Summary
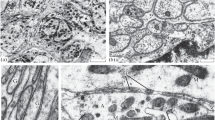
Electron microscopic investigations of M. stapedius of the guinea pig reveal structural peculiarities of the muscle cells. Frequently the cells are provided with one or two myofibrils only and show the characteristics of embryonic muscle, e.g. abundance of glycogen and a large number of polysomes. The large number of mitochondria is reason to believe that the muscle contracts frequently but with little strength. Numerous neuromuscular synapses seem to indicate that the muscle contractions are short and fast.
The morphological findings confirm the opinion of numerous authors that M. stapedius not only protects the inner ear, but also has other important functions. A permanent activity of the muscle even at low or medium sound intensities is therefore necessary.
Zusammenfassung
Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen am Musculus stapedius des Meerschweinchens haben gezeigt, daß seine Zellen zumindest bei Cavia strukturelle Besonderheiten gegenüber allen anderen Muskeln aufweisen. Die Muskelzellen besitzen häufig nur eine oder zwei Myofibrillen und weisen viele Charakteristika embryonaler Muskelzellen auf, z.B. den Glykogenreichtum und die große Zahl von Polysomen. Der hohe Anteil an Mitochondrien spricht dafür, daß es sich beim M. st. um einen Muskel mit häufigen Kontraktionen, aber einer geringen Kraftentwicklung handelt. Die große Zahl neuromuskulärer Synapsen läßt ebenfalls vermuten, daß im M.st. kurze schnelle Kontraktionen ablaufen.
Unsere Befunde stützen demnach die Ansicht einer Reihe von Autoren, daß der M.st. neben der Schallschutzfunktion für das Innenohr noch eine Reihe weiterer wichtiger Aufgaben hat, die seine ständige Aktivität auch bei niedrigen und mittleren Schallpegeln erfordern.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Berendes, J.: Die Leistung der Kehlkopfmuskulatur unter dem Aspekt der Elektronenmikroskopie und der Enzymchemie. Mschr. Ohrenheilk. 98, 524–528 (1964).
Bergman, R. A.: Further observations on the localization of glycogen in frog striated muscle. Bull. Johns Hopk. Hosp. 107, 307–319 (1960).
—: Observations on the morphogenesis of rat sceletal muscle. Bull. Johns Hopk. Hosp. 110, 187–201 (1962).
Berlendis, P. A.: L'unità motorica del muscolo tensore del timpano. Boll. Soc. med.-chir. Pavia 69, 37–40 (1955).
Brzezinski, D. K. v.: Feinbau, Muskelspindeln und Funktion der Mittelohrmuskeln des Menschen. Arch. Ohr.-, Nas.- u. Kehlk.-Heilk. 179, 550–566 (1962).
David, H.: Ergebnisse und Prinzipien der submikroskopischen Pathomorphologie der Herzmuskulatur. Z. ges. inn. Med. 18, 481–486, 533–545 (1963).
Eliasson, S., and L. Gisselsson: Electromyographic studies of the middle ear muscles of the cat. Clin. Neurophysiol. 7, 399–406 (1955).
Fisch, U., and G. v. Schulthess: Electromyographic studies on the human stapedial muscle. Acta oto-laryng. (Stockh.) 56, 287–297 (1963).
Galambos, R., and A. Rupert: Action of the middle ear muscles in normal cats. J. acoust. Soc. Amer. 31, 349–355 (1959).
Ganz, H.: Enzymmuster von Kehlkopfmuskeln des Menschen und ihre Bedeutung für deren Funktion an der Glottis. Arch. Ohr.-, Nas.- u. Kehlk.-Heilk. 184, 1–10 (1964).
Gerhardt, H.-J., H. David u. I. Marx: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen am Musculus tensor tympani des Meerschweinchens. Arch. Ohr.-, Nas.- u. Kehlk.-Heilk. (in Vorbereitung).
Hallpike, C. S., and A. F. Rawdon-Smith: The function of the tensor tympani muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 81, 25 P (1934).
Hay, E. D.: The fine structure of differentiating muscle in the salamander tail. Z. Zellforsch. 59, 6–34 (1963).
Hilding, D. A.: The intratympanic muscle reflex as a protective mechanism against loud impulsive noise. Ann. Otol (St. Louis) 69, 51–60 (1960).
—: The protective value of the stapedius reflex: An experimental study. Trans. Amer. Acad. Ophthal. Otolaryng. 65, 297–307 (1961).
Holst, H.-E., S. Ingelstedt, and U. Örtegren: Ear drum movements following stimulation of middle ear muscles. Acta oto-laryng. (Stockh.), Suppl. 182, 73–83 (1963).
Jepsen, O.: The threshold of the reflexes of the intra-tympanic muscles in normal material examined by means of the impedance method. Acta oto-laryng. (Stockh.) 39, 406–408 (1951).
- Studies on the acoustic stapedius reflex in man. Thesis Aarhus Universitet, Universitetsforlaget in Aarhus (Denmark) 1955.
Kato, T.: Zur Physiologie der Binnenmuskeln des Ohres. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 150, 569–625 (1913).
Krüger, P.: Die Innervation der tetanischen und tonischen Fasern der quergestreiften Skeletmuskulatur der Wirbeltiere. Anat. Anz. 97, 169–175 (1949).
Lidén, G., B. Nordlund, and J. E. Hawkins jr.: Significance of the stapedius reflex for the understanding of speech. Acta oto-laryng. (Stockh.), Suppl. 188, 275–279 (1963).
Lindsay, J. R., H. G. Kobrak, and H. B. Perlman: Relation of the stapedius reflex to hearing sensation in man. Arch. Otolaryng. 23, 671–678 (1963).
Malmfors, T., and J. Wersäll: Innervation of the middle ear muscles in the rabbit with special reference to nerve calibres and motor units. I. Acta morph. neerl.-scand. 3, 157 (1960).
Metz, O.: Threshold of reflex contractions of muscles of middle ear and recruitment of loudness. Arch. Otolaryng. 55, 536–543 (1952).
Möller, A. R.: The sensitivity of contraction of the tympanic muscles in man. Ann. Otol. (St. Louis) 71, 86–95 (1962).
Nojiri, J.: The innervation of human stapedius muscle. Acta anat. nipp. 38, 212–231 (1963).
Rudolph, G.:Die Enzymhistochemie des normalen und geschädigten Skelettmuskels. Verh. Deutsch. Ges. Path. 43. Tagg, 1959, S. 78–83.
—: Der histochemische Nachweis dehydrogenasehaltiger Sarkosomen (Mitochondrien) in der Herz-, Skelet- und glatten Muskulatur. Acta histochem. (Jena) 12, 48–68 (1961).
Shafiq, S. A.: Electron microscopic studies on the indirect flight muscles of Drosophila melanogaster. II. Differentiation of myofibrils. J. Cell Biol. 17, 363–373 (1963).
Simmons, F. B.: Middle ear muscle activity at moderate sound levels. Ann. Otol. (St. Louis) 68, 1126–1143 (1959).
—, and D. L. Beatty: A theory of middle ear muscle function at moderate sound levels. Science 138, 590–591 (1962).
Taruya, T.: Studies on the function of the intrinsic ear muscles. II. Studies on the function of the stapedial muscle of rabbit. Hiroshima J. med. Sci. 2, 351–364 (1954).
Tsukamoto, H.: Zur Physiologie der Binnenohrmuskeln. Z. Biol. 95, 146–154 (1934).
Waddington, C. H., and M. M. Perry: Helical arrangement of ribosomes in differentiating muscle cells. Exp. Cell Res. 30, 599–600 (1963).
Wersäll, R.: The tympanic muscles and their reflexes. Acta oto-laryng. (Stockh.), Suppl. 139, 1–112 (1958).
Wigand, M. E.: Der Stapediusreflex des wachen Kaninchens auf Tonreize mittlerer Lautstärke. Acta oto-laryng. (Stockh.) 59, 361–367 (1965).
—. u. St. Brauer: Die Reflexaktivität motorischer Einheiten von Nervus und Musculus stapedius des wachen Kaninchens. Arch. Ohr.-, Nas.- u. Kehlk.-Heilk. 183, 237–241 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
David, H., Gerhardt, H.J. & Uerlings, I. Die submikroskopische Struktur des Musculus Stapedius des Meerschweinchens. Zeitschrift für Zellforschung 70, 334–346 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00336501
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00336501