxicity of styrene. Environm. Health Perspectives 11, 115–119 (1975)
Loprieno, N., Abbandandolo, A., Barale, R., Baroncelli, S., Bonatti, S., Bronzetti, G., Cammellini, A., Corsi, C., Corti, G., Frezza, D., Leporini, C., Mazzaccaro, A., Nieri, R., Rosellini, D., Rossi, A. M.: Mutagenicity of industrial compounds: Styrene and its possible metabolite styrene oxide. Mutation Res. 40, 317–324 (1976)
Maling, H. M., Eichelbaum, F. M., Saul, G., Sipes, J. G., Brown, E. A. B., Gillette, J. R.: Nature of the protection against carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity produced by pretreatment with dibenamine [N-(2-chloroethyl) dibenzylamine]. Biochem. Pharmacol. 23, 1479–1491 (1974)
Malling, H. V.: Dimethylnitrosamine: Formation of mutagenic compounds by interaction with mouse liver microsomes. Mutation Res. 13, 425–429 (1971)
Malling, H. V., Frantz C. N.: Metabolic activation of dimethylnitrosamine and diethylnitrosamine to mutagens. Mutation Res. 25, 179–186 (1974)
McLean, A. E. M.: Conversion by the liver of inactive molecules into toxic molecules. In: Selectivetoxicity (Adrien Albert, ed.), Vth ed., pp. 219–228. London: Chapman & Hall 1973
Memorandum, Dept. of Health, Education and Welfare, Washington, 20. 3. 1975
Miller, J. A., Miller, E. C.: The metabolic activation of carcinogenic aromatic amines and amides. Progr. exp. Tumor Res. 11, 273–301 (1969)
Miller, J. A.: Carcinogenesis by chemicals: An overview. Cancer Res. 30, 559–576 (1970)
Milvy, P., Garro, A. J.: Mutagenic activity of styrene oxide (1,2-epoxyethyl benzene), a presumed styrene metabolite. Mutation Res. 40, 15–18 (1976)
Mitchell, J. R., Jollow, D. J., Gillette, J. R., Brodie, B. B.: Drug metabolism as a cause of drug toxicity. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1, 418–423 (1973)
Mohn, G., Ellenberger, J., McGregor, D.: Development of mutagenicity tests using E. coli K 12 as indicator organisms. Mutation Res. 25, 187–196 (1974)
Natarajan, A. T., Tates, A. D., Van Buul, P. P. W., Meijers, M., De Vogel, N.: Cytogenetic effects of mutagens/carcinogens after activation in a microsomal system in vitro. I. Induction of chromosome aberrations and sister chromatid exchanges by diethylnitrosamine (DEN) and dimethylnitrosamine (DMN) in CHO cells in the presence of rat liver microsomes. Mutation Res. 37, 83–90 (1976)
Ohtsuji, H., Ikeda, M.: The metabolism of styrene in the rat and the stimulatory effect of phenobarbital. Toxicol. appl. Pharmacol. 18, 321–328 (1971)
Perry, P., Evans, H. J.: Cytological detection of mutagen-carcinogen exposure by sister chromatid exchange. Nature (Lond.) 258, 121–125 (1975)
Popper, H., Czygan, P., Greim, H., Schaffner, F., Garro, A.: Mutagenicity of primary and secondary carcinogens altered by normal and induced hepatic microsomes. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.) 142, 727–729 (1973)
Purchase, I. F. H., Longstaff, E., Ashby, J., Styles, J. A., Anderson, D., Lefevre, P. A., Westwood, F.R: Evaluation of six short term tests for detecting organic chemical carcinogens and recommendations for their use. Nature (Lond.) 264, 624–527 (1976)
Purchase, I. F. H., Longstaff, E., Ashby, J., Styles, J. A., Anderson, D., Lefevre, P. A., Westwood, F. R.: Short term testing for carcinogens. Arch. Toxicol. 39, 171 (1977)
Recknagel, R. O.: Carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity. Pharmacol. Rev. 19, 145–208 (1967)
Regan, J. D., Setlow, R. B., Francis, A. A., Lijinsky, W.: Nitrosocarbaryl: Its effect on human DNA. Mutation Res. 38, 293–302 (1976)
San, R. H. C., Stich, H. F.: DNA repair synthesis of cultured human cells as a rapid bioassay for chemical carcinogens. Int. J. Cancer 16, 284–291 (1975)
Sander, J., Bürkle, G.: Induktion maligner Tumoren bei Ratten durch gleichzeitige Verfütterung von Nitrit und sekundären Aminen. Z. Krebsforsch. 73, 54–66 (1969)
Slater, T. F.: Necrogenic action of carbon tetrachloride in the rat: a speculative mechanism based on activation. Nature (Lond.) 209, 36–40 (1966)
Solomon, E., Bubrow, M.: Sister chromatid exchanges. — A sensitive assay of agents damaging human chromosomes. Mutation Res. 30, 273–278 (1975)
Stetka, D. G., Wolff, S.: Sister chromatid exchanges as an assay for genetic damage induced by mutagens-carcinogens. II. In vitro test for compounds requiring metabolic activation. Mutation Res. 41, 343–350 (1976)
Stich, H. F., Stich, W., San, R. H. C.: Elevated frequency of chromosome aberrations in repairdeficient human cells exposed to the carcinogen and mutagen 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.) 142, 1141–1144 (1973)
Sugimura, T., Yahagi, T., Nagao, M., Takeuchi, M., Kawachi, T., Hara, K., Yamasaki, E., Matsushima, T., Hashimoto, Y., Okada, M.: Validity of mutagenicity tests using microbes as a rapid screening method for environmental carcinogens. In: Screening tests in chemical carcinogenesis (R. Montesano, H. Bartsch, L. Tomatis, eds.). IARC Scientific Publ. 12, 81–101 (1976)
Uehleke, H.: The model system of microsomal drug activation and covalent binding to endoplasmic proteins. Excerpta Med. Int. Congr. Ser. 311, 119–129 (1973)
Uehleke, H., Werner, T., Greim, H., Krämer, M.: Metabolic activation of haloalkanes and in vitro tests for mutagenicity. Xenobiotica 7, 393–400 (1977)
Viola, Bigotti, Caputo: In: The predictive value of tissue-mediated mutagenicity assays to assess the carcinogenic risk of chemicals (H. Bartsch, C. Malaveille, R. Montesano, eds.). IARC-Scientific Publ. 12, 479 (1976)
Watabe, R., Maynert, E. W.: Role of epoxides in the metabolism of olefins. Pharmacologist 10, 203 (1968)
Williams, G.: Carcinogen-induced DNA repair in primary rat liver cell cultures: a possible screen for chemical carcinogens. Cancer Lett. 1, 231–236 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greim, H., Bimboes, D., Egert, G. et al. Mutagenicity and chromosomal aberrations as an analytical tool for in vitro detection of mammalian enzyme-mediated formation of reactive metabolites. Arch. Toxicol. 39, 159–169 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00343283
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00343283