Summary
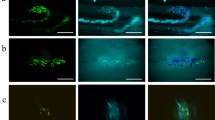
After staining of the motor nerve endings with a cholinesterase technique and of nerve and muscle fibers with Sudanschwarz B, single muscle spindles were isolated from lumbrical muscles of rats and examined by means of light microscopy.
Two types of intrafusal muscle fibres were found: a) pale ones corresponding to nuclear bag fibres and b) dark ones corresponding to nuclear chain fibres.
On both types of muscle fibres distinct motor end plates were observed; two types of endplates can be distinguished: a) Larger ones consisting of circular subunits in loose arrangement; they occur on pale muscle fibres only. Their number per muscle fibre pole may amount up to three, b) Smaller ones with more compact arrangement of their subunits occurring on dark fibres only. Their number per muscle fibre pole never exceeds one.
Besides these distinct endplates with more mid-polar positions, a second kind of motor nerve ending is to be found in the juxtaequatorial region of every spindle pole: the multiterminal motor ending. These endings are located predominantly on pale intrafusal muscle fibres.
An often very thin γ-fibre leads to every juxtaequatorial region, looses its myelin sheath and divides into several thin branches; these non-myelinated axon-branches may be observed over rather long distances, finally forming the multiterminal endings.
Every distinct motor endplate receives its own — usually somewhat thicker—γ-fibre which looses its myelin sheath immediately before its termination at the endplate. The terminal parts of these fibres show no branching.
The dark intrafusal muscle fibres receiving one motor end plate only, correspond to those intrafusal fibres of the rat which, according to other authors, show properties of twitch fibres. The pale fibres receiving multiterminal endings and multiple motor endplates, correspond to fibres which show some criteria of slow fibres.
Zusammenfassung
An isolierten Muskelspindeln aus Lumbrical-Muskeln der Ratte, deren motorische Endigungen mit einer Cholinesterase-Technik dargestellt, deren Nerven- und Muskelfasern mit Sudanschwarz gefärbt worden waren, wurden lichtmikroskopisch folgende Befunde erhoben: Es gibt 2 Typen intrafusaler Muskelfasern: a) helle, den „nuclear bag fibres“ entsprechende, b) dunkle, den „nuclear chain fibres“ entsprechende.
An beiden Fasertypen kommen distinkte motorische Endplatten vor, die gleichfalls in zwei Typen differenzierbar sind: a) Größere, aus locker gefügten, runden Untereinheiten bestehende; diese befinden sich nur an den hellen Fasern. Ihre Anzahl an jedem Polabschnitt kann bis zu drei betragen. b) Kleinere, kompakter gebaute motorische Endplatten; diese liegen nur an den dunklen intrafusalen Fasern, je Faserpol maximal eine.
Außer den mehr in Polmitte liegenden distinkten Endplatten sieht man in den paraäquatorialen Polabschnitten regelmäßig eine zweite Art intrafusaler motorischer Nervenendigungen: die multiterminalen motorischen Endigungen. Diese an jedem Spindelpol sichtbaren Endigungen sind vorwiegend an den hellen intrafusalen Fasern lokalisiert.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Adal, M. N., and D. Barker: Intramuscular branching of fusimotor fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond). 177, 288–299 (1965).
Barker, D.: The innervation of the muscle spindle. Quart. J. micr. Sci. 89, 143–186 (1948).
—: The motor innervation of the mammalian muscle spindle. In: Nobel Symposium I: Muscular afferents and motor control (R. Granit, ed.), S. 51–58. Stockholm: Almqvist and Wiksell (1966a).
—: Three types of motor ending in cat spindles. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 186, 27–28P (1966b).
—: The innervation of mammalian skeletal muscle. In: Ciba Foundation Symposium on myotatic, kinesthetic and vestibular mechanisms (A. V. S. de Reuck and J. Knight, eds.), S. 3–15. London: J. u. A. Churchill Ltd. 1967.
—, and J. P. Hunt: Mammalian intrafusal muscle fibres. Nature (Lond.) 203, 1193 (1964).
—, and M. C. Ip: The motor innervation of cat and rabbit muscle spindles. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 177, 27–28P (1965).
Boyd, I. A.: The nuclear-bag fibre and nuclear-chain fibre systems in the muscle spindles of the cat. In: Symposium on muscle receptors (D. Barker, ed.), S. 185–190. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press 1962 (a).
—: The structure and innervation of the nuclear bag muscle fibre system and the nuclear chain muscle fibre system in mammalian muscle spindles. Phil. Trans. B 245, 81–136 (1962b).
—: Diskussionsbeitrag am Nobel Symposium I: Muscular afferents and motor control (R. Granit, ed.), S. 115–119. Stockholm: Almqvist and Wiksell 1966.
—, and M. R. Davey: The groups of origin in the nerves to skeletal muscle of the γ1 and γ2 fusimotor fibres present close to, and within, mammalian muscle spindles. In: Symposium on muscle receptors (D. Barker, ed.), S. 191–198. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press 1962.
Brown, M. C., and P. B. C. Matthews: On the sub-division of the efferent fibres to muscle spindles into static and dynamic fusimotor fibres. In: Control and innervation of skeletal muscle (B. L. Andrew, ed.), S. 18–34. Dundee, Scotland: D. C. Thomson & Co., Ltd. 1966.
Coërs, C.: Histochemical identification of motor nerve endings in muscle spindles. In: Symposium on muscle receptors (D. Barker, ed.), S. 221–226. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press 1962.
Cooper, S., and P. M. Daniel: Muscle spindles in man; their morphology in the lumbricals and the deep muscles of the neck. Brain 86, 563–586 (1963).
Düring, M. v., u. K. H. Andres: Die Feinstruktur der Muskelspindeln von Mammalia. Verh. Anat. Ges. 63. Vers. (im Druck).
Hess, A.: Two kinds of motor nerve endings on mammalian intrafusal muscle fibres revealed by the cholinesterase technique. Anat. Rec. 139, 173–184 (1961).
Jones, E. G.: The innervation of muscle spindles in the Australian opossum, Trichosurus vulpecula, with special reference to the motor nerve endings. J. Anat. (Lond.) 100, 733–759 (1966).
Karnovsky, M. J.: The localization of cholinesterase activity in rat cardiac muscle by electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 23, 217–232 (1964).
Koelle, G. B.: The elimination of enzymatic diffusion artifacts in the histochemical localization of cholinesterase and a survey of their cellular distribution. J. Pharmacol. 103, 153–171 (1951).
Landon, D. N.: Electron microscopy of muscle spindles. In: Control and innervation of skeletal muscle (B.L. Andrew, ed.), S. 96–110. Dundee, Scotland: D. C. Thomson & Co., Ltd. 1966.
Matthews, P. B. C.: The differentiation of two types of fusimotor fibre by their effects on the dynamic response of muscle spindle primary endings. Quart. J. exp. Physiol. 47, 324–333 (1962).
Romeis, B.: Mikroskopische Technik, S. 429. München: R. Oldenbourg 1948.
Smith, R. S.: Properties of intrafusal muscle fibres. In: Nobel Symposium I: Muscular afferents and motor control (R. Granit, ed.), S. 69–80. Stockholm: Almqvist and Wiksell 1966.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Herrn Prof. Dr. med. E. Horstmann zum 60. Geburtstag gewidmet
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mayr, R. Untersuchungen an isolierten Muskelspindeln der Ratte nach Cholinesterasedarstellung und Sudanschwarz-Färbung. Z. Zellforsch. 93, 594–606 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00338541
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00338541